Abstract
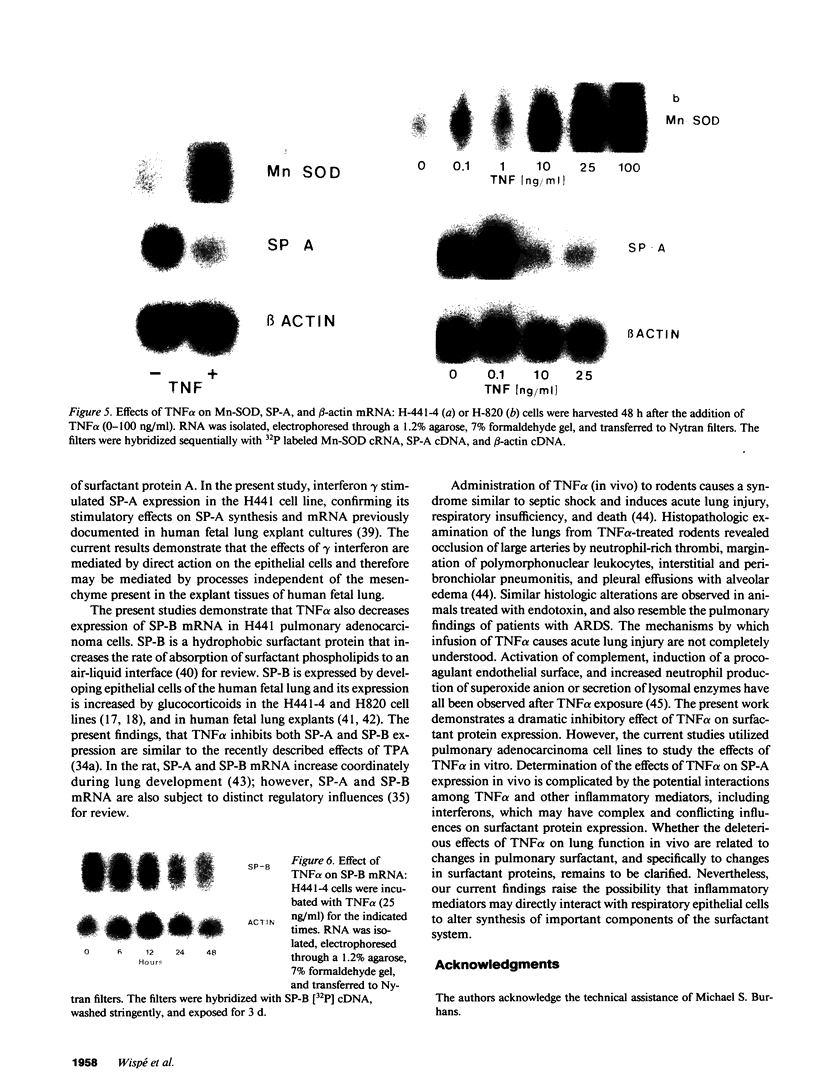
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) decreased the expression of pulmonary surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-B in human pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell lines. The effect of TNF alpha on SP-A content and mRNA in the pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell line, H441-4, was concentration and time dependent. TNF alpha decreased the cellular content of SP-A to less than 10% of control 48 h after addition. TNF alpha decreased de novo synthesis of SP-A and decreased the accumulation of SP-A in media. SP-A mRNA was decreased within 12 h of addition of TNF alpha, with nearly complete loss of SP-A mRNA observed after 24 h. Inhibitory effects of TNF alpha on SP-A mRNA were dose-related with nearly complete inhibition of SP-A mRNA caused by 25 ng/ml TNF alpha. The effects of TNF alpha on SP-A were distinct from the effects of interferon gamma which increased SP-A content approximately twofold in H441-4 cells. TNF alpha also decreased the content of SP-B mRNA. In contrast to the inhibitory effect of TNF alpha on SP-A and SP-B mRNA, TNF alpha increased mRNA encoding human manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD). TNF alpha did not inhibit growth, alter cell viability or beta-actin mRNA in either cell line. These in vitro studies demonstrate the marked pretranslational inhibitory effects of the cytokine, TNF alpha, on the expression of pulmonary surfactant proteins, SP-A and SP-B. The results support the concept that macrophage-derived cytokines may control surfactant protein expression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard P. L. Hormonal regulation of pulmonary surfactant. Endocr Rev. 1989 May;10(2):165–181. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-2-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard P. L., Liley H. G., Gonzales L. W., Odom M. W., Ammann A. J., Benson B., White R. T., Williams M. C. Interferon-gamma and synthesis of surfactant components by cultured human fetal lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Feb;2(2):137–143. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggaram V., Smith M. E., Mendelson C. R. Regulation of expression of the gene encoding the major surfactant protein (SP-A) in human fetal lung in vitro. Disparate effects of glucocorticoids on transcription and on mRNA stability. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11421–11427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Jones K. C., James T. W. Assay for nanogram quantities of DNA in cellular homogenates. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90690-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Wright J. R., Hawgood S., Gonzalez R., Venstrom K., Nellenbogen J. Pulmonary surfactant and its components inhibit secretion of phosphatidylcholine from cultured rat alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1010–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donato N. J., Gallick G. E., Steck P. A., Rosenblum M. G. Tumor necrosis factor modulates epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation and kinase activity in human tumor cells. Correlation with cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20474–20481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erba H. P., Gunning P., Kedes L. Nucleotide sequence of the human gamma cytoskeletal actin mRNA: anomalous evolution of vertebrate non-muscle actin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5275–5294. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. M., Avery M. E. Hyaline membrane disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 May;111(5):657–688. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. L. Lung surfactant. Prog Lipid Res. 1987;26(3):211–256. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(87)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Benson B. J., Hamilton R. L., Jr Effects of a surfactant-associated protein and calcium ions on the structure and surface activity of lung surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):184–190. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Cellular receptor for 125I-labeled tumor necrosis factor: specific binding, affinity labeling, and relationship to sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5756–5760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Larrick J. W. Mechanisms that regulate the production and effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Crit Rev Immunol. 1989;9(2):93–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liley H. G., White R. T., Warr R. G., Benson B. J., Hawgood S., Ballard P. L. Regulation of messenger RNAs for the hydrophobic surfactant proteins in human lung. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1191–1197. doi: 10.1172/JCI114000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson D. K., Maier R. V., Pohlman T. H. Protein kinase C: a potential pathway of endothelial cell activation by endotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-1. Surgery. 1989 Aug;106(2):216–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan M. J., Mimouni F., Miodovnik M., Hull W. M., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant associated protein (SAP-35) in amniotic fluid from diabetic and nondiabetic pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Jul;70(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. C., Ito H., Blau H. M., Torti F. M. Tumor necrosis factor inhibits human myogenesis in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2295–2301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M. A., Gazdar A. F., Clark J. C., Pilot-Matias T. J., Wert S. E., Hull W. M., Whitsett J. A. Glucocorticoids regulate surfactant protein synthesis in a pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell line. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):L385–L392. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.6.L385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M. A., Gazdar A. F., Morris R. E., Whitsett J. A. Differential effects of glucocorticoid on expression of surfactant proteins in a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 30;970(2):194–204. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons P. E., Worthen G. S., Moore E. E., Tate R. M., Henson P. M. The association of circulating endotoxin with the development of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Aug;140(2):294–301. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L., Silvers G. W., Paul G. W., Stanford R. E. Abnormalities in lung elastic properties and surfactant function in adult respiratory distress syndrome. Chest. 1979 May;75(5):571–574. doi: 10.1378/chest.75.5.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pison U., Seeger W., Buchhorn R., Joka T., Brand M., Obertacke U., Neuhof H., Schmit-Neuerburg K. P. Surfactant abnormalities in patients with respiratory failure after multiple trauma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Oct;140(4):1033–1039. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.4.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possmayer F. A proposed nomenclature for pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):990–998. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Ross G. F., Singleton F. M., Dingle S., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant-associated protein inhibits phospholipid secretion from type II cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):692–698. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Sarin V. K., Fox J. L., Baatz J., Wert S., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant peptides stimulate uptake of phosphatidylcholine by isolated cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 28;1006(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. F., Notter R. H., Meuth J., Whitsett J. A. Phospholipid binding and biophysical activity of pulmonary surfactant-associated protein (SAP)-35 and its non-collagenous COOH-terminal domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14283–14291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellhase D. E., Emrie P. A., Fisher J. H., Shannon J. M. Ontogeny of surfactant apoproteins in the rat. Pediatr Res. 1989 Sep;26(3):167–174. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198909000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Walther Z., Tamm I. Rapid enhancement of beta 2-interferon/B-cell differentiation factor BSF-2 gene expression in human fibroblasts by diacylglycerols and the calcium ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3663–3667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. M., Mendelson C. R. Insulin inhibits the accumulation of the major lung surfactant apoprotein in human fetal lung explants maintained in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1250–1257. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solis-Herruzo J. A., Brenner D. A., Chojkier M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits collagen gene transcription and collagen synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5841–5845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K. E., Ishizaka A., Larrick J. W., Raffin T. A. Tumor necrosis factor causes increased pulmonary permeability and edema. Comparison to septic acute lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1364–1370. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Fujita Y., Kogishi K. Reconstitution of tubular myelin from synthetic lipids and proteins associated with pig pulmonary surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jul;140(1):75–81. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver T. E. Pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Gen Pharmacol. 1988;19(3):361–368. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(88)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Pilot T., Clark J. C., Weaver T. E. Induction of surfactant protein in fetal lung. Effects of cAMP and dexamethasone on SAP-35 RNA and synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5256–5261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Weaver T. E., Clark J. C., Sawtell N., Glasser S. W., Korfhagen T. R., Hull W. M. Glucocorticoid enhances surfactant proteolipid Phe and pVal synthesis and RNA in fetal lung. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15618–15623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Weaver T. E., Lieberman M. A., Clark J. C., Daugherty C. Differential effects of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta on synthesis of Mr = 35,000 surfactant-associated protein in fetal lung. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7908–7913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wispé J. R., Clark J. C., Burhans M. S., Kropp K. E., Korfhagen T. R., Whitsett J. A. Synthesis and processing of the precursor for human mangano-superoxide dismutase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 19;994(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Enhancement of cAMP levels and of protein kinase activity by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in human fibroblasts: role in the induction of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6802–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]