Abstract
Although Escherichia coli strains possessing the K1 capsule are predominant among isolates from neonatal E. coli meningitis and most of these K1 isolates are associated with a limited number of 0 lipopolysaccharide (LPS) types, the basis of this association of K1 and certain 0 antigens with neonatal E. coli meningitis is not clear. The present study examined in experimental E. coli bacteremia and meningitis in newborn and adult rats whether or not the K1 capsule and/or O-LPS antigen are critical determinants in the development of meningitis. Rats received subcutaneously at K1 E. coli strain (018+K1+) or mutants lacking either the K1 capsule (018+K1-) or 0 side-chain (018-K1+). 12-24 h later, blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimens were obtained for quantitative cultures. The isolation of E. coli from CSF was observed in both newborn and adult rats infected with K1+ strains regardless of LPS phenotype (018+ or 18-) who also developed a high degree of bacteremia (e.g., greater than 10(4) CFU/ml of blood). In contrast, none of the newborn and adult rats infected with 018+K1- and developing bacteremia of greater than 10(4) were found to have positive CSF cultures. These findings indicate that the presence of the K1 capsule and a high degree of bacteremia are key determinants in the development of E. coli meningitis, suggesting that there may be specific binding sites present in the brain which have an affinity for the K1 capsule and thus may be responsible for the entry of K1-encapsulated E. coli into the meninges.
Full text
PDF



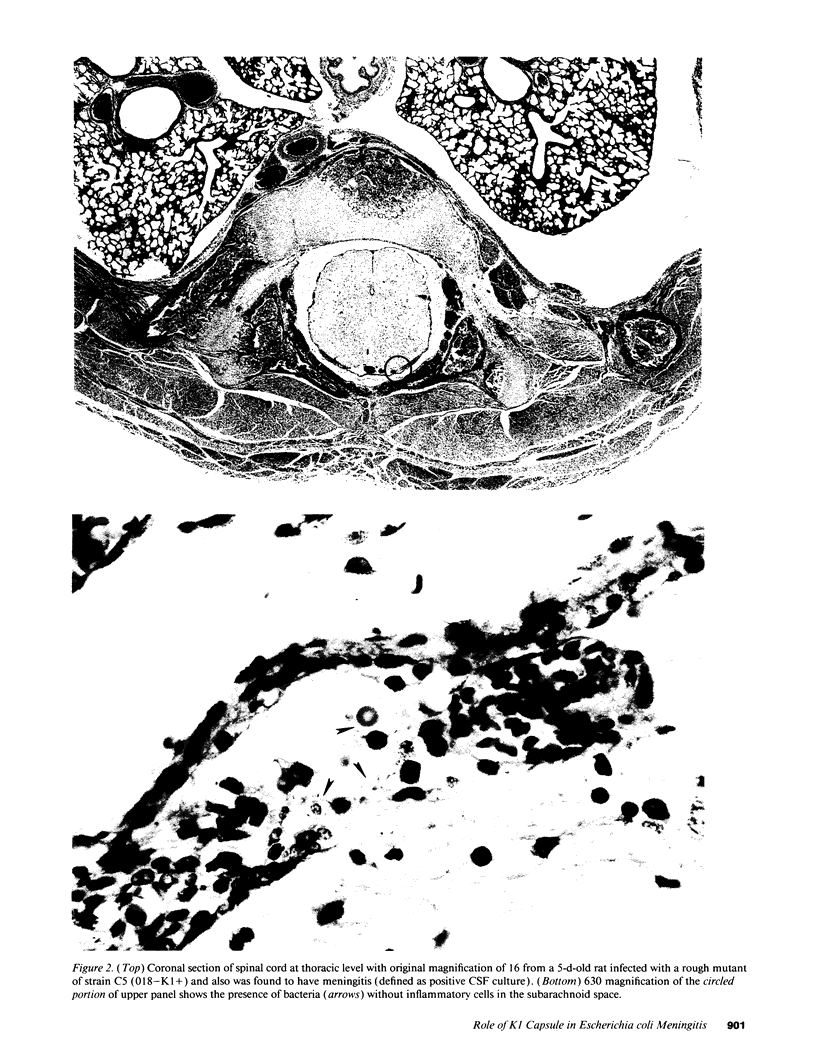
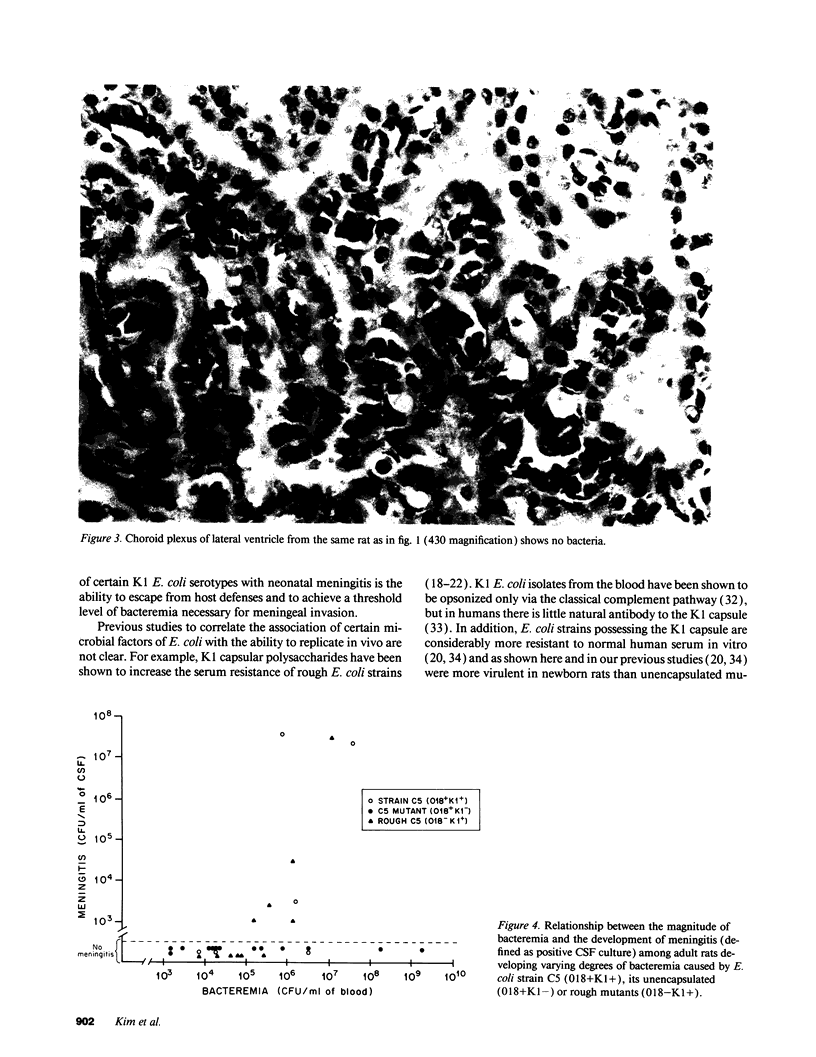



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell L. M., Alpert G., Campos J. M., Plotkin S. A. Routine quantitative blood cultures in children with Haemophilus influenzae or Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia. Pediatrics. 1985 Dec;76(6):901–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand K. P., Postle K., Wray L. V., Jr, Reznikoff W. S. Overlapping divergent promoters control expression of Tn10 tetracycline resistance. Gene. 1983 Aug;23(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumley F. G., Menzel R., Roth J. R. Hfr formation directed by tn10. Genetics. 1979 Apr;91(4):639–655. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Gemski P., Sadoff J. C., Orskov F., Orskov I. The importance of the K1 capsule in invasive infections caused by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):184–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Kim K. S., Wright D. C., Sadoff J. C., Gemski P. Role of lipopolysaccharide and capsule in the serum resistance of bacteremic strains of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):497–503. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Zollinger W., Mandrell R., Gemski P., Sadoff J. Evaluation of immunotherapeutic approaches for the potential treatment of infections caused by K1-positive Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):68–76. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryz S. J., Jr, Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Fürer E. Synthesis and characterization of Escherichia coli O18 O-polysaccharide conjugate vaccines. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):373–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.373-377.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzman D. E., Fischer G. W., Schoenknecht F. D. Neonatal Escherichia coli septicemia--bacterial counts in blood. J Pediatr. 1974 Jul;85(1):128–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin R. D. Bacterial meningitis in the newborn infant. Clin Perinatol. 1977 Mar;4(1):103–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J., Ward L. R., Threlfall E. J., Cheasty T., Rowe B. Drug resistance among Escherichia coli strains isolated from cerebrospinal fluid. J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Apr;90(2):195–198. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400028850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Winkelhake J. L., Zollinger W. D., Brandt B. L., Artenstein M. S. Immunochemical similarity between polysaccharide antigens of Escherichia coli 07: K1(L):NM and group B Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Anthony B. F. Efficacy of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in experimental Escherichia coli bacteremia and meningitis. Chemotherapy. 1983;29(6):428–435. doi: 10.1159/000238231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Bayer A. S. Efficacy of BMY-28142 in experimental bacteremia and meningitis caused by Escherichia coli and group B streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):51–54. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S. Comparison of cefotaxime, imipenem-cilastatin, ampicillin-gentamicin, and ampicillin-chloramphenicol in the treatment of experimental Escherichia coli bacteremia and meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):433–436. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S. Comparison of gentamicin and kanamycin alone and in combination with ampicillin in experimental Escherichia coli bacteremia and meningitis. Pediatr Res. 1985 Nov;19(11):1152–1155. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198511000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Cross A. S., Zollinger W., Sadoff J. Prevention and therapy of experimental Escherichia coli infection with monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):734–737. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.734-737.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S. Efficacy of cefmenoxime in experimental Escherichia coli bacteremia and meningitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):389–392. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S. Efficacy of human immunoglobulin and penicillin G in treatment of experimental group B streptococcal infection. Pediatr Res. 1987 Mar;21(3):289–292. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198703000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S. High-dose intravenous immune globulin impairs antibacterial activity of antibiotics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989 Oct;84(4 Pt 2):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(89)90194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Kang J. H., Cross A. S., Kaufman B., Zollinger W., Sadoff J. Functional activities of monoclonal antibodies to the O side chain of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharides in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):47–53. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Manocchio M., Anthony B. F. Paradox between the responses of Escherichia coli K1 to ampicillin and chloramphenicol in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Nov;26(5):689–693. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.5.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Manocchio M., Bayer A. S. Efficacy of cefotaxime and latamoxef for Escherichia coli bacteremia and meningitis in newborn rats. Chemotherapy. 1984;30(4):262–269. doi: 10.1159/000238278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Valtonen M. V., Parkkinen J., Väisänen-Rhen V., Finne J., Orskov F., Orskov I., Svenson S. B., Mäkelä P. H. Serotypes, hemolysin production, and receptor recognition of Escherichia coli strains associated with neonatal sepsis and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):486–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.486-491.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Scolea L. J., Jr, Dryja D. Quantitation of bacteria in cerebrospinal fluid and blood of children with meningitis and its diagnostic significance. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):187–190. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.187-190.