Abstract
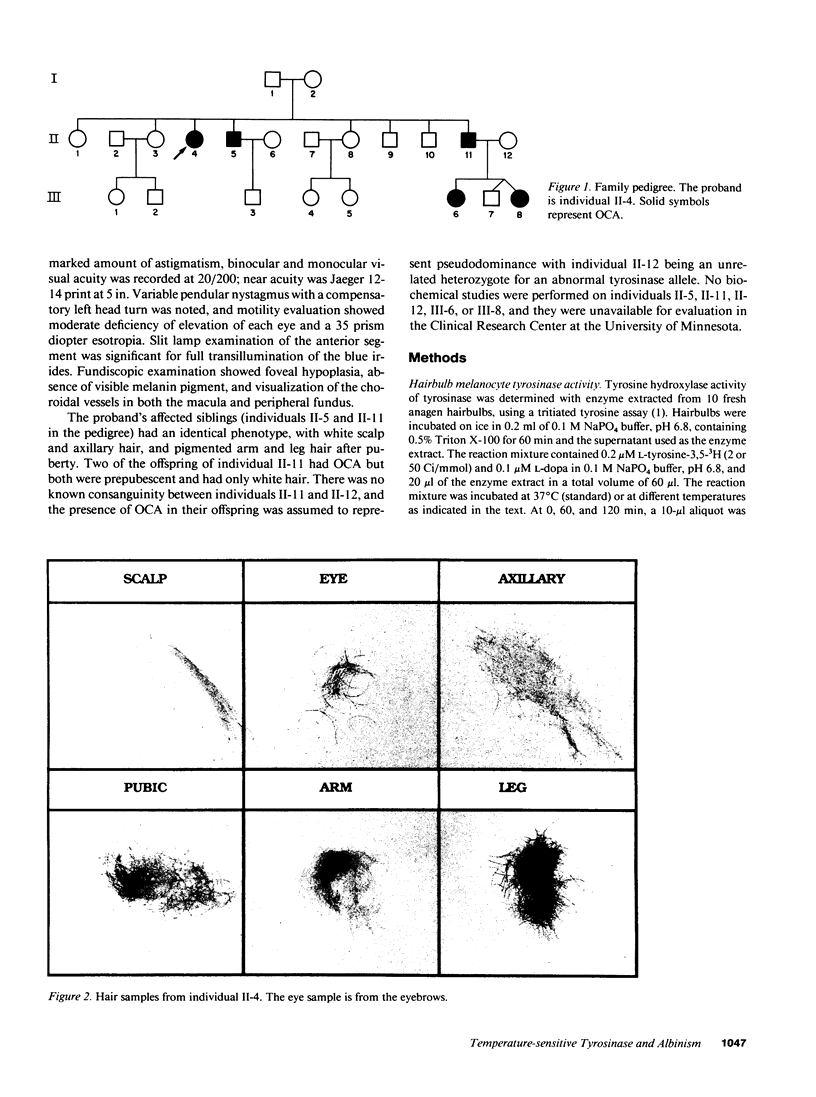
Several types of autosomal recessive oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) are associated with abnormal tyrosinase function and a generalized reduction in or absence of cutaneous and eye melanin. Each is thought to result from a different mutant allele at the tyrosinase locus, with the mutation producing an enzyme with little or no activity in all involved tissues. In this paper, we report a new type of OCA that results from a tyrosinase allele producing a temperature-sensitive enzyme. The proband had white hair in the warmer areas (scalp and axilla) and progressively darker hair in the cooler areas (extremities) of her body. Melanocyte and melanosome architecture were normal. Quantitative hairbulb tyrosinase (dopa oxidase) assay demonstrated a loss of activity above 35-37 degrees C. Plasma pheomelanin and urine eumelanin intermediates were reduced and correlated with hair melanin content. This is the first temperature-sensitive tyrosinase mutation to be reported in humans and is analogous to the Siamese mutation in the cat and the Himalayan mutation in the mouse.
