Abstract
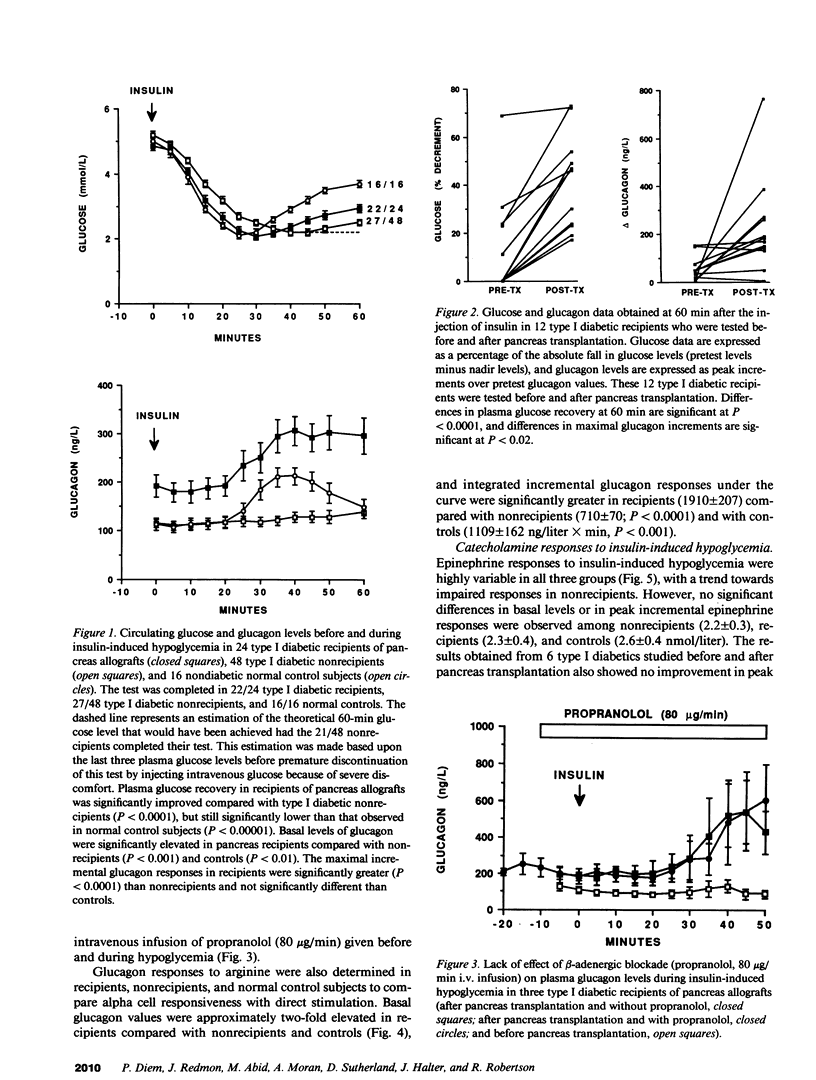
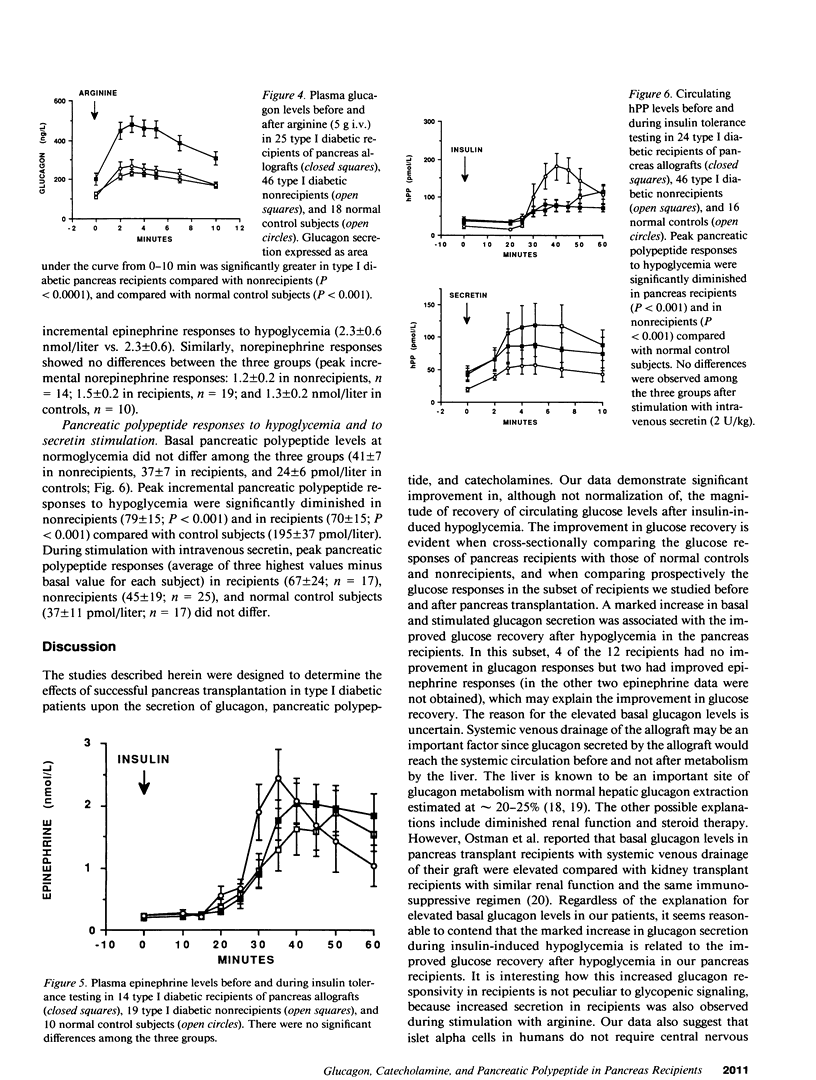
Successful pancreas transplantation in type I diabetic patients restores normal fasting glucose levels and biphasic insulin responses to glucose. However, virtually no data from pancreas recipients are available relative to other islet hormonal responses or hormonal counterregulation of hypoglycemia. Consequently, glucose, glucagon, catecholamine, and pancreatic polypeptide responses to insulin-induced hypoglycemia and to stimulation with arginine and secretin were examined in 38 diabetic pancreas recipients, 54 type I diabetic nonrecipients, and 26 nondiabetic normal control subjects. Glucose recovery after insulin-induced hypoglycemia in pancreas recipients was significantly improved. Basal glucagon levels were significantly higher in recipients compared with nonrecipients and normal subjects. Glucagon responses to insulin-induced hypoglycemia were significantly greater in the pancreas recipients compared with nonrecipients and similar to that observed in control subjects. Glucagon responses to intravenous arginine were significantly greater in pancreas recipients than that observed in both the nonrecipients and normal subjects. No differences were observed in epinephrine responses during insulin-induced hypoglycemia. No differences in pancreatic polypeptide responses to hypoglycemia were observed when comparing the recipient and nonrecipient groups, both of which were less than that observed in the control subjects. Our data demonstrate significant improvement in glucose recovery after hypoglycemia which was associated with improved glucagon secretion in type I diabetic recipients of pancreas transplantation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson J. W., Jr, Johnson D. G., Palmer J. P., Werner P. L., Ensinck J. W. Glucagon and catecholamine secretion during hypoglycemia in normal and diabetic man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Mar;44(3):459–464. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-3-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergenstal R. M., Polonsky K. S., Pons G., Jaspan J. B., Rubenstein A. H. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in type I diabetics after long-term optimal therapy with a continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump. Diabetes. 1983 May;32(5):398–402. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.5.