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Kaijser B., Olling S., Uwaydah M., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli in bacteremia: K and O antigens and serum sensitivity of strains from adults and neonates. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Threlkeld N., Mize S., Baker C. J., Kaplan S. L., Faingezicht I., Feldman W. E., Schaad U. Moxalactam therapy for neonatal meningitis due to gram-negative enteric bacilli. A prospective controlled evaluation. JAMA. 1984 Sep 21;252(11):1427–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Camitta B. M., Heath E. C. Cell wall composition and virulence in Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. E. Current topics in host defenses of the newborn. Adv Pediatr. 1978;25:59–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opal S., Cross A., Gemski P. K antigen and serum sensitivity of rough Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):956–960. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.956-960.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J. Structure and biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:501–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSDORF R. G., SWARNER D. R., GARCIA M. Studies on the pathogenesis of meningitis. II. Development of meningitis during pneumococcal bacteremia. J Clin Invest. 1962 Feb;41:320–327. doi: 10.1172/JCI104485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst H. F., Kreth H. W. Ontogeny of the immune response as a basis of childhood disease. J Pediatr. 1980 Oct;97(4):519–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluschke G., Mayden J., Achtman M., Levine R. P. Role of the capsule and the O antigen in resistance of O18:K1 Escherichia coli to complement-mediated killing. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):907–913. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.907-913.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr, Gotschlich E. C., Orskov F., Orskov I., Hanson L. A. Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide associated with neonatal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1216–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarff L. D., McCracken G. H., Schiffer M. S., Glode M. P., Robbins J. B., Orskov I., Orskov F. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli K1 in healthy and diseased newborns. Lancet. 1975 May 17;1(7916):1099–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hale T. L., Zollinger W. D., Seid R. C., Jr, Hammack C. A., Griffiss J. M. Heterogeneity of molecular size and antigenic expression within lipooligosaccharides of individual strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.544-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. D., McCracken G. H., Jr Sepsis neonatorum. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 12;304(11):642–647. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103123041105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Huang S. N., Welch W. D., Young L. S. Restricted complement activation by Escherichia coli with the K-1 capsular serotype: a possible role in pathogenicity. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2174–2180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan T. D., LaScolea L. J., Jr, Neter E. Relationship between the magnitude of bacteremia in children and the clinical disease. Pediatrics. 1982 Jun;69(6):699–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen C., Cross A., Byrne W. R., Zollinger W. Quantitative relationship between capsular content and killing of K1-encapsulated Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2723–2730. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2723-2730.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggener J. D. The pathophysiology of bacterial meningitis and cerebral abscesses: an anatomical interpretation. Adv Neurol. 1974;6:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







