Abstract
C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP), the third member of the natriuretic peptide family, is thus far known to be distributed mainly in the central nervous system and is considered to act as a neuropeptide, in contrast to atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), which act as cardiac hormones. Recently, we and others have demonstrated that the ANP-B receptor, which is selectively activated by CNP, is localized not only in the central nervous system but in peripheral tissues, including blood vessels. This finding has made us speculate regarding the peripheral production of CNP. In the present study, cultured endothelial cells were examined for CNP production by RIA and Northern blot analysis. CNP-like immunoreactivity was detected in the conditioned media of endothelial cells. Northern blot analysis detected CNPmRNA with a size of 1.2 kb. In addition, transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta, one of the key growth factors for vascular remodeling, markedly stimulated the expression of CNPmRNA and induced a tremendous increase in CNP secretion. We could also detect CNP transcript in the bovine thoracic aorta using the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction method. The present study demonstrates the endothelial production of CNP and suggests that a member of the natriuretic peptide family may act as a local regulator in vascular walls. Since evidence for the pathophysiological importance of the vascular renin-angiotensin system has been accumulating and the natriuretic peptide system is known to be antagonistic to the renin-angiotensin system, the possible existence of "vascular natriuretic peptide system" may prove to be of physiological and clinical relevance.
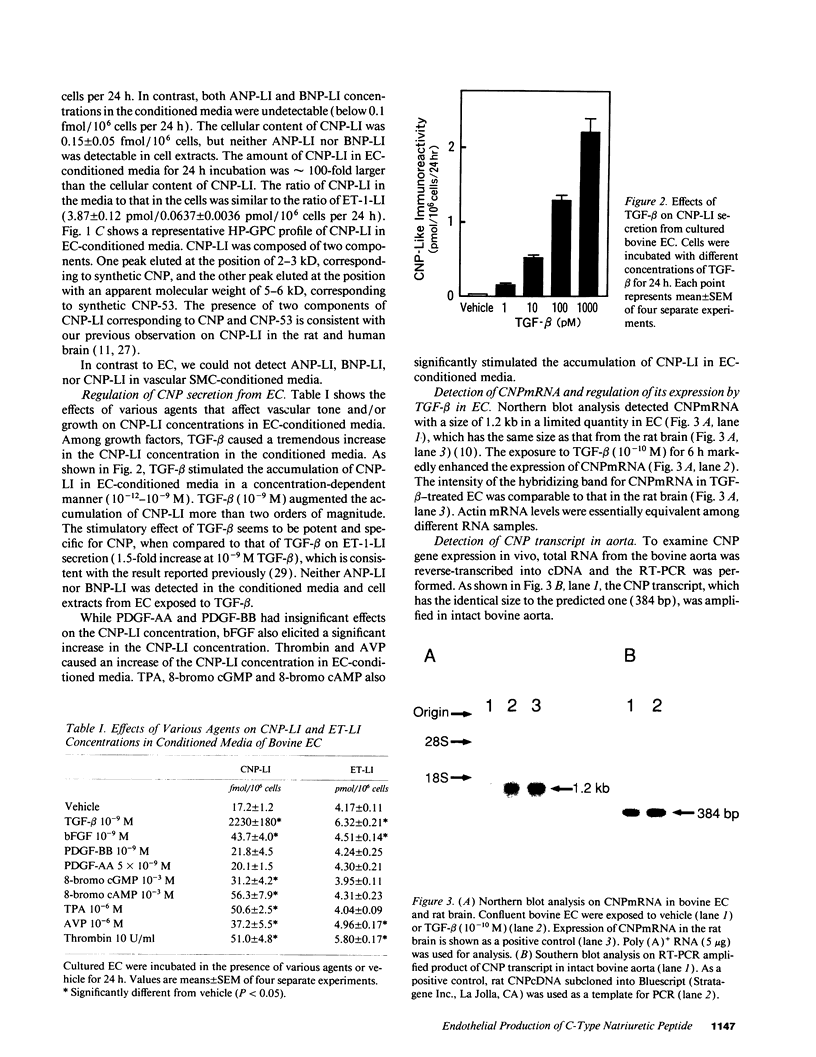
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L. Signal transduction by guanylyl cyclases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:553–575. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganten D., Hermann K., Bayer C., Unger T., Lang R. E. Angiotensin synthesis in the brain and increased turnover in hypertensive rats. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6879184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara H., Shimonaka M., Morisaki M., Ikekawa N., Inada Y. Sitosterol-stimulative production of plasminogen activator in cultured endothelial cells from bovine carotid artery. Thromb Res. 1984 Feb 15;33(4):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Nakao K., Saito Y., Yamada T., Shirakami G., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Hosoda K., Suga S., Minamino N. Radioimmunoassay for brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) detection of BNP in canine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Pratt R. E., Dzau V. J. Atrial natriuretic polypeptide inhibits hypertrophy of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1690–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI114893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Pratt R. E., Ohno M., Dzau V. J. Atrial natriuretic polypeptide as a novel antigrowth factor of endothelial cells. Hypertension. 1992 Jun;19(6 Pt 2):758–761. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.19.6.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Purification and complete amino acid sequence of alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide (alpha-hANP). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima M., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding a precursor for rat C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP). FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80544-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller K. J., Lowe D. G., Bennett G. L., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Goeddel D. V. Selective activation of the B natriuretic peptide receptor by C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP). Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):120–123. doi: 10.1126/science.1672777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu Y., Nakao K., Suga S., Ogawa Y., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Shirakami G., Hosoda K., Nakagawa O., Hama N. C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) in rats and humans. Endocrinology. 1991 Aug;129(2):1104–1106. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-2-1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara H., Yoshizumi M., Sugiyama T., Takaku F., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Hamaoki M., Kato H., Yazaki Y. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of endothelin mRNA by vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92270-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majesky M. W., Lindner V., Twardzik D. R., Schwartz S. M., Reidy M. A. Production of transforming growth factor beta 1 during repair of arterial injury. