Abstract
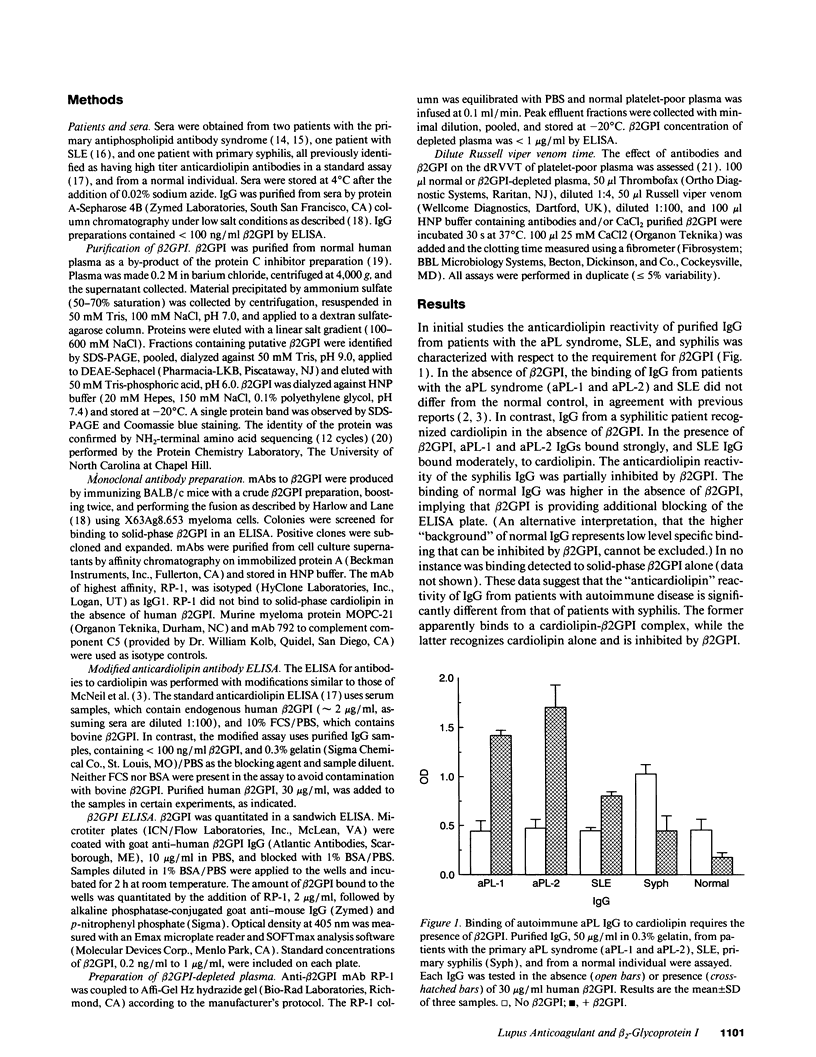
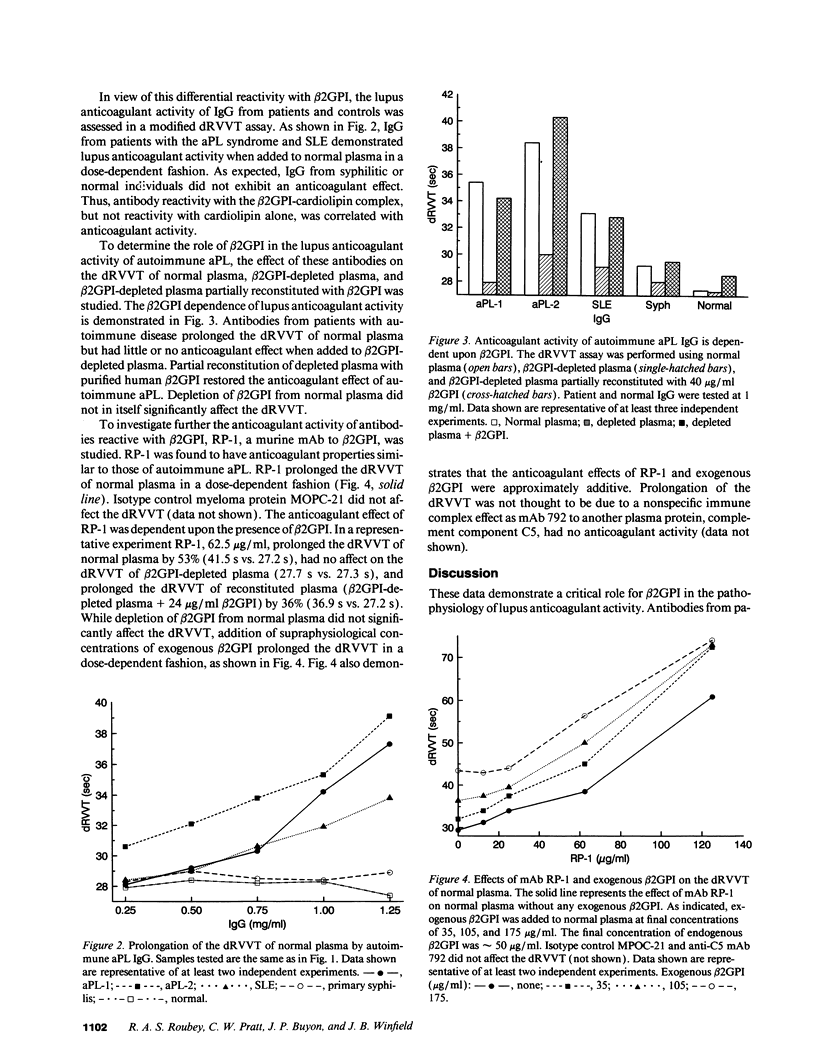
It has been reported that antiphospholipid autoantibodies do not recognize phospholipid alone, but rather the plasma protein beta 2-glycoprotein I (beta 2GPI), or a beta 2GPI-phospholipid complex. In vitro beta 2GPI binds to anionic phospholipids and inhibits the prothrombinase activity of procoagulant membranes. In light of the fact that lupus anticoagulants, a type of antiphospholipid antibody, have similar anticoagulant properties, the relationship of beta 2GPI to lupus anticoagulant activity was investigated. IgG from patients with autoimmune diseases or syphilis were tested for anticardiolipin reactivity and lupus anticoagulant activity in the presence and absence of beta 2GPI. As expected, anti-cardiolipin reactivity associated with autoimmune disease was beta 2GPI dependent. In contrast, IgG from a patient with syphilis recognized cardiolipin alone and binding was inhibited by beta 2GPI. Autoimmune antiphospholipid antibodies prolonged the dilute Russell viper venom time of normal plasma, but had no effect on beta 2GPI-depleted plasma. Antiphospholipid antibodies associated with syphilis had no anticoagulant effect. RP-1, an anti-beta 2GPI mAb, had anticoagulant effects similar to those of autoimmune antiphospholipid antibodies. These data demonstrate that antiphospholipid autoantibodies exert lupus anticoagulant activity via an interaction with beta 2GPI. These antibodies and RP-1 appear to amplify the anticoagulant effect of beta 2GPI itself.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asherson R. A., Khamashta M. A., Ordi-Ros J., Derksen R. H., Machin S. J., Barquinero J., Outt H. H., Harris E. N., Vilardell-Torres M., Hughes G. R. The "primary" antiphospholipid syndrome: major clinical and serological features. Medicine (Baltimore) 1989 Nov;68(6):366–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevers E. M., Galli M., Barbui T., Comfurius P., Zwaal R. F. Lupus anticoagulant IgG's (LA) are not directed to phospholipids only, but to a complex of lipid-bound human prothrombin. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Dec 2;66(6):629–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleve H. Genetic Studies on the Deficiency of beta 2-Glycoprotein I of Human Serum. Humangenetik. 1968;5(4):294–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00291637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleve H., Rittner C. Further family studies on the genetic control of beta 2-glycoprotein I concentration in human serum. Humangenetik. 1969;7(2):93–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00287072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohnen G. Immunochemical quantitation of beta2-glycoprotein I in various diseases. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Feb;75(2):212–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exner T., Sahman N., Trudinger B. Separation of anticardiolipin antibodies from lupus anticoagulant on a phospholipid-coated polystyrene column. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):1001–1007. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80596-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli M., Comfurius P., Maassen C., Hemker H. C., de Baets M. H., van Breda-Vriesman P. J., Barbui T., Zwaal R. F., Bevers E. M. Anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA) directed not to cardiolipin but to a plasma protein cofactor. Lancet. 1990 Jun 30;335(8705):1544–1547. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91374-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharavi A. E., Harris E. N., Asherson R. A., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: isotype distribution and phospholipid specificity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jan;46(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt H., Schwick H. G., Störiko K. Uber einen erblichen beta-2-Glykoprotein I-Mangel. Humangenetik. 1968;5(4):291–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00291636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson E. A., Lassus A. The occurrence of circulating anticoagulants in patients with syphilitic and biologically false positive antilipoidal antibodies. Ann Clin Res. 1974 Apr;6(2):105–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppe A. L., Walter H., Chopra V. P., Bajatzadeh M. Investigations on the genetics and population genetics of the beta 2-glycoprotein I polymorphism. Humangenetik. 1970;9(2):164–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00278932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Salem H. H., Howard M. A., Oldmeadow M. J., Firkin B. G. Studies of natural anticoagulant proteins and anticardiolipin antibodies in patients with the lupus anticoagulant. Br J Haematol. 1990 Nov;76(3):380–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb06372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier J., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of human plasma beta 2-glycoprotein I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3640–3644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malia R. G., Kitchen S., Greaves M., Preston F. E. Inhibition of activated protein C and its cofactor protein S by antiphospholipid antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1990 Sep;76(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak E., Romond E. H. Impaired catalytic function of activated protein C: a new in vitro manifestation of lupus anticoagulant. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2426–2432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anticardiolipin antibodies and lupus anticoagulants comprise separate antibody subgroups with different phospholipid binding characteristics. Br J Haematol. 1989 Dec;73(4):506–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Immunology and clinical importance of antiphospholipid antibodies. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:193–280. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60777-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil H. P., Simpson R. J., Chesterman C. N., Krilis S. A. Anti-phospholipid antibodies are directed against a complex antigen that includes a lipid-binding inhibitor of coagulation: beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimpf J., Bevers E. M., Bomans P. H., Till U., Wurm H., Kostner G. M., Zwaal R. F. Prothrombinase activity of human platelets is inhibited by beta 2-glycoprotein-I. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 29;884(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimpf J., Wurm H., Kostner G. M. Beta 2-glycoprotein-I (apo-H) inhibits the release reaction of human platelets during ADP-induced aggregation. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Feb;63(2-3):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt C. W., Macik B. G., Church F. C. Protein C inhibitor: purification and proteinase reactivity. Thromb Res. 1989 Mar 15;53(6):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammaritano L. R., Gharavi A. E., Lockshin M. D. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: immunologic and clinical aspects. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Oct;20(2):81–96. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(90)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I. beta 2-Glycoprotein I: a plasma inhibitor of the contact activation of the intrinsic blood coagulation pathway. Blood. 1985 Nov;66(5):1086–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Thiagarajan P. Lupus anticoagulants. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1982;6:263–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiagarajan P., Pengo V., Shapiro S. S. The use of the dilute Russell viper venom time for the diagnosis of lupus anticoagulants. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):869–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurm H. beta 2-Glycoprotein-I (apolipoprotein H) interactions with phospholipid vesicles. Int J Biochem. 1984;16(5):511–515. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(84)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



