Abstract
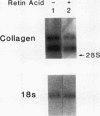
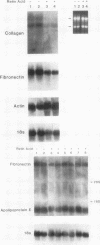
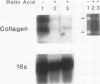
Recent studies suggest that vitamin A plays an inhibitory role with respect to "activation" of the hepatic Ito cell, a likely effector of hepatic fibrogenesis. Ito cell "activation" during fibrogenesis is characterized by a decrease in intracellular vitamin A and an increase in cellular proliferation and collagen production. To explore the hypothesis that retinoids have the capacity to diminish Ito cell activation, cultured Ito cells were exposed to retinoic acid and its effects assessed on three key features: cell proliferation, collagen protein production and mRNA abundance, and transforming growth factor beta protein production. Retinoic acid was 100-1,000X more potent than retinol with respect to inhibition of Ito cell proliferation. Interstitial collagen and transforming growth factor beta production were also reduced by 10(-6) M retinoic acid. The relative abundance of type I collagen mRNA however, was not significantly altered. By contrast, retinoic acid administration to rats caused a marked reduction in the abundance of type I collagen mRNA in both total hepatic and purified Ito cell RNA. The relative abundance of rat hepatic fibronectin or apolipoprotein E mRNA was not significantly altered. These studies demonstrate that retinoic acid can differentially modulate several key features of hepatic fibrogenesis in vitro and in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assoian R. K., Fleurdelys B. E., Stevenson H. C., Miller P. J., Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Ross R., Sporn M. B. Expression and secretion of type beta transforming growth factor by activated human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6020–6024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball M. D., Olson J. A. 13-cis-retinoic acid stimulates in vitro mannose 6-phosphate hydrolysis and inhibits retinol esterification and benzo[a]pyrene hydroxylation by rat-liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 1;961(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballardini G., Degli Esposti S., Bianchi F. B., de Giorgi L. B., Faccani A., Biolchini L., Busachi C. A., Pisi E. Correlation between Ito cells and fibrogenesis in an experimental model of hepatic fibrosis. A sequential stereological study. Liver. 1983 Feb;3(1):58–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1983.tb00850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkai U., Sherman M. I. Analyses of the interactions between retinoid-binding proteins and embryonal carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D., Lernhardt E., Pfahl M. A new retinoic acid receptor identified from a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):669–672. doi: 10.1038/333669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat P. V., Jetten A. M. Metabolism of all-trans-retinol and all-trans-retinoic acid in rabbit tracheal epithelial cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 31;922(1):18–27. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff R., Norum K. R., Berg T. Hepatic uptake of [3H]retinol bound to the serum retinol binding protein involves both parenchymal and perisinusoidal stellate cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13571–13575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff R., Rasmussen M., Nilsson A., Norum K. R., Berg T., Blaner W. S., Kato M., Mertz J. R., Goodman D. S., Eriksson U. Hepatic retinol metabolism. Distribution of retinoids, enzymes, and binding proteins in isolated rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13560–13565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun L., Mead J. E., Panzica M., Mikumo R., Bell G. I., Fausto N. Transforming growth factor beta mRNA increases during liver regeneration: a possible paracrine mechanism of growth regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1539–1543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Gendrault J. L., Steffan A. M., Jeandidier E., Kirn A. Isolation, culture and main characteristics of mouse fat-storing cells: interaction with viruses. Hepatology. 1989 Mar;9(3):352–362. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiocca E. A., Davies P. J., Stein J. P. The molecular basis of retinoic acid action. Transcriptional regulation of tissue transglutaminase gene expression in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11584–11589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chojkier M. Hepatocyte collagen production in vivo in normal rats. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):333–339. doi: 10.1172/JCI112581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement B., Grimaud J. A., Campion J. P., Deugnier Y., Guillouzo A. Cell types involved in collagen and fibronectin production in normal and fibrotic human liver. Hepatology. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):225–234. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope F. O., Wille J. J. Retinoid receptor antisense DNAs inhibit alkaline phosphatase induction and clonogenicity in malignant keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5590–5594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaja M. J., Weiner F. R., Eghbali M., Giambrone M. A., Eghbali M., Zern M. A. Differential effects of gamma-interferon on collagen and fibronectin gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13348–13351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czaja M. J., Weiner F. R., Flanders K. C., Giambrone M. A., Wind R., Biempica L., Zern M. A. In vitro and in vivo association of transforming growth factor-beta 1 with hepatic fibrosis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2477–2482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielpour D., Dart L. L., Flanders K. C., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Immunodetection and quantitation of the two forms of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2) secreted by cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jan;138(1):79–86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. H., Pratt B. M., Madri J. A. Retinol and extracellular collagen matrices modulate hepatic Ito cell collagen phenotype and cellular retinol binding protein levels. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10280–10286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. H. Transforming growth factor beta responsiveness is modulated by the extracellular collagen matrix during hepatic ito cell culture. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Sep;136(3):547–553. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. H., Vucic A. Modulation of vitamin A metabolism during hepatic and intestinal cell culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 6;1010(3):318–324. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. H., Vucic A. The effect of retinol on Ito cell proliferation in vitro. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):788–793. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson P. A., Lukaszewski L. M., Ells P. F., Malbon C. C., Williams D. L. Quantification and regulation of apolipoprotein E expression in rat Kupffer cells. J Lipid Res. 1989 Mar;30(3):403–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F., Zile M., Sietsema W. K. The metabolism of retinoic acid to 5,6-epoxyretinoic acid, retinoyl-beta-glucuronide, and other polar metabolites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981 Feb 27;359:25–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb12734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. L., Roll F. J., Boyles J., Bissell D. M. Hepatic lipocytes: the principal collagen-producing cells of normal rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8681–8685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geerts A., Vrijsen R., Rauterberg J., Burt A., Schellinck P., Wisse E. In vitro differentiation of fat-storing cells parallels marked increase of collagen synthesis and secretion. J Hepatol. 