Full text
PDF

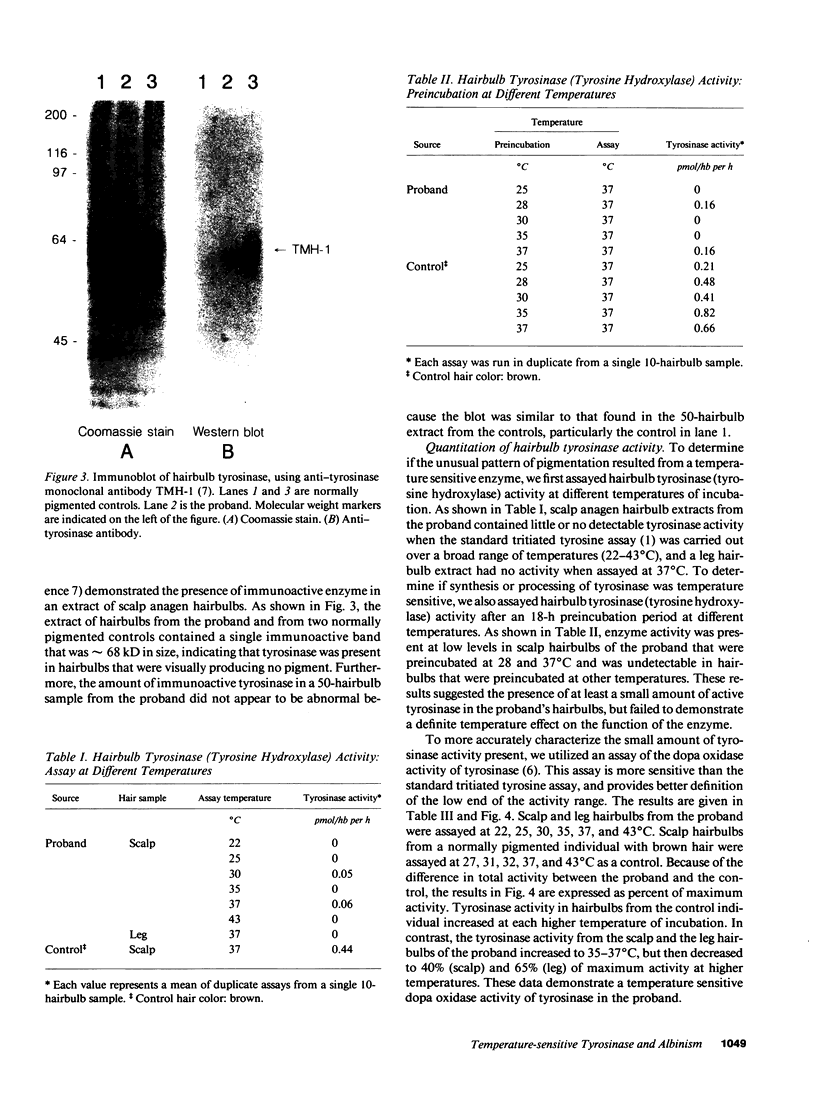
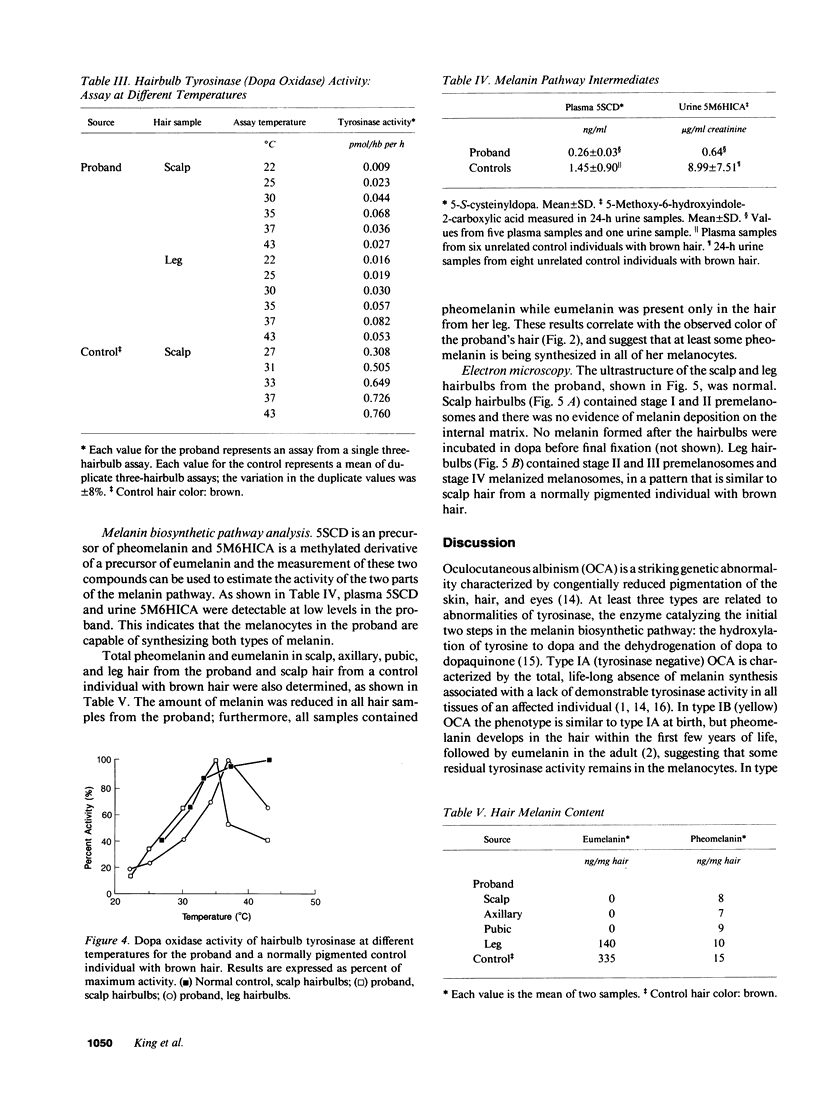
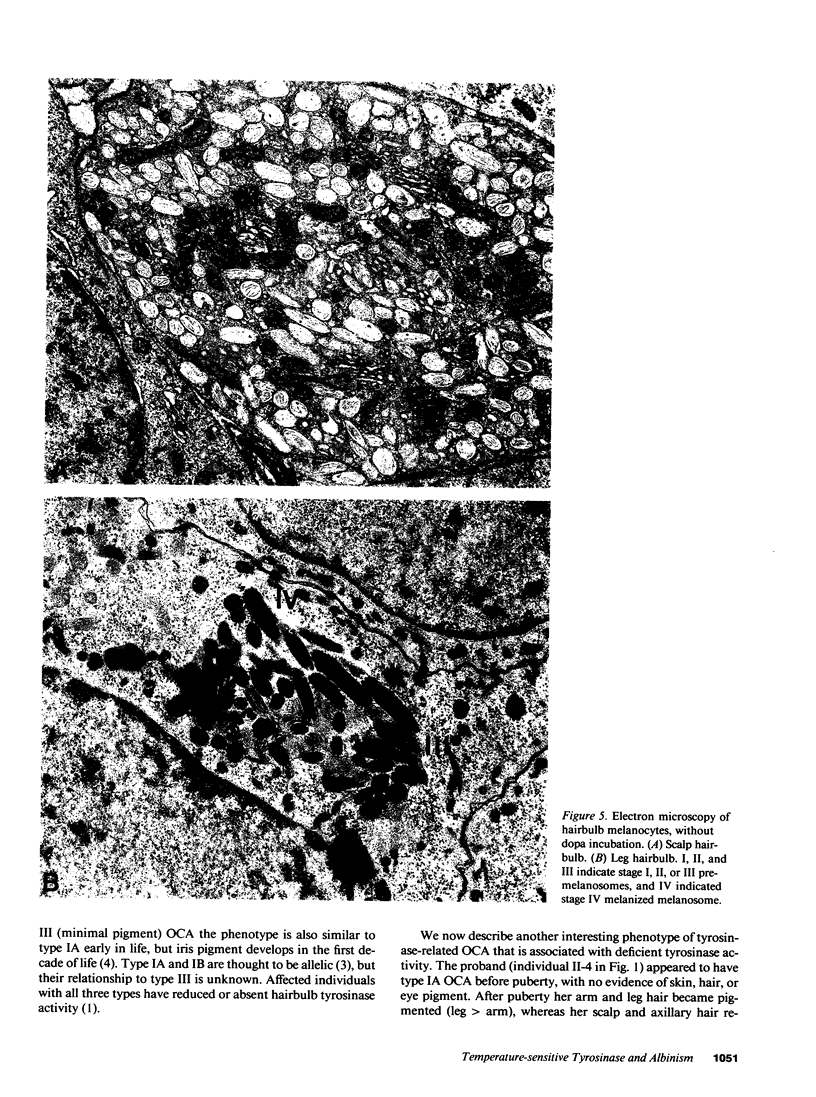


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benedetto J. P., Ortonne J. P., Voulot C., Khatchadourian C., Prota G., Thivolet J. Role of thiol compounds in mammalian melanin pigmentation: Part I. Reduced and oxidized glutathione. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Nov;77(5):402–405. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12494592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebel L. B., Strunk K. M., King R. A., Hanifin J. M., Spritz R. A. A frequent tyrosinase gene mutation in classic, tyrosinase-negative (type IA) oculocutaneous albinism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3255–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaban R., Moellmann G., Tamura A., Kwon B. S., Kuklinska E., Pomerantz S. H., Lerner A. B. Tyrosinases of murine melanocytes with mutations at the albino locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7241–7245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson C. 6-Hydroxy-5-methoxyindole-2-carboxylic acid in normal human urine. Acta Derm Venereol. 1984;64(3):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu F., Hanifin J. M., Prescott G. H., Tongue A. C. Yellow mutant albinism: cytochemical, ultrastructural, and genetic characterization suggesting multiple allelism. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):387–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Fujita K. Microanalysis of eumelanin and pheomelanin in hair and melanomas by chemical degradation and liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;144(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Kato T., Maruta K., Fujita K., Kurahashi T. Determination of DOPA, dopamine, and 5-S-cysteinyl-DOPA in plasma, urine, and tissue samples