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Reichard G. A., Jr, Hoeldtke R. D., Rezvani I., Owen O. E. Severe insulin-induced hypoglycemia associated with deficiencies in the release of counterregulatory hormones. N Engl J Med. 1981 Nov 12;305(20):1200–1205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111123052007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., Calabrese G., De Feo P., Compagnucci P., Zega G., Angeletti G., Cartechini M. G., Santeusanio F., Brunetti P. Lack of glucagon response in glucose counter-regulation in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetics: absence of recovery after prolonged optimal insulin therapy. Diabetologia. 1982 Feb;22(2):100–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00254837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. V., Kraegen E. W., Meler H., Lazarus L. Hormonal responses to insulin infusion in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1979 Jun;16(6):359–364. doi: 10.1007/BF01223155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dafoe D. C., Campbell D. A., Jr, Merion R. M., Rosenberg L., Rocher L. L., Vinik A. I., Vine A. K., Turcotte J. G. Pancreatic transplantation--University of Michigan. Transplant Proc. 1987 Aug;19(4 Suppl 4):55–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diem P., Abid M., Redmon J. B., Sutherland D. E., Robertson R. P. Systemic venous drainage of pancreas allografts as independent cause of hyperinsulinemia in type I diabetic recipients. Diabetes. 1990 May;39(5):534–540. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.5.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. I., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr Comparison of double- and single-isotope enzymatic derivative methods for measuring catecholamines in human plasma. Clin Chem. 1978 Apr;24(4):567–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Langlois M., Noacco C., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetes: evidence for an intrinsic pancreatic alpha cell defect. Science. 1973 Oct 12;182(4108):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4108.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E. Lilly lecture 1988. Glucose counterregulation and its impact on diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1608–1617. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Tsalikian E., Karam J. H. Studies on the mechanism of epinephrine-induced hyperglycemia in man. Evidence for participation of pancreatic glucagon secretion. Diabetes. 1976 Jan;25(1):65–71. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser B., Vinik A. I., Sive A. A., Floyd J. C., Jr Plasma human pancreatic polypeptide responses to administered secretin: effects of surgical vagotomy, cholinergic blockade, and chronic pancreatitis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jun;50(6):1094–1099. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-6-1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspan J. B., Polonsky K. S., Lewis M., Pensler J., Pugh W., Moossa A. R., Rubenstein A. H. Hepatic metabolism of glucagon in the dog: contribution of the liver to overall metabolic disposal of glucagon. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):E233–E244. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.3.E233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher T. D., Tanenberg R. J., Greenberg B. Z., Hoffman J. E., Doe R. P., Goetz F. C. Lack of glucagon response to hypoglycemia in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):196–200. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marco J., Diego J., Villanueva M. L., Diaz-Fierros M., Valverde I., Segovia J. M. Elevated plasma glucagon levels in cirrhosis of the liver. N Engl J Med. 1973 Nov 22;289(21):1107–1111. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311222892103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostman J., Bolinder J., Gunnarsson R., Brattström C., Tydén G., Wahren J., Groth C. G. Effects of pancreas transplantation on metabolic and hormonal profiles in IDDM patients. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38 (Suppl 1):88–93. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.s88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozza G., Bosi E., Secchi A., Piatti P. M., Touraine J. L., Gelet A., Pontiroli A. E., Dubernard J. M., Traeger J. Metabolic control of type I (insulin dependent) diabetes after pancreas transplantation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Aug 24;291(6494):510–513. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6494.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozza G., Traeger J., Dubernard J. M., Secchi A., Pontiroli A. E., Bosi E., Malik M. C., Ruitton A., Blanc N. Endocrine responses of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients following successful pancreas transplantation. Diabetologia. 1983 Apr;24(4):244–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00282707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T. W. Pancreatic polypeptide: a hormone under vagal control. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1411–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Dunn D. L., Goetz F. C., Kennedy W., Ramsay R. C., Steffes M. W., Mauer S. M., Gruessner R., Moudry-Munns K. C., Morel P. A 10-year experience with 290 pancreas transplants at a single institution. Ann Surg. 1989 Sep;210(3):274–288. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198909000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S., Greenberg B. Z., Senske B. J., Anderson G. E., Francis R. S., Goetz F. C. Hormonal and metabolic effects of a pancreatic endocrine graft. Vascularized segmental transplantation in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Nov;95(5):537–541. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-5-537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


