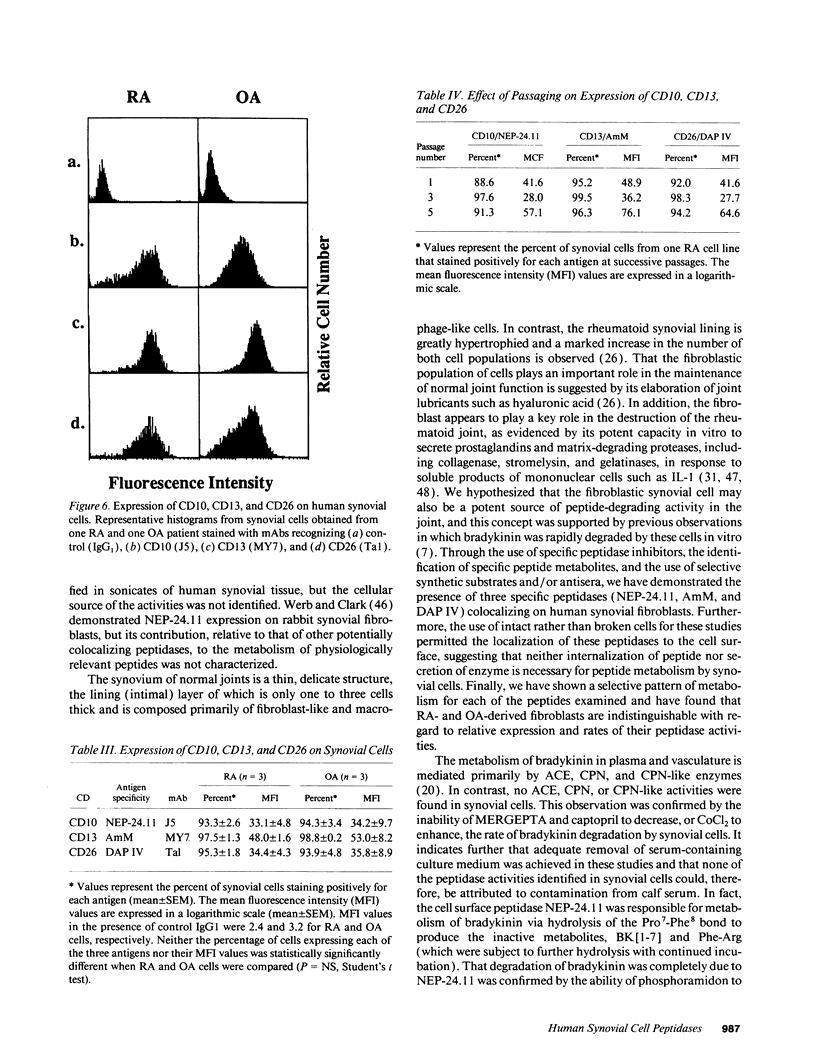
Abstract
Kinins and substance P have been implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory arthritis by virtue of their abilities to induce vasodilation, edema, and pain. The relative biological potencies of these peptides in vivo would depend at least in part upon their rates of catabolism in the joint. We hypothesized that human synovial lining cells may regulate intraarticular levels of kinins and neuropeptides via degradation by cell surface-associated peptidases. We exposed intact human synovial fibroblasts to kinins and substance P, in the presence or absence of specific peptidase inhibitors, and measured the amount of intact substrate remaining and degradation product(s) generated over time. Aminopeptidase M (AmM; EC 3.4.11.2), neutral endopeptidase-24.11 (NEP-24.11; EC 3.4.24.11), and dipeptidyl(amino)peptidase IV (DAP IV; EC 3.4.14.5) were identified on the cell surface of synovial cells. Bradykinin degradation was due entirely to NEP-24.11 (1.39 +/- 0.29 nmol/min per well). Lysylbradykinin was also degraded by NEP-24.11 (0.80 +/- 0.19 nmol/min per well); however, in the presence of phosphoramidon, AmM-mediated conversion to bradykinin (3.74 +/- 0.46 nmol/min per well) could be demonstrated. The combined actions of NEP-24.11 (0.93 +/- 0.15 nmol/min per well) and DAP IV (0.84 +/- 0.18 nmol/min per well) were responsible for the degradation of substance P. AmM (2.44 +/- 0.33 nmol/min per well) and NEP-24.11 (1.30 +/- 0.45 nmol/min per well) were responsible for the degradation of the opioid peptide, [Leu5]enkephalin. The identity of each of the three peptidases was confirmed via synthetic substrate hydrolysis, inhibition profile, and immunological identification. The profiles of peptidase enzymes identified in cells derived from rheumatoid and osteoarthritic joints were identical. These data demonstrate the human synovial fibroblast to be a rich source of three specific peptidases and suggest that it may play a prominent role in regulating peptide levels in the joint.