by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr. 1984 Nov 9;311(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84702-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jara J. R., Aroca P., Solano F., Martinez J. H., Lozano J. A. The role of sulfhydryl compounds in mammalian melanogenesis: the effect of cysteine and glutathione upon tyrosinase and the intermediates of the pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 17;967(2):296–303. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(88)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidson S. H., Fabian B. C. The effect of temperature on tyrosinase activity in Himalayan mouse skin. J Exp Zool. 1981 Jan;215(1):91–97. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402150111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. A., Olds D. P. Hairbulb tyrosinase activity in oculocutaneous albinism: suggestions for pathway control and block location. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jan;20(1):49–55. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. A., Summers C. G. Albinism. Dermatol Clin. 1988 Apr;6(2):217–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. A., Wirtschafter J. D., Olds D. P., Brumbaugh J. Minimal pigment: a new type of oculocutaneous albinism. Clin Genet. 1986 Jan;29(1):42–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Halaban R., Chintamaneni C. Molecular basis of mouse Himalayan mutation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 30;161(1):252–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91588-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERNER A. B., FITZPATRICK T. B. Biochemistry of melanin formation. Physiol Rev. 1950 Jan;30(1):91–126. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1950.30.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard L. J., Townsend D., King R. A. Function of dopachrome oxidoreductase and metal ions in dopachrome conversion in the eumelanin pathway. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):6156–6159. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavel S., van der Slik W. Analysis of eumelanin-related indolic compounds in urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. J Chromatogr. 1986 Mar 7;375(2):392–398. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83733-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prota G. Recent advances in the chemistry of melanogenesis in mammals. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jul;75(1):122–127. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Strunk K. M., Giebel L. B., King R. A. Detection of mutations in the tyrosinase gene in a patient with type IA oculocutaneous albinism. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 14;322(24):1724–1728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006143222407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita Y., Montague P. M., Hearing V. J. Anti-T4-tyrosinase monoclonal antibodies--specific markers for pigmented melanocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Nov;85(5):426–430. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend D. W., Olds D. P., King R. A. Dopa oxidase activity in human hair bulbs measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 May;86(5):570–572. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12355192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamatsu K., Ito S., Fujita K. Melanin-related metabolites in urine of B16 melanoma-bearing mice. Acta Derm Venereol. 1988;68(5):385–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkop C. J., Jr, Nance W. E., Rawls R. F., White J. G. Autosomal recessive oculocutaneous albinism in man. Evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Jan;22(1):55–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]