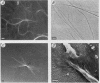
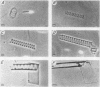
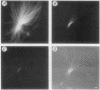
Abstract
Precipitation of cholesterol in gallbladder bile is believed to produce platelike cholesterol monohydrate crystals directly. We report complementary time-lapse microscopic studies of cholesterol crystallization from model bile that reveal initial assembly of filamentous cholesterol crystals covered by a monomolecular layer of lecithin. Over a few days, the filaments evolved through needle, helical, and tubular microstructures to form classical platelike cholesterol monohydrate crystals. Similar crystallization phenomena were observed in human gallbladder biles from cholesterol but not pigment stone patients. Synchrotron x-ray diffraction of the earliest filaments suggested a cholesterol monohydrate polymorph or admixture with an anhydrous cholesterol precursor. However, density gradient centrifugation of filamentous crystals revealed that their density was 1.032 g/ml, consistent with anhydrous cholesterol. Conventional x-ray diffraction of transitional crystalline forms was consistent with pure cholesterol monohydrate crystals, as were the equilibrium platelike crystals. These novel findings suggest that crystalline cholesterol in bile may not be completely mature or hydrated initially, but undergoes a series of transformations to become thermodynamically stable monohydrate plates. These observations have important implications for understanding the control of cholesterol crystallization in bile, as well as explaining putative crystal cytotoxicity during gallstone formation.
Full text
PDF


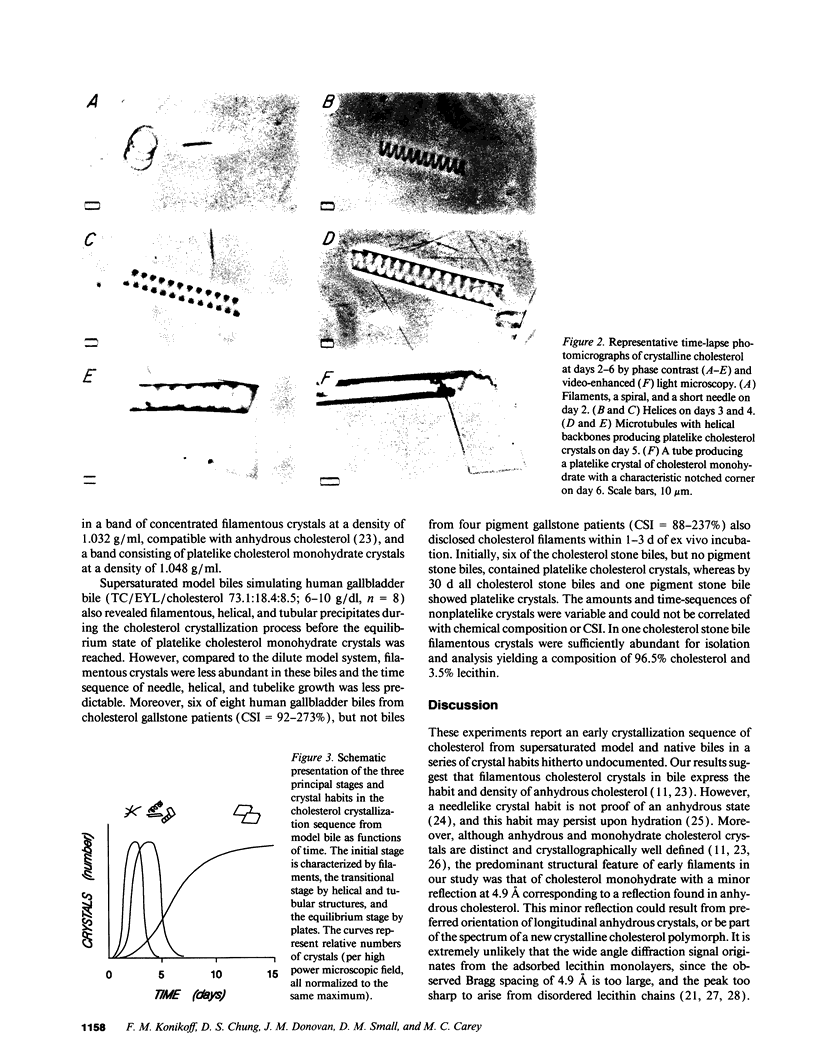
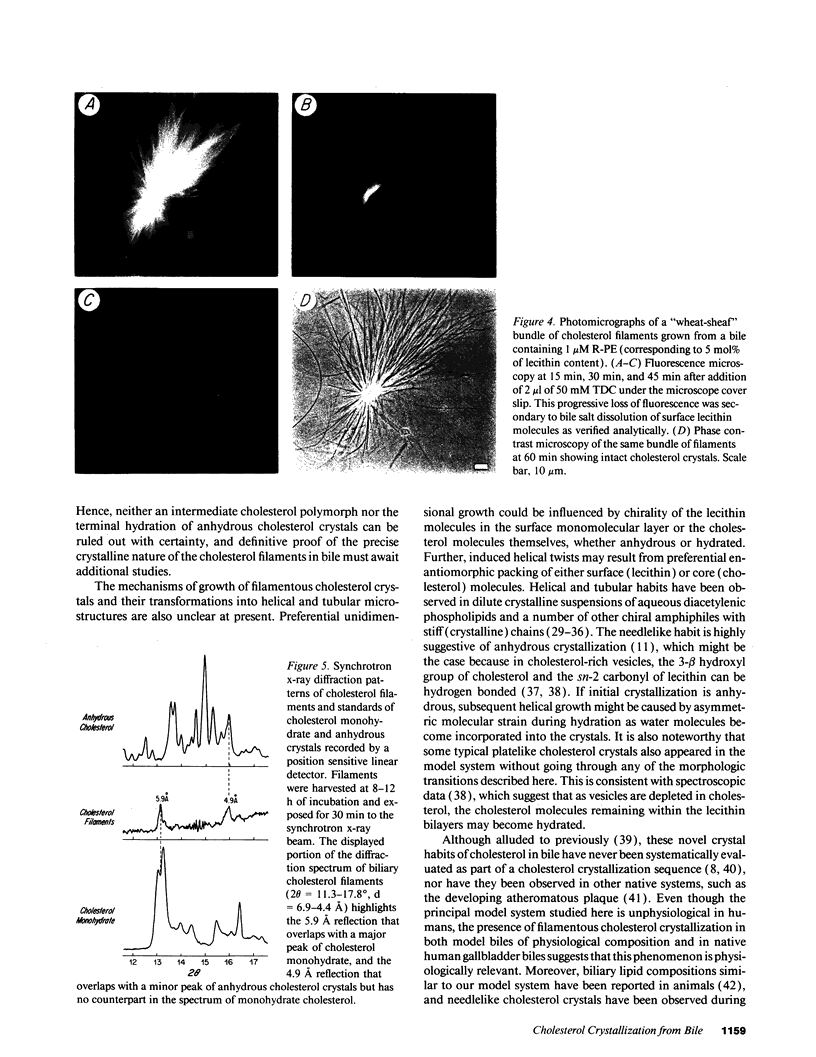

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt H. M., Jackson J. K., Wu W. Crystal-induced inflammation: studies of the mechanism of crystal-membrane interactions. Scanning Microsc. 1991 Mar;5(1):273–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Small D. M. The physical chemistry of cholesterol solubility in bile. Relationship to gallstone formation and dissolution in man. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):998–1026. doi: 10.1172/JCI109025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. E., Carey M. C. Rapid (1 hour) high performance gel filtration chromatography resolves coexisting simple micelles, mixed micelles, and vesicles in bile. J Lipid Res. 1990 Nov;31(11):2103–2112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. E., Fisch M. R., Carey M. C. Principles of laser light-scattering spectroscopy: applications to the physicochemical study of model and native biles. Hepatology. 1990 Sep;12(3 Pt 2):113S–122S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven B. M. Crystal structure of cholesterol monohydrate. Nature. 