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):904–910. doi: 10.1172/JCI115393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. N-terminally extended form of C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP-53) identified in porcine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):973–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92187-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukoyama M., Nakao K., Hosoda K., Suga S., Saito Y., Ogawa Y., Shirakami G., Jougasaki M., Obata K., Yasue H. Brain natriuretic peptide as a novel cardiac hormone in humans. Evidence for an exquisite dual natriuretic peptide system, atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1402–1412. doi: 10.1172/JCI115146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Morii N., Itoh H., Yamada T., Shiono S., Sugawara A., Saito Y., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Sakamoto M. Atrial natriuretic polypeptide in the brain: implication of central cardiovascular control. J Hypertens Suppl. 1986 Dec;4(6):S492–S496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Sugawara A., Morii N., Sakamoto M., Suda M., Soneda J., Ban T., Kihara M., Yamori Y., Shimokura M. Radioimmunoassay for alpha-human and rat atrial natriuretic polypeptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):815–821. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse M., Sussman C. R., Naruse K., Jackson R. V., Inagami T. Renin exists in human adrenal tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Sep;57(3):482–487. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-3-482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Adams S. P., Cole B. R., Currie M. G., Geller D. M., Michener M. L., Saper C. B., Schwartz D., Standaert D. G. Atriopeptins as cardiac hormones. Hypertension. 1985 Jul-Aug;7(4):469–482. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen T. T., Lazure C., Babinski K., Chretien M., Ong H., De Lean A. Aldosterone secretion inhibitory factor: a novel neuropeptide in bovine chromaffin cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Mar;124(3):1591–1593. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-3-1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Nakao K., Mukoyama M., Shirakami G., Itoh H., Hosoda K., Saito Y., Arai H., Suga S., Jougasaki M. Rat brain natriuretic peptide--tissue distribution and molecular form. Endocrinology. 1990 Apr;126(4):2225–2227. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-4-2225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Nakao K., Nakagawa O., Komatsu Y., Hosoda K., Suga S., Arai H., Nagata K., Yoshida N., Imura H. Human C-type natriuretic peptide. Characterization of the gene and peptide. Hypertension. 1992 Jun;19(6 Pt 2):809–813. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.19.6.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. K. Control of hypertrophic versus hyperplastic growth of vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 2):H1755–H1765. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.6.H1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer M. A., Braunwald E. Ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Experimental observations and clinical implications. Circulation. 1990 Apr;81(4):1161–1172. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.81.4.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. S., Clozel J. P., Müller R. K., Kuhn H., Hefti F., Hosang M., Baumgartner H. R. Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme prevent myointimal proliferation after vascular injury. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):186–188. doi: 10.1126/science.2526370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig A., Seidman C. E. Atrial natriuretic factor and related peptide hormones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:229–255. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito Y., Nakao K., Mukoyama M., Shirakami G., Itoh H., Yamada T., Arai H., Hosoda K., Suga S., Jougasaki M. Application of monoclonal antibodies for endothelin to hypertensive research. Hypertension. 1990 Jun;15(6 Pt 2):734–738. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.6.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Tsuboi R., Lyons R., Moses H., Rifkin D. B. Characterization of the activation of latent TGF-beta by co-cultures of endothelial cells and pericytes or smooth muscle cells: a self-regulating system. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):757–763. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., de Crombrugghe B. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudoh T., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP): a new member of natriuretic peptide family identified in porcine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):863–870. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92401-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suga S., Nakao K., Hosoda K., Mukoyama M., Ogawa Y., Shirakami G., Arai H., Saito Y., Kambayashi Y., Inouye K. Receptor selectivity of natriuretic peptide family, atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, and C-type natriuretic peptide. Endocrinology. 1992 Jan;130(1):229–239. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.1.1309330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suga S., Nakao K., Kishimoto I., Hosoda K., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Shirakami G., Ogawa Y., Komatsu Y., Nakagawa O. Phenotype-related alteration in expression of natriuretic peptide receptors in aortic smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1992 Jul;71(1):34–39. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J. Atrial natriuretic factor: a hormone produced by the heart. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):767–770. doi: 10.1126/science.2932797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]