Full text
PDF

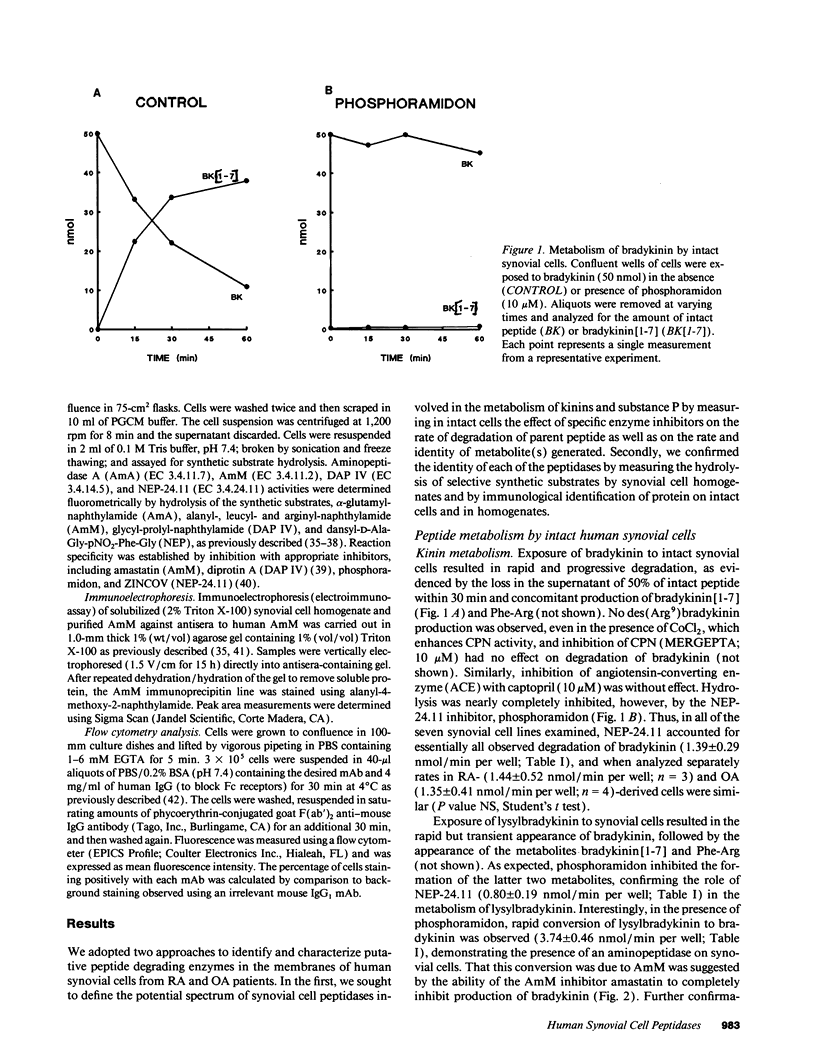
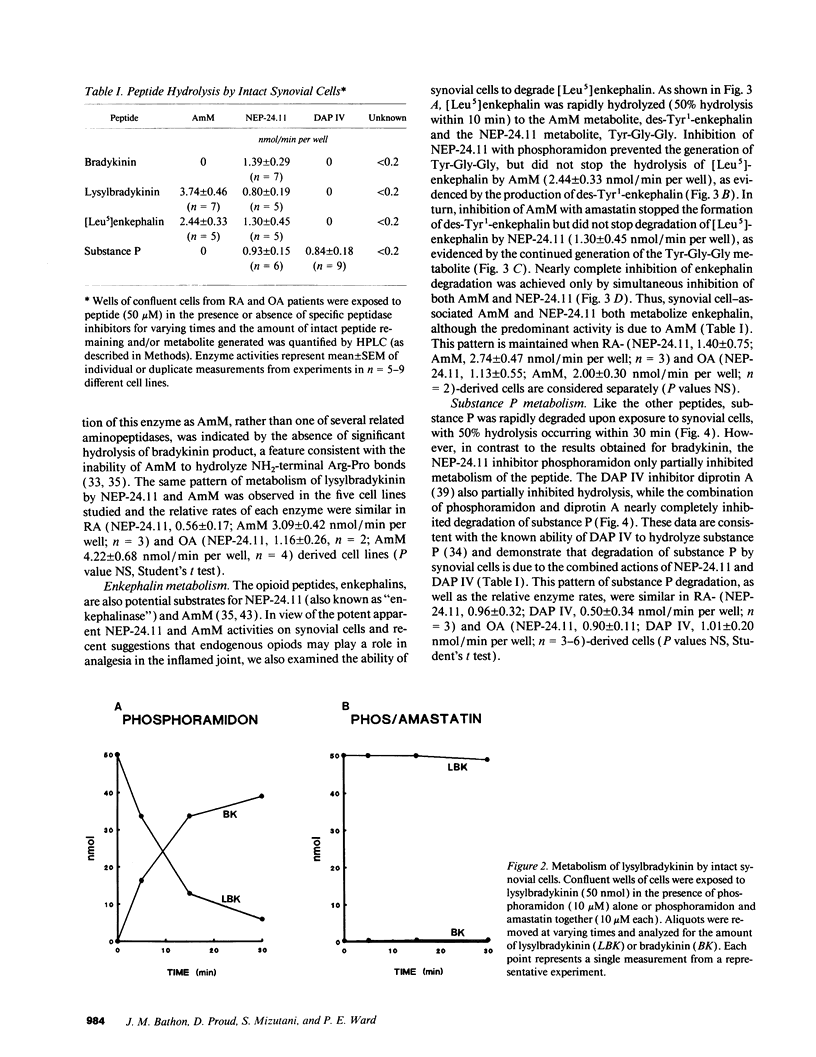
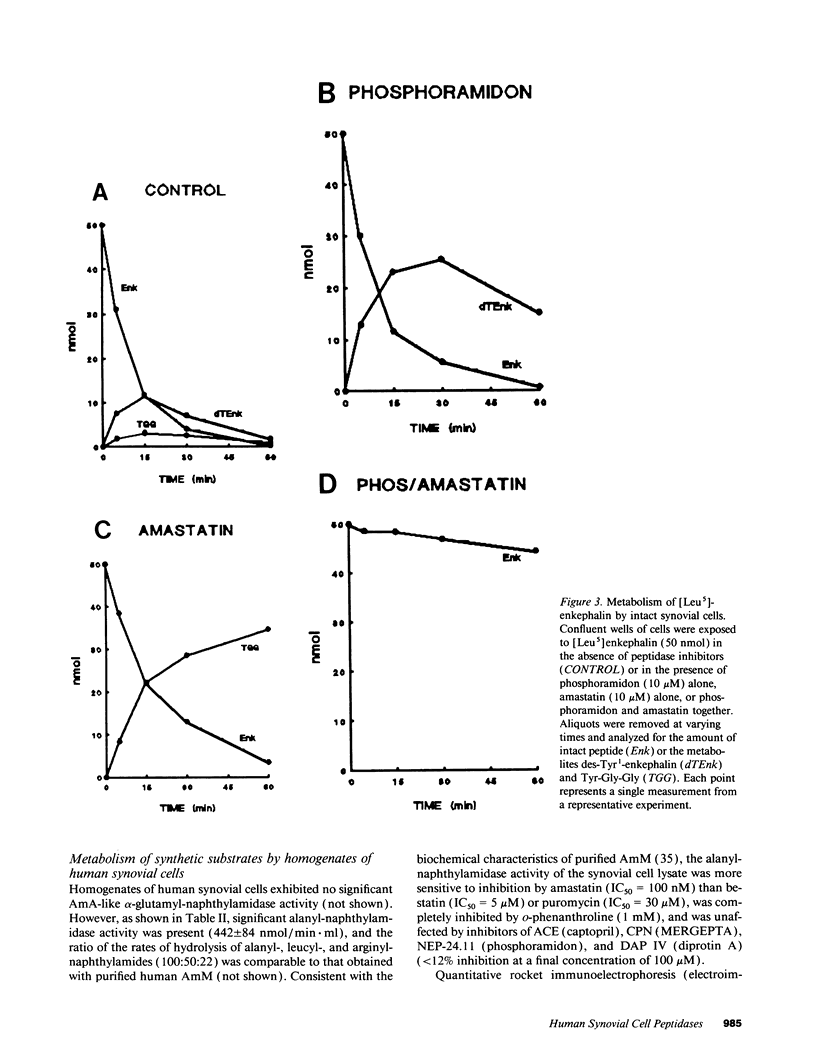
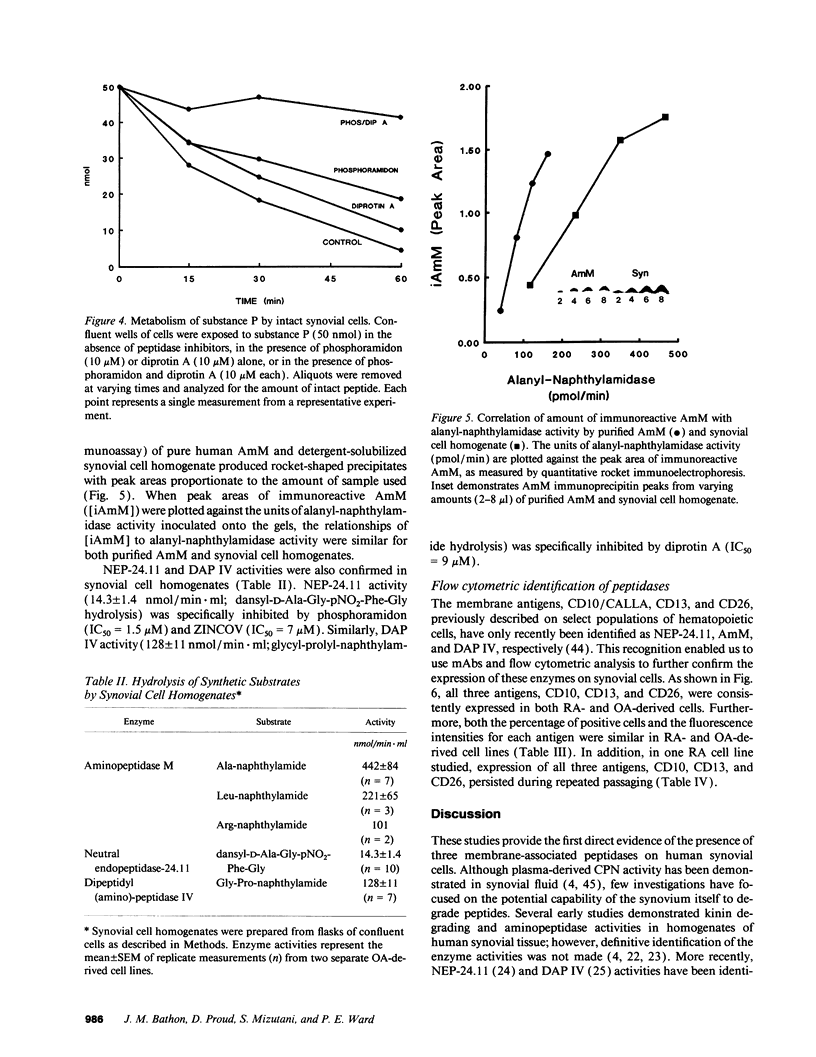




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad S., Ward P. E. Role of aminopeptidase activity in the regulation of the pressor activity of circulating angiotensins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):643–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman R., Asch E., Bloch D., Bole G., Borenstein D., Brandt K., Christy W., Cooke T. D., Greenwald R., Hochberg M. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):1039–1049. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelboom T., de Maertelaer V., de Prez E., Hauzeur J. P., Deschodt-Lanckman M. Enkephalinase: a physiologic neuroimmunomodulator detected in the synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Aug;34(8):1048–1051. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathon J. M., Manning D. C., Goldman D. W., Towns M. C., Proud D. Characterization of kinin receptors on human synovial cells and upregulation of receptor number by interleukin-1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):384–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathon J. M., Proud D. Bradykinin antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991;31:129–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.31.040191.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathon J. M., Proud D., Krackow K., Wigley F. M. Preincubation of human synovial cells with IL-1 modulates prostaglandin E2 release in response to bradykinin. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):579–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bausback H. H., Ward P. E. Degradation of low-molecular-weight opioid peptides by vascular plasma membrane aminopeptidase M. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 16;882(3):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90268-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauvois B. A collagen-binding glycoprotein on the surface of mouse fibroblasts is identified as dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):723–731. doi: 10.1042/bj2520723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjurholm A., Kreicbergs A., Ahmed M., Schultzberg M. Noradrenergic and peptidergic nerves in the synovial membrane of the Sprague-Dawley rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jun;33(6):859–865. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. S., McKelvey A. A., Schleimer R. P., Hildreth J. E., MacGlashan D. W., Jr Flow cytometric methods for the analysis of human basophil surface antigens and viability. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Dec 20;125(1-2):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borson D. B., Gruenert D. C. Glucocorticoids induce neutral endopeptidase in transformed human tracheal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):L83–L89. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.260.2.L83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTOR C. W., PRINCE R. K., DORSTEWITZ E. L. Characteristics of human "fibroblasts" cultivated in vitro from different anatomical sites. Lab Invest. 1962 Sep;11:703–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chercuitte F., Beaulieu A. D., Poubelle P., Marceau F. Carboxypeptidase N (kininase I) activity in blood and synovial fluid from patients with arthritis. Life Sci. 1987 Sep 7;41(10):1225–1232. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90200-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill L., Bausback H. H., Gerritsen M. E., Ward P. E. Metabolism of opioid peptides by cerebral microvascular aminopeptidase M. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 20;923(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Krane S. M., Russell R. G., Robinson D. R. Production of collagenase and prostaglandins by isolated adherent rheumatoid synovial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):945–949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., de Rochemonteix B., Burrus B., Demczuk S., Dinarello C. A. Human recombinant interleukin 1 stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):645–648. doi: 10.1172/JCI112350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., Chow A., Ward P. E. Metabolism of bradykinin analogs by angiotensin I converting enzyme and carboxypeptidase N. Peptides. 1991 May-Jun;12(3):631–638. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(91)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V. Plasma kinins in synovial exudates. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Jun;51(3):322–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman S. C., Schwartz J. M., Milner R. J., Bloom F. E., Feldman J. D. beta-Endorphin enhances lymphocyte proliferative responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4226–4230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönblad M., Konttinen Y. T., Korkala O., Liesi P., Hukkanen M., Polak J. M. Neuropeptides in synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Dec;15(12):1807–1810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 3;322(18):1277–1289. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005033221805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegen M., Niedobitek G., Klein C. E., Stein H., Fleischer B. The T cell triggering molecule Tp103 is associated with dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV activity. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2908–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hojima Y., Cochrane C. G., Wiggins R. C., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. In vitro activation of the contact (Hageman factor) system of plasma by heparin and chondroitin sulfate E. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1453–1459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Charleson S. E., Zimmerman M., Mumford R., Wood P. L. Enkephalinase: selective peptide inhibitors. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 21;29(25):2593–2601. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Biogenesis, release and inactivation of enkephalins and dynorphins. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):17–24. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasani M. K., Katori M., Lewis G. P. Intracellular enzymes and kinin enzymes in synovial fluid in joint diseases. Origin and relation to disease category. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Sep;28(5):497–512. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.5.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamori M., Hagihara M., Nagatsu T., Iwata H., Miura T. Activities of dipeptidyl peptidase II, dipeptidyl peptidase IV, prolyl endopeptidase, and collagenase-like peptidase in synovial membrane from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1991 Apr;45(2):154–160. doi: 10.1016/0885-4505(91)90016-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Nagatsu T., Fukasawa K., Harada M., Nagatsu I., Sakakibara S. Successive cleavage of N-terminal Arg1--Pro2 and Lys3-Pro4 from substance P but no release of Arg1-Pro2 from bradykinin, by X-Pro dipeptidyl-aminopeptidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 7;525(2):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90237-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Booth A. G., George S. G., Ingram J., Kershaw D., Wood E. J., Young A. R. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a kidney brush-border serine peptidase. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):169–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1570169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball E. S., Persico F. J., Vaught J. L. Substance P, neurokinin A, and neurokinin B induce generation of IL-1-like activity in P388D1 cells. Possible relevance to arthritic disease. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3564–3569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konttinen Y. T., Rees R., Hukkanen M., Grönblad M., Tolvanen E., Gibson S. J., Polak J. M., Brewerton D. A. Nerves in inflammatory synovium: immunohistochemical observations on the adjuvant arthritis rat model. J Rheumatol. 1990 Dec;17(12):1586–1591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurauchi O., Mizutani S., Okano K., Narita O., Tomoda Y. Purification and characterization of human placental microsomal aminopeptidase: immunological difference between placental microsomal aminopeptidase and pregnancy serum cystyl-aminopeptidase. Enzyme. 1986;35(4):197–205. doi: 10.1159/000469343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence I. D., Warner J. A., Cohan V. L., Hubbard W. C., Kagey-Sobotka A., Lichtenstein L. M. Purification and characterization of human skin mast cells. Evidence for human mast cell heterogeneity. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3062–3069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner U. H., Jones I. L., Gustafson G. T. Bradykinin, a new potential mediator of inflammation-induced bone resorption. Studies of the effects on mouse calvarial bones and articular cartilage in vitro. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):530–540. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letarte M., Vera S., Tran R., Addis J. B., Onizuka R. J., Quackenbush E. J., Jongeneel C. V., McInnes R. R. Common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen is identical to neutral endopeptidase. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1247–1253. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Clark R., Devor M., Helms C., Moskowitz M. A., Basbaum A. I. Intraneuronal substance P contributes to the severity of experimental arthritis. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):547–549. doi: 10.1126/science.6208609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Look A. T., Ashmun R. A., Shapiro L. H., Peiper S. C. Human myeloid plasma membrane glycoprotein CD13 (gp150) is identical to aminopeptidase N. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1299–1307. doi: 10.1172/JCI114015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Carson D. A., Vaughan J. H. Substance P activation of rheumatoid synoviocytes: neural pathway in pathogenesis of arthritis. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):893–895. doi: 10.1126/science.2433770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Effect of neuropeptides on production of inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1218–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.2457950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. R., Snyder S. H. Neuropeptides: multiple molecular forms, metabolic pathways, and receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:773–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. W., Chiu B., Inman R. D. Substance P and arthritis: analysis of plasma and synovial fluid levels. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jan;33(1):87–90. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melmon K. L., Webster M. E., Goldfinger S. E., Seegmiller J. E. The presence of a kinin in inflammatory synovial effusion from arthritides of varying etiologies. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Feb;10(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri F. E., Bausback H. H., Ward P. E. Metabolism of vasoactive peptides by vascular endothelium and smooth muscle aminopeptidase M. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 1;38(1):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri F. E., Ward P. E. Mesentery vascular metabolism of substance P. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 22;755(3):522–525. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G., Goetzl E. J. Modulation of lymphocyte function by sensory neuropeptides. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2 Suppl):783s–786s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira da Silva J. A., Carmo-Fonseca M. Peptide containing nerves in human synovium: immunohistochemical evidence for decreased innervation in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1990 Dec;17(12):1592–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow B. Role of tachykinins in neurogenic inflammation. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2 Suppl):812s–815s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piazza G. A., Callanan H. M., Mowery J., Hixson D. C. Evidence for a role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in fibronectin-mediated interactions of hepatocytes with extracellular matrix. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):327–334. doi: 10.1042/bj2620327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierart M. E., Najdovski T., Appelboom T. E., Deschodt-Lanckman M. M. Effect of human endopeptidase 24.11 ("enkephalinase") on IL-1-induced thymocyte proliferation activity. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3808–3811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Kaplan A. P. Kinin formation: mechanisms and role in inflammatory disorders. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:49–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Florentin D., Waksman G., Sassi A., Chaillet P., Collado H., Costentin J. New enkephalinase inhibitors as probes to differentiate "enkephalinase" and angiotensin-converting-enzyme active sites. Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1749–1752. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell N. J., Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Opiates inhibit the discharges of fine afferent units from inflamed knee joint of the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Apr 23;76(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C., Peyroux J., Noble F., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Analgesic responses elicited by endogenous enkephalins (protected by mixed peptidase inhibitors) in a variety of morphine-sensitive noxious tests. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 10;192(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90050-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn B. M., Figueroa C. D., Fink E., Swan A., Dieppe P. A., Bhoola K. D. A tissue kallikrein in the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Feb;48(2):128–133. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma J. N., Zeitlin I. J., Deodhar S. D., Buchanan W. W. Detection of kallikrein-like activity in inflamed synovial tissue. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1983 Apr;262(2):279–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S. P., Goetzl E. J., Malfroy B. Elevated synovial tissue concentration of the common acute lymphoblastic leukaemia antigen (CALLA)-associated neutral endopeptidase (3.4.24.11) in human chronic arthritis. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):142–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Hassan A. H., Przewłocki R., Gramsch C., Peter K., Herz A. Opioids from immunocytes interact with receptors on sensory nerves to inhibit nociception in inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5935–5939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Aoyagi T., Ogawa K., Naganawa H., Hamada M., Takeuchi T. Diprotins A and B, inhibitors of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV, produced by bacteria. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Apr;37(4):422–425. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemori E. N., Hibbs M. S., Amento E. P. Constitutive expression of a 92-kD gelatinase (type V collagenase) by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts and its induction in normal human fibroblasts by inflammatory cytokines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1656–1662. doi: 10.1172/JCI115480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemori E. N., Werb Z. Collagenase expression and endogenous activation in rabbit synovial fibroblasts stimulated by the calcium ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16252–16259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio U. A histochemical study on leucinoaminopeptidase activity in the synovial membrane of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1966 May;25(3):253–258. doi: 10.1136/ard.25.3.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainio U. Leucineaminopeptidase in rheumatoid arthritis. Localization in subchondral bone and in synovial fluid cells. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Jul;29(4):434–438. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.4.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Ahmad S., Benter I. F., Chow A., Mizutani S., Ward P. E. Differential processing of substance P and neurokinin A by plasma dipeptidyl(amino)peptidase IV, aminopeptidase M and angiotensin converting enzyme. Peptides. 1991 Nov-Dec;12(6):1357–1364. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(91)90220-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Benter I. F., Dick L., Wilk S. Metabolism of vasoactive peptides by plasma and purified renal aminopeptidase M. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Oct 15;40(8):1725–1732. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90348-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Chow A., Drapeau G. Metabolism of bradykinin agonists and antagonists by plasma aminopeptidase P. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 25;42(4):721–727. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E. Immunoelectrophoretic analysis of vascular, membrane-bound angiotensin I converting enzyme, aminopeptidase M, and dipeptidyl(amino)peptidase IV. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 15;33(20):3183–3193. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Clark E. J. Phorbol diesters regulate expression of the membrane neutral metalloendopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) in rabbit synovial fibroblasts and mammary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9111–9113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J. Enkephalins and endorphins as modifiers of the immune system: present and future. Fed Proc. 1985 Jan;44(1 Pt 1):92–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Epps D. E., Saland L. Beta-endorphin and met-enkephalin stimulate human peripheral blood mononuclear cell chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3046–3053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


