Abstract
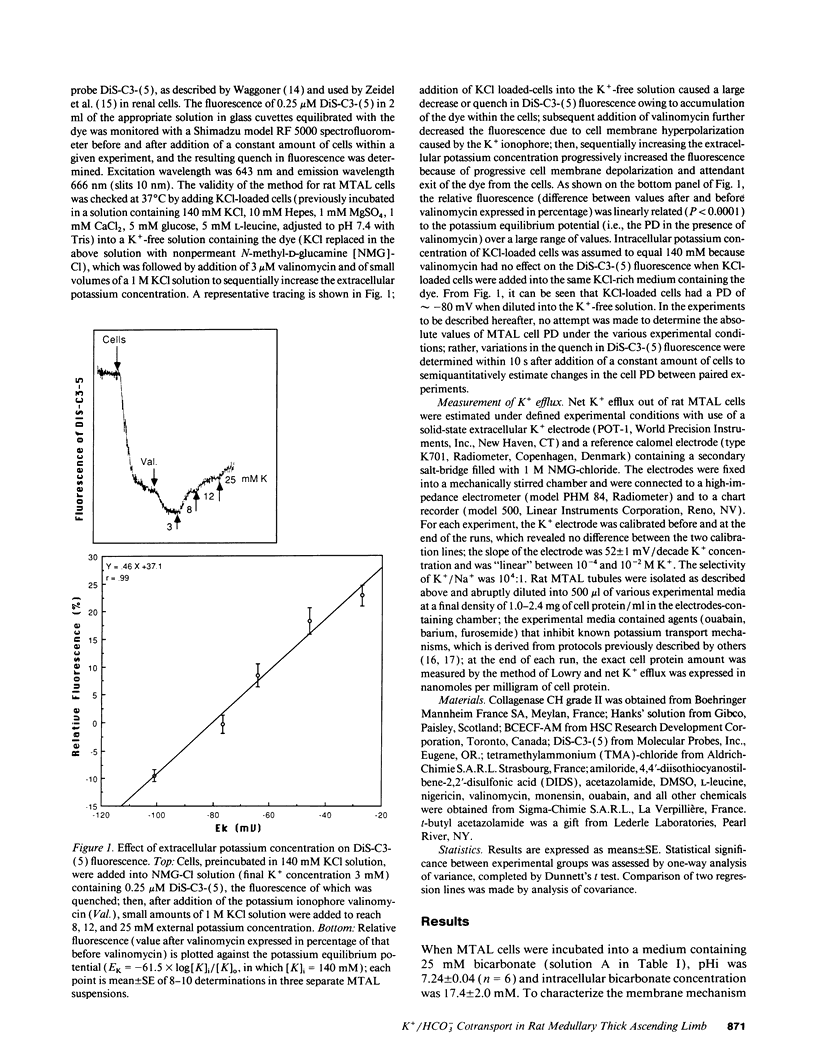
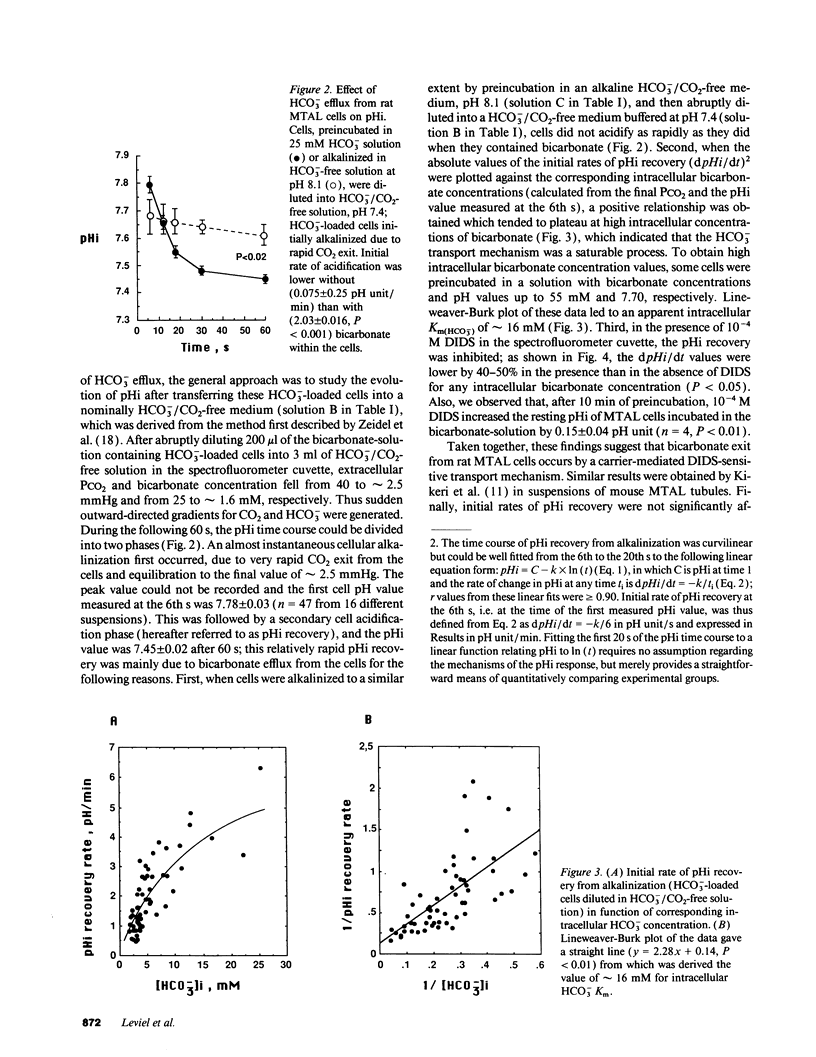
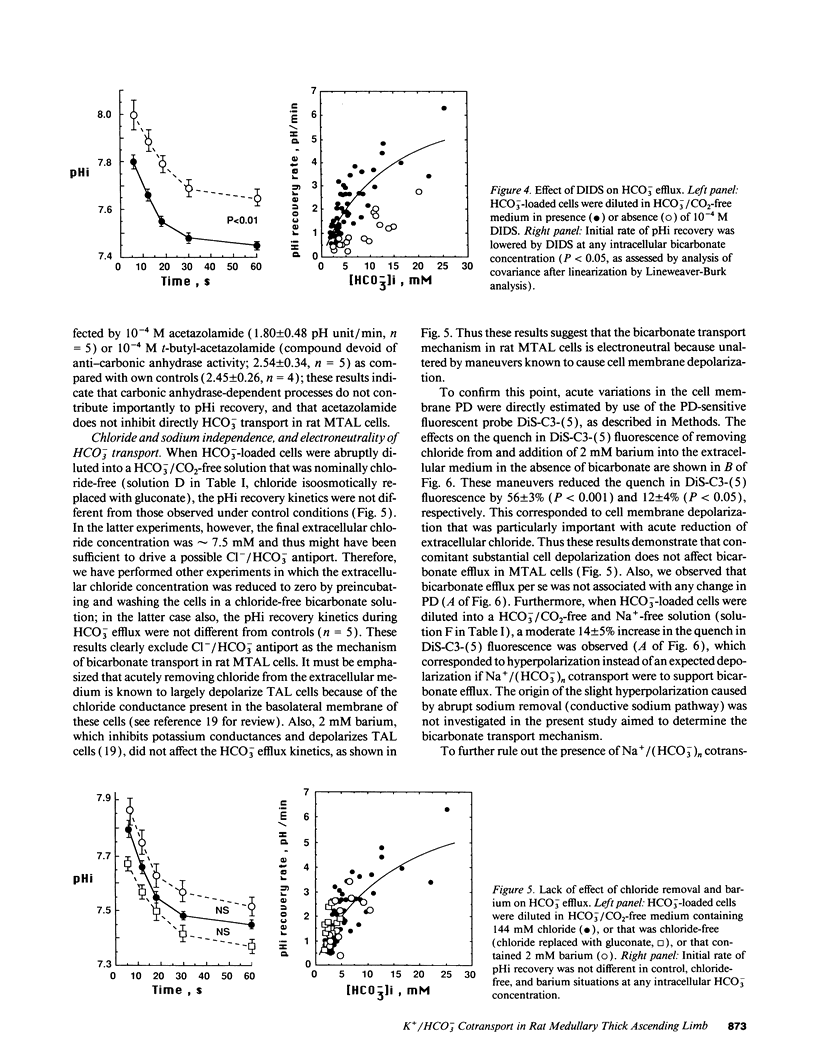
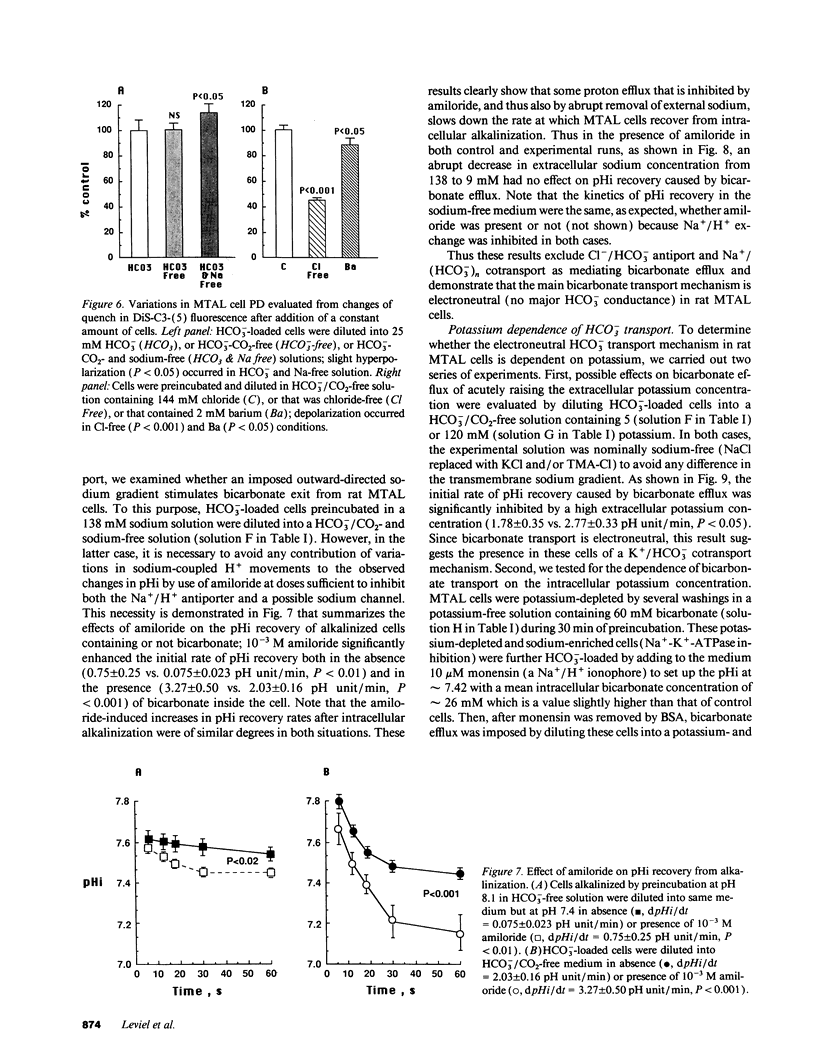
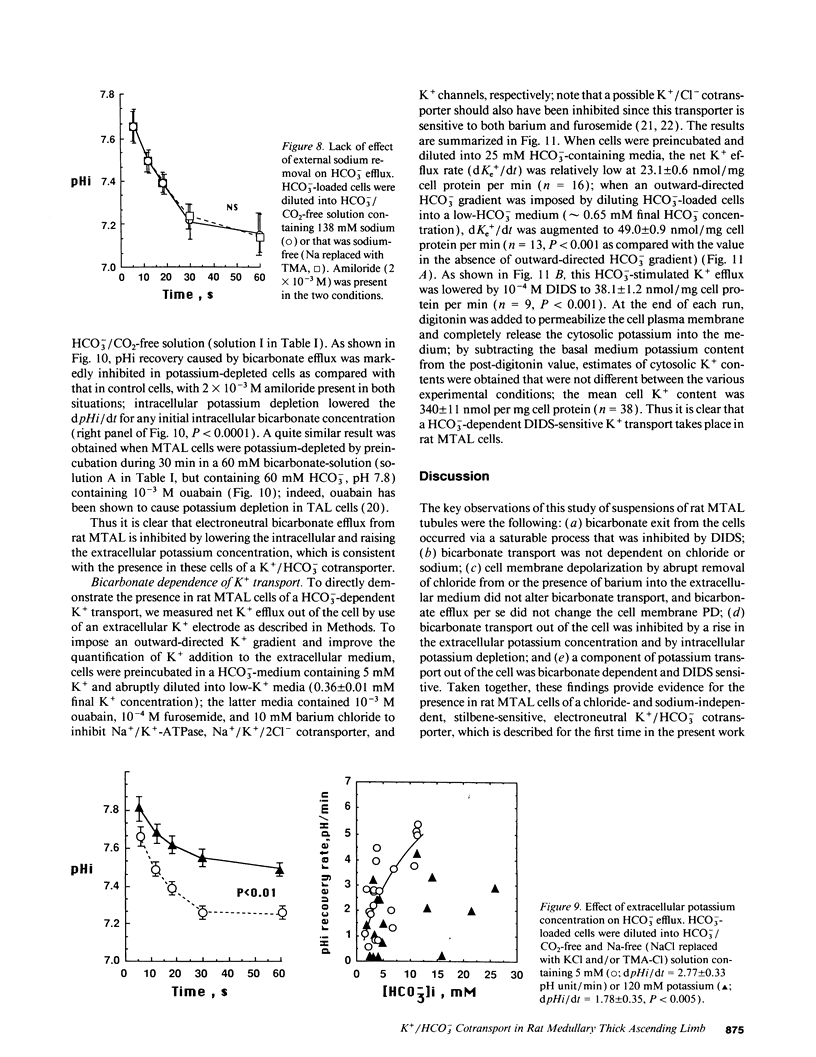
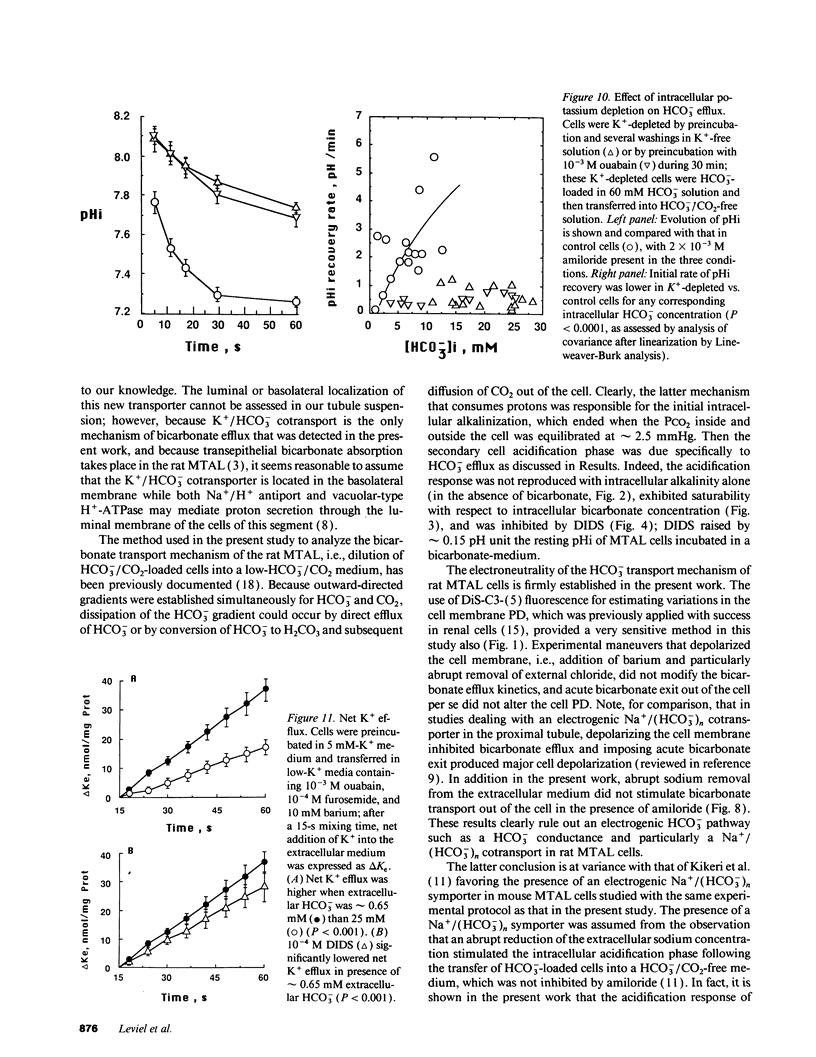
The renal medullary thick ascending limb (MTAL) of the rat absorbs bicarbonate through luminal H+ secretion and basolateral HCO3- transport into the peritubular space. To characterize HCO3- transport, intracellular pH (pHi) was monitored by use of the pH-sensitive fluorescent probe (2',7')-bis-(carboxyethyl)-(5,6)-carboxyfluorescein in fresh suspensions of rat MTAL tubules. When cells were preincubated in HCO3-/CO2-containing solutions and then abruptly diluted into HCO3-/CO2-free media, the pHi response was an initial alkalinization due to CO2 efflux, followed by an acidification (pHi recovery). The pHi recovery required intracellular HCO3-, was inhibited by 10(-4) M diisothiocyanostilbene-2-2'-disulphonic acid (DIDS), and was not dependent on Cl- or Na+. As assessed by use of the cell membrane potential-sensitive fluorescent probe 3,3'-dipropylthiadicarbocyanine, cell depolarization by abrupt Cl- removal from or addition of 2 mM barium into the external medium did not affect HCO3(-)-dependent pHi recovery, and the latter was not associated per se with any change in potential difference, which indicated that HCO3- transport was electroneutral. The HCO3(-)-dependent pHi recovery was inhibited by raising extracellular potassium concentration and by intracellular potassium depletion. Finally, as measured by use of a K(+)-selective extracellular electrode, a component of K+ efflux out of the cells was HCO3- dependent and DIDS sensitive. The