1989 Jul;9(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(89)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genovese C., Rowe D., Kream B. Construction of DNA sequences complementary to rat alpha 1 and alpha 2 collagen mRNA and their use in studying the regulation of type I collagen synthesis by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):6210–6216. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb M. T., Ellis C. N., Voorhees J. J. Retinoids in dermatology. Mayo Clin Proc. 1987 Dec;62(12):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62514-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks H. F., Blaner W. S., Wennekers H. M., Piantedosi R., Brouwer A., de Leeuw A. M., Goodman D. S., Knook D. L. Distributions of retinoids, retinoid-binding proteins and related parameters in different types of liver cells isolated from young and old rats. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):237–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Erlanger B. F., Guntaka R. V. Evidence for extensive methylation of ribosomal RNA genes in a rat XC cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 15;739(3):258–264. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent G., Gay S., Inouye T., Bahu R., Minick O. T., Popper H. Vitamin A-containing lipocytes and formation of type III collagen in liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3719–3722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. Y., Wolf G. Vitamin A deficiency alters genomic expression for fibronectin in liver and hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):365–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. H., DiGiovanna J. J., Moshell A. N., Tarone R. E., Peck G. L. Prevention of skin cancer in xeroderma pigmentosum with the use of oral isotretinoin. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 23;318(25):1633–1637. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806233182501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhok R., Muller S. A., Dicken C. H. Treatment of psoriasis with etretin: a preliminary report. Mayo Clin Proc. 1987 Dec;62(12):1084–1089. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62500-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher J. J., Bissell D. M., Friedman S. L., Roll F. J. Collagen measured in primary cultures of normal rat hepatocytes derives from lipocytes within the monolayer. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):450–459. doi: 10.1172/JCI113618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak K. M., Leo M. A., Lieber C. S. Alcoholic liver injury in baboons: transformation of lipocytes to transitional cells. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):188–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. A., Strain A. J., Bucher N. L. DNA synthesis in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes in a defined medium: effects of epidermal growth factor, insulin, glucagon, and cyclic-AMP. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Sep;108(3):353–363. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Fukazawa C., Taylor J. M. Rat apolipoprotein E mRNA. Cloning and sequencing of double-stranded cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8993–9000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J. E., Fausto N. Transforming growth factor alpha may be a physiological regulator of liver regeneration by means of an autocrine mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1558–1562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minato Y., Hasumura Y., Takeuchi J. The role of fat-storing cells in Disse space fibrogenesis in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):559–566. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtaugh M. P., Dennison O., Stein J. P., Davies P. J. Retinoic acid-induced gene expression in normal and leukemic myeloid cells. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1325–1330. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli J. L., Race K. R. The biosynthesis of retinoic acid from retinol by rat tissues in vitro. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 May 15;255(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara K., Nakanishi K., Hagiwara H., Wakita K., Kojima S., Hirose S. Retinol-induced morphological changes of cultured bovine endothelial cells are accompanied by a marked increase in transglutaminase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19308–19312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen H., Oikarinen A. I., Tan E. M., Abergel R. P., Meeker C. A., Chu M. L., Prockop D. J., Uitto J. Modulation of procollagen gene expression by retinoids. Inhibition of collagen production by retinoic acid accompanied by reduced type I procollagen messenger ribonucleic acid levels in human skin fibroblast cultures. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1545–1553. doi: 10.1172/JCI111859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piacentini M., Fesus L., Sartori C., Ceru M. P. Retinoic acid-induced modulation of rat liver transglutaminase and total polyamines in vivo. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):33–38. doi: 10.1042/bj2530033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori G., Rieder H., Knittel T., Dienes H. P., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Fat storing cells (FSC) of rat liver synthesize and secrete fibronectin. Comparison with hepatocytes. J Hepatol. 1987 Apr;4(2):190–197. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reue K. L., Quon D. H., O'Donnell K. A., Dizikes G. J., Fareed G. C., Lusis A. J. Cloning and regulation of messenger RNA for mouse apolipoprotein E. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2100–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiratori Y., Ichida T., Geerts A., Wisse E. Modulation of collagen synthesis by fat-storing cells, isolated from CCl4- or vitamin A-treated rats. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Nov;32(11):1281–1289. doi: 10.1007/BF01296379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):217–219. doi: 10.1038/332217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. L., Rosner M. R. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression by retinoic acid and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3230–3234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Roche N. S., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 positively regulates its own expression in normal and transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7741–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G. W., Gold J. D., Petkovich M., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. A retinoic acid-responsive element is present in the 5' flanking region of the laminin B1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9099–9103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent P. A., Cho E., Saba T. M. Effect of repetitive low-dose endotoxin on liver parenchymal and Kupffer cell fibronectin release. Hepatology. 1989 Apr;9(4):562–569. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B. Latent transforming growth factor-beta from human platelets. A high molecular weight complex containing precursor sequences. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7646–7654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]