Abstract
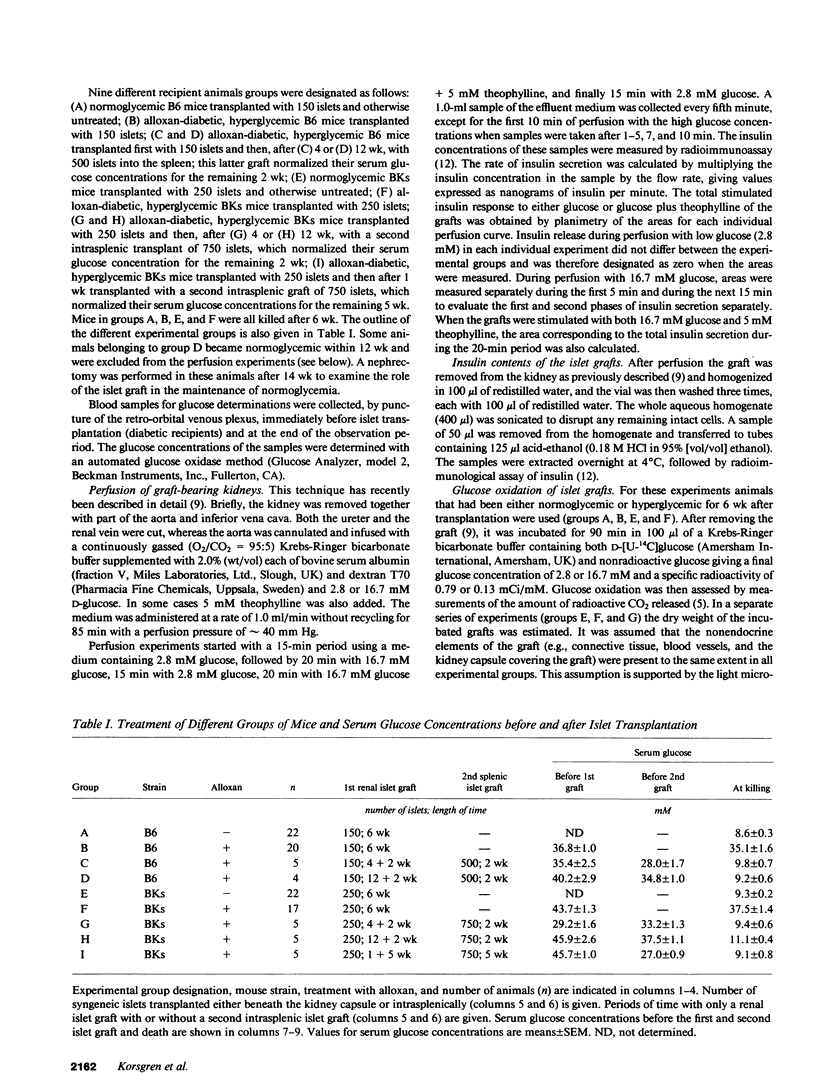
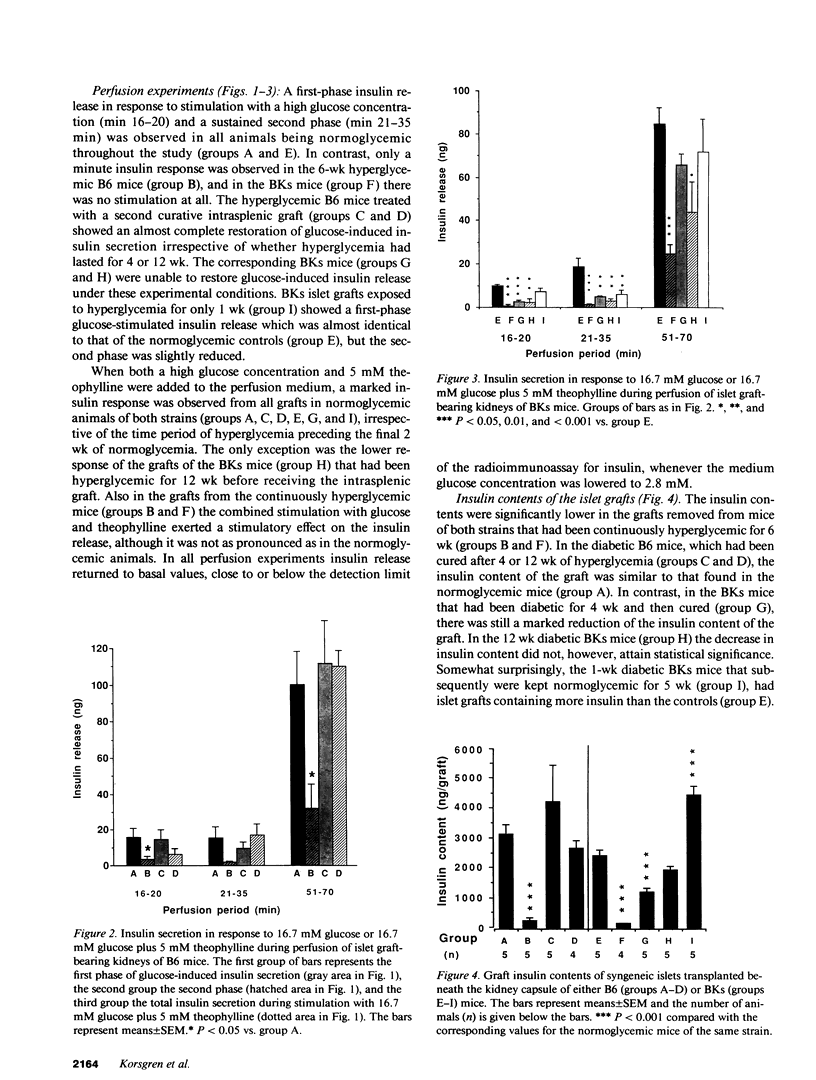
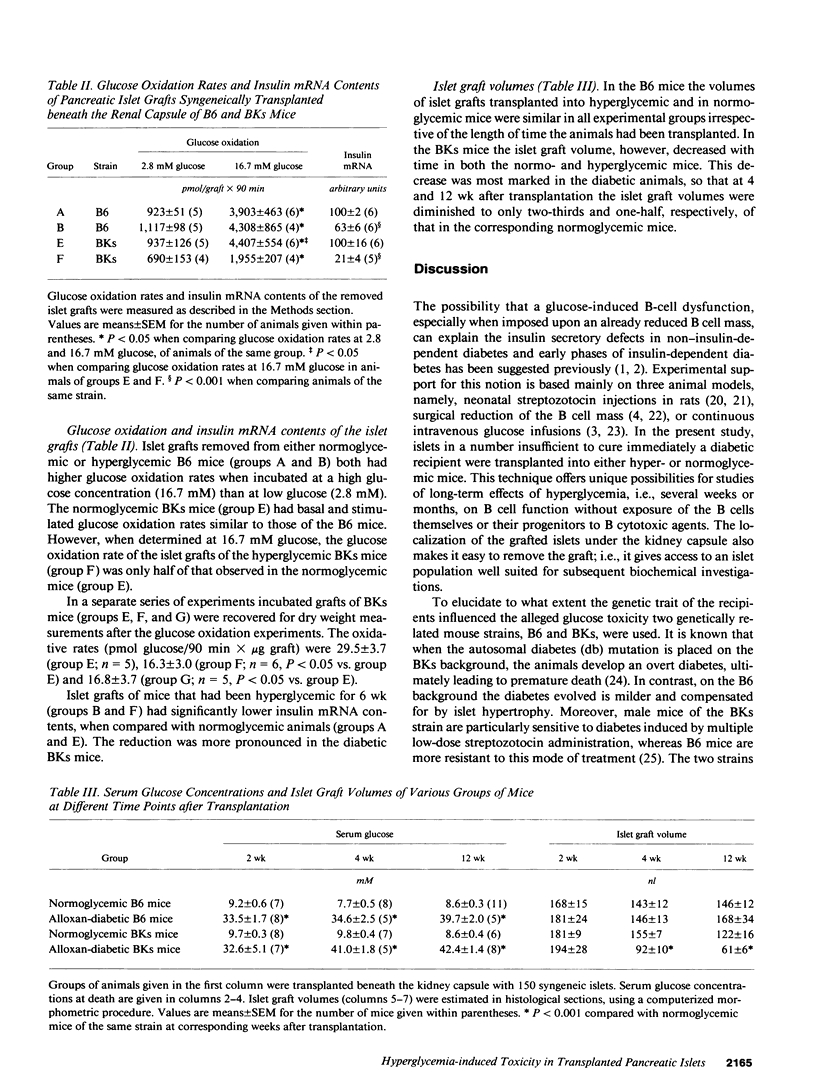
The role of pancreatic B cell dysfunction in the phase preceding clinical onset of insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus has been much debated. In this investigation, the impact of a prolonged diabetic environment on pancreatic islet B cells transplanted syngeneically under the kidney capsule of C57BL/6 (B6) and C57BL/Ks (BKs) mice was studied. Alloxan-diabetic mice bearing a subcapsular islet graft insufficient to normalize the blood glucose level were rendered normoglycemic by a second intrasplenic islet graft after various period of hyperglycemia to examine the reversibility of hyperglycemia-induced B cell dysfunction. Using a perfusion technique of the graft-bearing, it was found that both strains of mice exhibited a diminished glucose-induced insulin secretion after 6 wk of hyperglycemia, when compared with normoglycemic mice carrying islet grafts. When normoglycemia was restituted by the splenic graft after 4 or 12 wk, there was a normalization of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the renal islet grafts in B6 mice, whereas insulin secretion from the grafted BKs islets remained impaired. Morphometric measurements of the islet grafts demonstrated a 50% reduction in the graft volume in diabetic BKs mice after 12 wk, compared with normoglycemic animals, whereas no such decrease was observed in B6 mice. Islet grafts removed from hyperglycemic mice of both strains exhibited diminished insulin mRNA contents, and in the BKs mice there was also a reduced glucose oxidation rate in the islet grafts in vitro. This metabolic dysfunction can only partly be explained by a reduced graft size. The present findings emphasize the genetic constitution as a decisive factor for the survival and function during a period of sustained stress on a limited B cell mass.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson A. Isolated mouse pancreatic islets in culture: effects of serum and different culture media on the insulin production of the islets. Diabetologia. 1978 Jun;14(6):397–404. doi: 10.1007/BF01228134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A. Long-term effects of glucose on insulin release and glucose oxidation by mouse pancreatic islets maintained in tissue culture. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;140(3):377–382. doi: 10.1042/bj1400377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A. The influence of hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinaemia and genetic background on the fate of intrasplenically implanted mouse islets. Diabetologia. 1983 Sep;25(3):269–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00279942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Trent D. F., Weir G. C. Partial pancreatectomy in the rat and subsequent defect in glucose-induced insulin release. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1544–1553. doi: 10.1172/JCI110910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunstedt J., Chan S. J. Direct effect of glucose on the preproinsulin mRNA level in isolated pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1383–1389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Noyes B. E., Agarwal K. L., Steiner D. F. Construction and selection of recombinant plasmids containing full-length complementary DNAs corresponding to rat insulins I and II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5036–5040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia. 1978 Mar;14(3):141–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00429772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik D. L., Sandler S. Sustained exposure of toxically damaged mouse pancreatic islets to high glucose does not increase beta-cell dysfunction. J Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;123(1):47–51. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1230047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik D. L., Sandler S., Welsh N., Hellerström C. Preferential reduction of insulin production in mouse pancreatic islets maintained in culture after streptozotocin exposure. Endocrinology. 1988 Apr;122(4):1242–1249. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-4-1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik D. L., Strandell E., Bendtzen K., Sandler S. Functional characteristics of rat pancreatic islets maintained in culture after exposure to human interleukin 1. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):916–919. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. A new phase of insulin secretion. How will it contribute to our understanding of beta-cell function? Diabetes. 1989 Jun;38(6):673–678. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.6.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heding L. G. Determination of total serum insulin (IRI) in insulin-treated diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1972 Aug;8(4):260–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01225569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura T., Koffler M., Helderman J. H., Prince D., Thirlby R., Inman L., Unger R. H. Severe diabetes induced in subtotally depancreatized dogs by sustained hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 1988 May;37(5):600–609. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.5.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren O., Jansson L., Andersson A. Effects of hyperglycemia on function of isolated mouse pancreatic islets transplanted under kidney capsule. Diabetes. 1989 Apr;38(4):510–515. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren O., Sandler S., Landström A. S., Jansson L., Andersson A. Large-scale production of fetal porcine pancreatic isletlike cell clusters. An experimental tool for studies of islet cell differentiation and xenotransplantation. Transplantation. 1988 Mar;45(3):509–514. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198803000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Cooper H. E., Weir G. C. Impaired insulin secretion associated with near normoglycemia. Study in normal rats with 96-h in vivo glucose infusions. Diabetes. 1987 Apr;36(4):459–464. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.4.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Weir G. C. Evolution of abnormal insulin secretory responses during 48-h in vivo hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 1988 Feb;37(2):217–222. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H. Analysis of differential survival of syngeneic islets transplanted into hyperglycemic C57BL/6J versus C57BL/KsJ mice. Transplantation. 1987 Sep;44(3):401–406. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198709000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Fewell J. W., Kuff E. L. Glucose induces intracisternal type A retroviral gene transcription and translation in pancreatic beta cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Jan 1;163(1):87–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H. The genetics of diabetes susceptibility in mice. FASEB J. 1989 Sep;3(11):2231–2241. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.11.2673897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Can desensitization of the B-cell to D-glucose be simulated in cultured pancreatic islets? Acta Diabetol Lat. 1987 Jan-Mar;24(1):17–25. doi: 10.1007/BF02732049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J. Insulin release : the fuel concept. Diabete Metab. 1983 Dec;9(4):313–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A. Hexose metabolism in pancreatic islets. Feedback control of D-glucose oxidation by functional events. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 7;971(3):246–254. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen D. A., Welsh M., Casadaban M. J., Steiner D. F. Control of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells and in an insulin-producing cell line, RIN-5F cells. I. Effects of glucose and cyclic AMP on the transcription of insulin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13585–13589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orland M. J., Chyn R., Permutt M. A. Modulation of proinsulin messenger RNA after partial pancreatectomy in rats. Relationships to glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):2047–2055. doi: 10.1172/JCI111924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orland M. J., Permutt M. A. Quantitative analysis of pancreatic proinsulin mRNA in genetically diabetic (db/db) mice. Diabetes. 1987 Mar;36(3):341–347. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.3.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portha B., Giroix M. H., Serradas P., Welsh N., Hellerström C., Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Insulin production and glucose metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets of rats with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1988 Sep;37(9):1226–1233. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.9.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portha B., Levacher C., Picon L., Rosselin G. Diabetogenic effect of streptozotocin in the rat during the perinatal period. Diabetes. 1974 Nov;23(11):889–895. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.11.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Pukel C., Baquerizo H. Interleukin-1 inhibits glucose-modulated insulin and glucagon secretion in rat islet monolayer cultures. Endocrinology. 1988 Jun;122(6):2393–2398. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-6-2393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P. Type II diabetes, glucose "non-sense," and islet desensitization. Diabetes. 1989 Dec;38(12):1501–1505. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.12.1501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini A. A., Appel M. C., Williams R. M., Like A. A. Genetic influence of the streptozotocin-induced insulitis and hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 1977 Oct;26(10):916–920. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.10.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler S., Andersson A., Hellerström C. Inhibitory effects of interleukin 1 on insulin secretion, insulin biosynthesis, and oxidative metabolism of isolated rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1987 Oct;121(4):1424–1431. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler S., Jansson L. Blood flow measurements in autotransplanted pancreatic islets of the rat. Impairment of the blood perfusion of the graft during hyperglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):17–21. doi: 10.1172/JCI113044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sener A., Rasschaert J., Zähner D., Malaisse W. J. Hexose metabolism in pancreatic islets stimulation by D-glucose of [2-3H]glycerol detritiation. Int J Biochem. 1988;20(6):595–598. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(88)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serreze D. V., Leiter E. H., Kuff E. L., Jardieu P., Ishizaka K. Molecular mimicry between insulin and retroviral antigen p73. Development of cross-reactive autoantibodies in sera of NOD and C57BL/KsJ db/db mice. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):351–358. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandell E., Eizirik D. L., Korsgren O., Sandler S. Functional characteristics of cultured mouse pancreatic islets following exposure to different streptozotocin concentrations. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Sep;59(1-2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandell E., Eizirik D. L., Sandler S. Reversal of beta-cell suppression in vitro in pancreatic islets isolated from nonobese diabetic mice during the phase preceding insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1944–1950. doi: 10.1172/JCI114657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I., Andersson A. Effect of genetic background on the capacity for islet cell replication in mice. Diabetologia. 1984 Oct;27(4):464–467. doi: 10.1007/BF00273912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Grundy S. Hyperglycaemia as an inducer as well as a consequence of impaired islet cell function and insulin resistance: implications for the management of diabetes. Diabetologia. 1985 Mar;28(3):119–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00273856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Clore E. T., Zmachinski C. J., Bonner-Weir S. Islet secretion in a new experimental model for non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1981 Jul;30(7):590–595. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.7.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir G. C., Leahy J. L., Bonner-Weir S. Experimental reduction of B-cell mass: implications for the pathogenesis of diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1986;2(1-2):125–161. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610020108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Brunstedt J., Hellerström C. Effects of D-glucose, L-leucine, and 2-ketoisocaproate on insulin mRNA levels in mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1986 Feb;35(2):228–231. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. Glucose regulation of insulin gene expression. Diabete Metab. 1989 Nov-Dec;15(6):367–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Nielsen D. A., MacKrell A. J., Steiner D. F. Control of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells and in an insulin-producing cell line, RIN-5F cells. II. Regulation of insulin mRNA stability. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13590–13594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