results provide evidence for an electroneutral K+/HCO3- cotransport in rat MTAL cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battilana C. A., Dobyan D. C., Lacy F. B., Bhattacharya J., Johnston P. A., Jamison R. L. Effect of chronic potassium loading on potassium secretion by the pars recta or descending limb of the juxtamedullary nephron in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1093–1103. doi: 10.1172/JCI109215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichara M., Mercier O., Paillard M., Leviel F. Effects of parathyroid hormone on urinary acidification. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 2):F444–F453. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.3.F444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichara M., Paillard M., Corman B., de Rouffignac C., Leviel F. Volume expansion modulates NaHCO3 and NaCl transport in the proximal tubule and Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):F140–F150. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.1.F140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. The electrogenic Na/HCO3 cotransporter. Kidney Int. 1989 Sep;36(3):392–402. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Abramow M. Localization of tissue sodium and potassium compartments in rabbit renal cortex. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):1011–1017. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diezi J., Michoud P., Aceves J., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of electrolyte transport across papillary collecting duct of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1973 Mar;224(3):623–634. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobyan D. C., Lacy F. B., Jamison R. L. Suppression of potassium-recycling in the renal medulla by short-term potassium deprivation. Kidney Int. 1979 Dec;16(6):704–709. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froissart M., Borensztein P., Houillier P., Leviel F., Poggioli J., Marty E., Bichara M., Paillard M. Plasma membrane Na(+)-H+ antiporter and H(+)-ATPase in the medullary thick ascending limb of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C963–C970. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W. Active absorption of NH4+ by rat medullary thick ascending limb: inhibition by potassium. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 2):F78–F87. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.1.F78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., Knepper M. A., Burg M. B. Ammonia and bicarbonate transport by thick ascending limb of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):F35–F44. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W. Sodium-dependent bicarbonate absorption by cortical thick ascending limb of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 2):F821–F829. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.6.F821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger R. Ion transport mechanisms in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mammalian nephron. Physiol Rev. 1985 Jul;65(3):760–797. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.3.760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger R., Schlatter E. Properties of the basolateral membrane of the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. A model for secondary active chloride transport. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Mar;396(4):325–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01063938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikeri D., Azar S., Sun A., Zeidel M. L., Hebert S. C. Na(+)-H+ antiporter and Na(+)-(HCO3-)n symporter regulate intracellular pH in mouse medullary thick limbs of Henle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):F445–F456. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.3.F445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kone B. C., Kikeri D., Zeidel M. L., Gullans S. R. Cellular pathways of potassium transport in renal inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):C823–C830. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.4.C823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R. Basolateral membrane H/OH/HCO3 transport in the rat cortical thick ascending limb. Evidence for an electrogenic Na/HCO3 cotransporter in parallel with a Na/H antiporter. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):234–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI113576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerholm G., Ridderstråle Y. Intracellular distribution of carbonic anhydrase in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1980 Feb;17(2):162–174. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerholm G., Wistrand P. J. Carbonic anhydrase in the human kidney: a histochemical and immunocytochemical study. Kidney Int. 1984 Jun;25(6):886–898. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Basolateral membrane H-OH-HCO3 transport in the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F751–F765. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., Mandel L. J. Potassium transport in the rabbit renal proximal tubule: effects of barium, ouabain, valinomycin, and other ionophores. J Membr Biol. 1986;94(2):153–161. doi: 10.1007/BF01871195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinh-Trang-Tan M. M., Bouby N., Coutaud C., Bankir L. Quick isolation of rat medullary thick ascending limbs. Enzymatic and metabolic characterization. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):228–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00580681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinh-Trang-Tan M. M., Levillain O., Bankir L. Contribution of leucine to oxidative metabolism of the rat medullary thick ascending limb. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jun;411(6):676–680. doi: 10.1007/BF00580865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. Optical probes of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1976 Jun 30;27(4):317–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01869143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. G., Eveloff J. K-Cl cotransport systems. Kidney Int. 1989 Sep;36(3):412–417. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Kikeri D., Silva P., Burrowes M., Brenner B. M. Atrial natriuretic peptides inhibit conductive sodium uptake by rabbit inner medullary collecting duct cells. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1067–1074. doi: 10.1172/JCI113663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Silva P., Seifter J. L. Intracellular pH regulation in rabbit renal medullary collecting duct cells. Role of chloride-bicarbonate exchange. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1682–1688. doi: 10.1172/JCI112486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



