Abstract
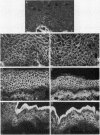
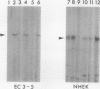
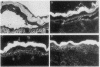
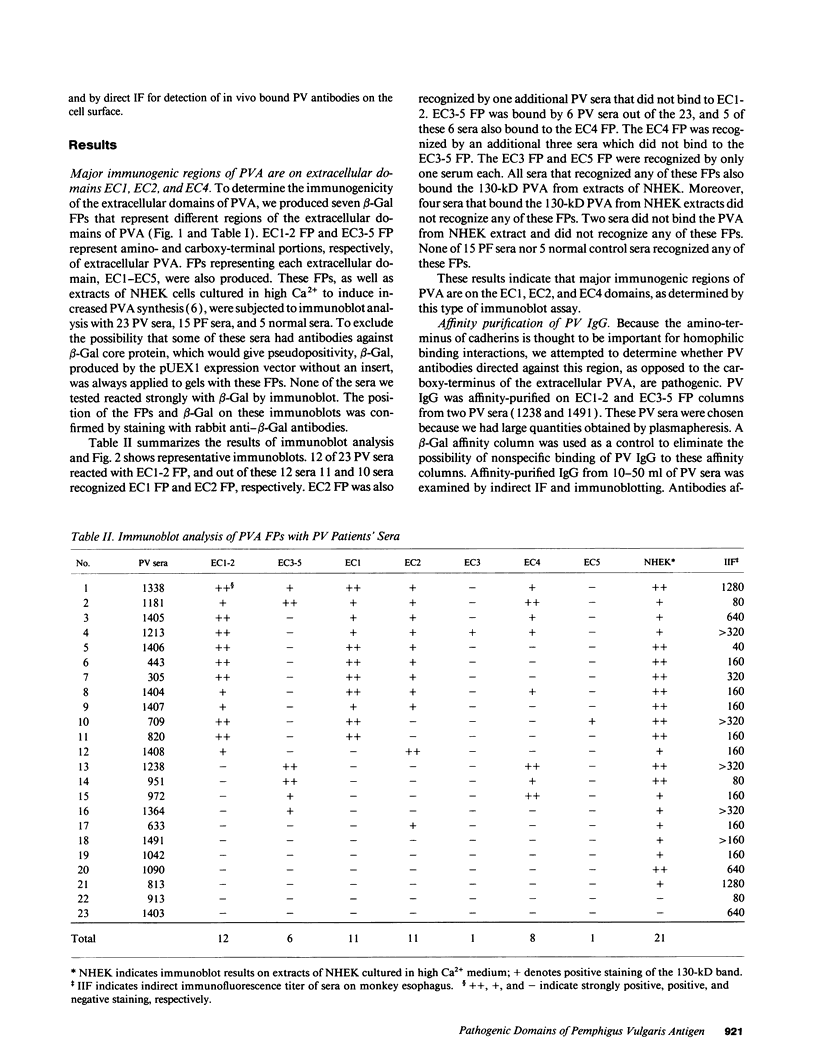
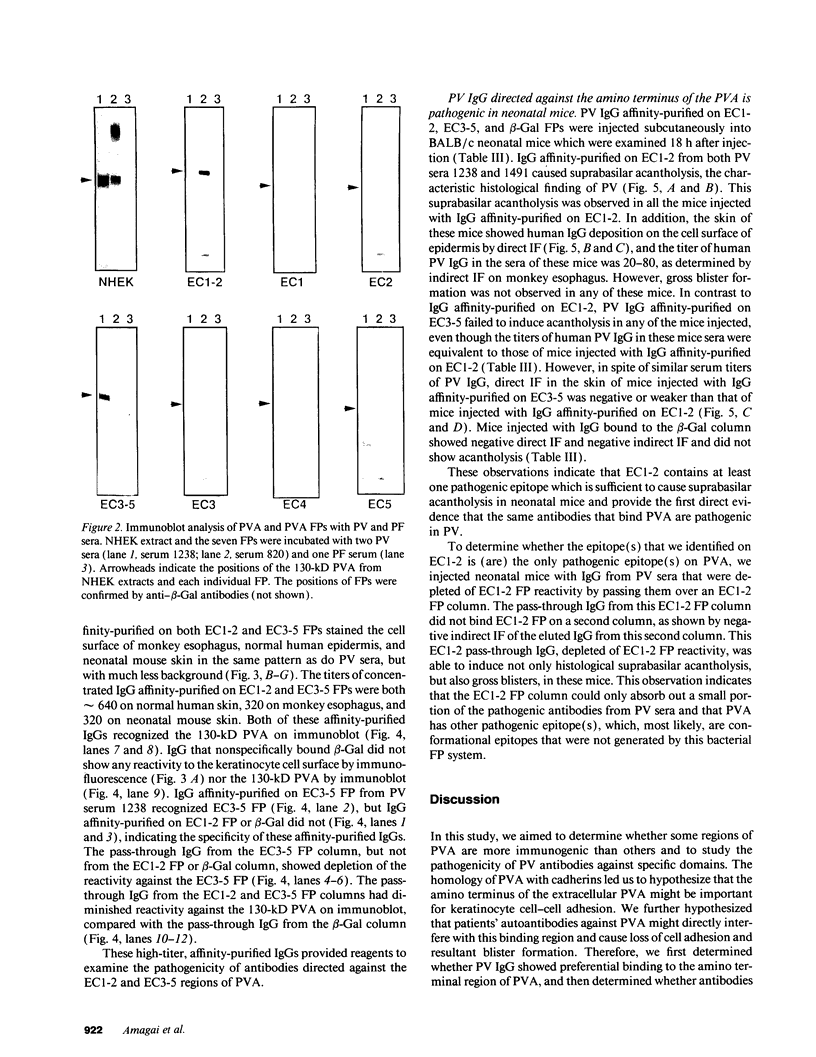
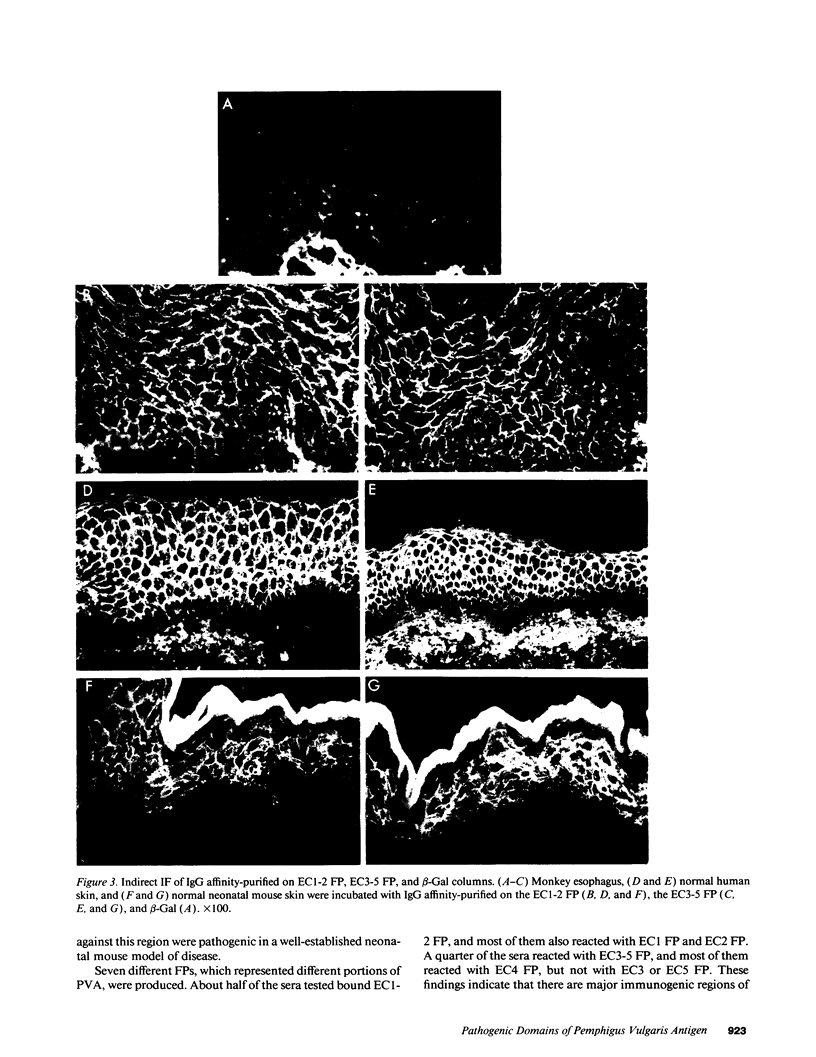
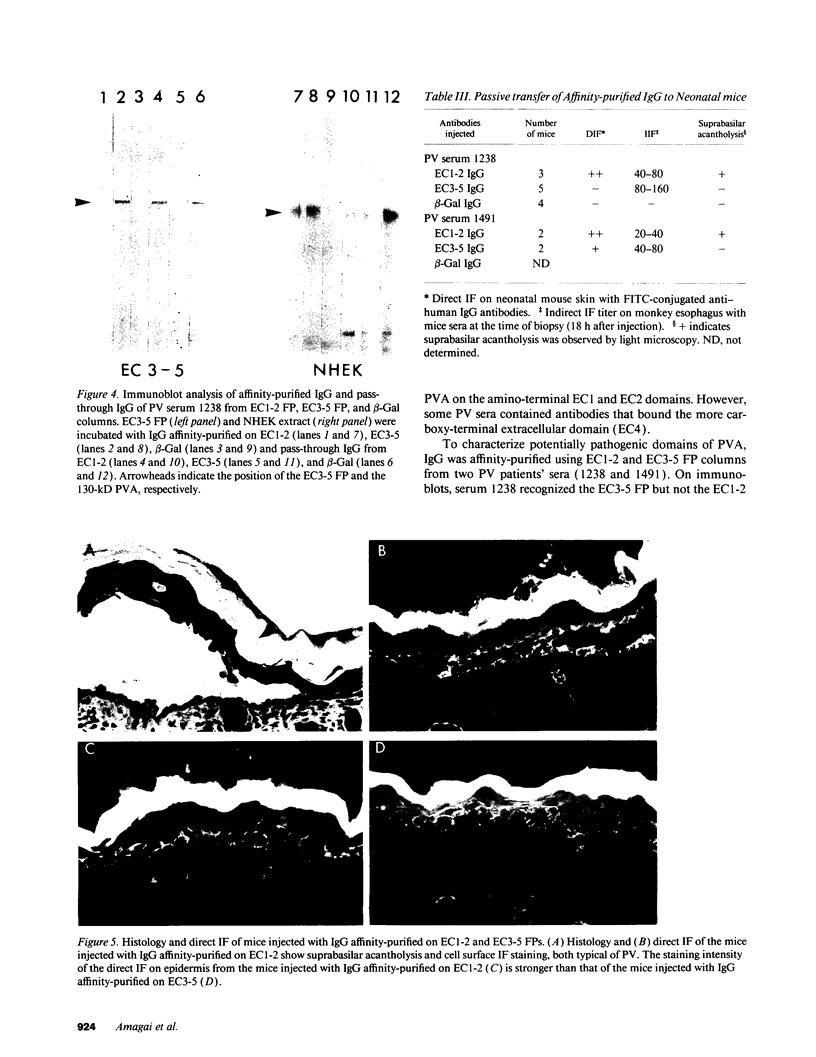
Complementary DNA cloning of the 130-kD pemphigus vulgaris (PV) autoantigen (PVA) has indicated that it is a member of the cadherin family of Ca(2+)-dependent cell adhesion molecules. By homology with typical cadherins, PVA has five extracellular domains (EC1 through EC5). To localize immunogenic domains and to determine whether antibodies against them might be pathogenic, we produced beta-galactosidase fusion proteins with cDNA encoding different portions of the extracellular domains of PVA (EC1-2, EC3-5, and each individual domain). Immunoblot analysis of these fusion proteins with 23 PV patients' sera demonstrated that major immunogenic regions of PVA are located on the EC1, EC2, and EC4 domains. IgG was affinity-purified from PV sera on fusion proteins representing the amino (EC1-2) and carboxy (EC3-5) terminus of the extracellular PVA, and injected into neonatal mice. PV IgG affinity-purified on the EC1-2 fusion protein caused suprabasilar acantholysis, the typical histological finding of PV, but IgG affinity-purified on the EC3-5 fusion protein or beta-galactosidase alone did not. These results indicate that at least one pathogenic epitope, which is sufficient to cause suprabasilar acantholysis in neonatal mice, is located on the amino-terminal region of PVA, an area thought to be important in cadherin homophilic adhesion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amagai M., Klaus-Kovtun V., Stanley J. R. Autoantibodies against a novel epithelial cadherin in pemphigus vulgaris, a disease of cell adhesion. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90360-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anhalt G. J., Labib R. S., Voorhees J. J., Beals T. F., Diaz L. A. Induction of pemphigus in neonatal mice by passive transfer of IgG from patients with the disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 20;306(20):1189–1196. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205203062001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschuk O. W., Sullivan R., David S., Pouliot Y. Identification of a cadherin cell adhesion recognition sequence. Dev Biol. 1990 May;139(1):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90290-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. E., Legan P. K., Kenny T. P., MacGarvie J., Holton J. L., Garrod D. R. Cloning and sequence analysis of desmosomal glycoproteins 2 and 3 (desmocollins): cadherin-like desmosomal adhesion molecules with heterogeneous cytoplasmic domains. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(2):381–391. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre R. W., Stanley J. R. Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal protein complex with a calcium-sensitive epitope are characteristic of pemphigus foliaceus patients. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1719–1724. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre R. W., Stanley J. R. Identification of pemphigus vulgaris antigen extracted from normal human epidermis and comparison with pemphigus foliaceus antigen. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):807–812. doi: 10.1172/JCI113387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin W. J., Sorkin B. C., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Sequence analysis of a cDNA clone encoding the liver cell adhesion molecule, L-CAM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2808–2812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin L., Hill J. E., Raynor K., Raszi L., Manabe M., Cowin P. Desmoglein shows extensive homology to the cadherin family of cell adhesion molecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1224–1230. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80917-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Shafran K. M., Webber P. S., Lazarus G. S., Singer K. H. Anti-cell surface pemphigus autoantibody stimulates plasminogen activator activity of human epidermal cells. A mechanism for the loss of epidermal cohesion and blister formation. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):259–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Ogawa M. M., Konohana A., Nishikawa T. Detection of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus antigens by immunoblot analysis using different antigen sources. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Mar;94(3):327–331. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta K., Nose A., Nagafuchi A., Takeichi M. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a neural calcium-dependent cell adhesion molecule: its identity in the cadherin gene family. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):873–881. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Yokoo K. M., Goldman R. D. Further analysis of pemphigus autoantibodies and their use in studies on the heterogeneity, structure, and function of desmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1109–1117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordon R. E., Bushkell L. L. The complement system in pemphigus, bullous pemphigoid and herpes gestationis. Int J Dermatol. 1979 May;18(4):271–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1979.tb01927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch P. J., Walsh M. J., Schmelz M., Goldschmidt M. D., Zimbelmann R., Franke W. W. Identification of desmoglein, a constitutive desmosomal glycoprotein, as a member of the cadherin family of cell adhesion molecules. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;53(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koulu L., Kusumi A., Steinberg M. S., Klaus-Kovtun V., Stanley J. R. Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal core protein in pemphigus foliaceus. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1509–1518. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Buxton R. S. Transmembrane molecular assemblies regulated by the greater cadherin family. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;3(5):854–861. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90060-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechanic S., Raynor K., Hill J. E., Cowin P. Desmocollins form a distinct subset of the cadherin family of cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4476–4480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatani S., Shimamura K., Hatta M., Nagafuchi A., Nose A., Matsunaga M., Hatta K., Takeichi M. Neural cadherin: role in selective cell-cell adhesion. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):631–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2762814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi A., Shirayoshi Y., Okazaki K., Yasuda K., Takeichi M. Transformation of cell adhesion properties by exogenously introduced E-cadherin cDNA. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):341–343. doi: 10.1038/329341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilles L. A., Parry D. A., Powers E. E., Angst B. D., Wagner R. M., Green K. J. Structural analysis and expression of human desmoglein: a cadherin-like component of the desmosome. J Cell Sci. 1991 Aug;99(Pt 4):809–821. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.4.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa T., Kurihara S., Harada T., Sugawara M., Hatano H. Capability of complement fixation of pemphigus antibodies in vitro. Arch Dermatol Res. 1977 Oct 27;260(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00558008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose A., Nagafuchi A., Takeichi M. Isolation of placental cadherin cDNA: identification of a novel gene family of cell-cell adhesion molecules. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3655–3661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose A., Tsuji K., Takeichi M. Localization of specificity determining sites in cadherin cell adhesion molecules. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90222-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringwald M., Schuh R., Vestweber D., Eistetter H., Lottspeich F., Engel J., Dölz R., Jähnig F., Epplen J., Mayer S. The structure of cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin. Insights into the molecular mechanism of Ca2+-dependent cell adhesion. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3647–3653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoyama Y., Yoshida T., Terada M., Shimosato Y., Abe O., Hirohashi S. Molecular cloning of a human Ca2+-dependent cell-cell adhesion molecule homologous to mouse placental cadherin: its low expression in human placental tissues. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1787–1794. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Alvarez O. M., Bere E. W., Jr, Eaglstein W. H., Katz S. I. Detection of basement membrane zone antigens during epidermal wound healing in pigs. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Aug;77(2):240–243. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12480082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Koulu L., Klaus-Kovtun V., Steinberg M. S. A monoclonal antibody to the desmosomal glycoprotein desmoglein I binds the same polypeptide as human autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1227–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Koulu L., Thivolet C. Distinction between epidermal antigens binding pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):313–320. doi: 10.1172/JCI111426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R. Pemphigus and pemphigoid as paradigms of organ-specific, autoantibody-mediated diseases. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1443–1448. doi: 10.1172/JCI114036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Patel H. P., Labib R. S., Diaz L. A., Anhalt G. J. Experimentally induced pemphigus vulgaris in neonatal BALB/c mice: a time-course study of clinical, immunologic, ultrastructural, and cytochemical changes. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jan;84(1):41–46. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12274679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.2006419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Cadherins: a molecular family important in selective cell-cell adhesion. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:237–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Barton C. H., Putt W., Moore S. E., Kelsell D., Spurr N., Goodfellow P. N. N-cadherin gene maps to human chromosome 18 and is not linked to the E-cadherin gene. J Neurochem. 1990 Sep;55(3):805–812. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler G. N., Parker A. E., Thomas C. L., Ataliotis P., Poynter D., Arnemann J., Rutman A. J., Pidsley S. C., Watt F. M., Rees D. A. Desmosomal glycoprotein DGI, a component of intercellular desmosome junctions, is related to the cadherin family of cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4796–4800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]