1976 Apr 22;260(5553):727–729. doi: 10.1038/260727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl A. K. Epidemiology and natural history of gallstone disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1991 Mar;20(1):1–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. M., Timofeyeva N., Carey M. C. Influence of total lipid concentration, bile salt:lecithin ratio, and cholesterol content on inter-mixed micellar/vesicular (non-lecithin-associated) bile salt concentrations in model bile. J Lipid Res. 1991 Sep;32(9):1501–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Amin P., Klein H., Kupke I. Use of a simple enzymatic assay for cholesterol analysis in human bile. J Lipid Res. 1980 Feb;21(2):259–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garti N., Karpuj L., Sarig S. Correlation between crystal habit and the composition of solvated and nonsolvated cholesterol crystals. J Lipid Res. 1981 Jul;22(5):785–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbach R. T. Nucleation of cholesterol crystals in native bile. Hepatology. 1990 Sep;12(3 Pt 2):155S–161S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janiak M. J., Loomis C. R., Shipley G. G., Small D. M. The ternary phase diagram of lecithin, cholesteryl linolenate and water: phase behavior and structure. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):325–339. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins S. A. Biliary lipids, bile acids and gallstone formation in hypovitaminotic C guinea-pigs. Br J Nutr. 1978 Sep;40(2):317–322. doi: 10.1079/bjn19780128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. S., Small D. M. Isolation and and partial characterization of the lipid phases of human atherosclerotic plaques. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9753–9759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F., Jr, Eriksson H., Curstedt T., Sjövall J. Effect of ethynylestradiol on biliary excretion of bile acids, phosphatidylcolines, and cholesterol in the bile fistula rat. J Lipid Res. 1977 Sep;18(5):623–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg D., Ragimova S., Bor A., Almog S., Vinkler C., Peled Y., Halpern Z. Stability of mixed micellar systems made by solubilizing phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol vesicles by bile salts. Hepatology. 1990 Sep;12(3 Pt 2):149S–154S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin K. C., Weis R. M., McConnell H. M. Induction of helical liposomes by Ca2+-mediated intermembrane binding. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):164–165. doi: 10.1038/296164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis C. R., Shipley G. G., Small D. M. The phase behavior of hydrated cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1979 May;20(4):525–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. L. Crystallization of sodium taurocholate. J Lipid Res. 1967 Mar;8(2):146–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renshaw P. F., Janoff A. S., Miller K. W. On the nature of dilute aqueous cholesterol suspensions. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):47–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph A. S., Ratna B. R., Kahn B. Self-assembling phospholipid filaments. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):52–55. doi: 10.1038/352052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad H. Y., Higuchi W. I. Water solubility of cholesterol. J Pharm Sci. 1965 Aug;54(8):1205–1206. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600540826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Thompson T. E. Cholesterol-induced fluid-phase immiscibility in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8686–8690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedaghat A., Grundy S. M. Cholesterol crystals and the formation of cholesterol gallstones. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1274–1277. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seul M., Eisenberger P., McConnell H. M. X-ray diffraction by phospholipid monolayers on single-crystal silicon substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5795–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh H. S., Hoard L. G., Nordman C. E. Crystal structure of anhydrous cholesterol. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):287–289. doi: 10.1038/267287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. Phase equilibria and structure of dry and hydrated egg lecithin. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):551–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Shipley G. G. Physical-chemical basis of lipid deposition in atherosclerosis. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):222–229. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer R. D., Bryson G., Bischoff F. Cholesterol plate deposition in a pathological transport environment. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1975 Aug;11(4):515–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toor E. W., Evans D. F., Cussler E. L. Cholesterol monohydrate growth in model bile solutions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6230–6234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Re-evaluation of the 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase assay for total bile acids in bile. J Lipid Res. 1978 Sep;19(7):924–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOMACK N. A., ZEPPA R., IRVIN G. L., 3rd The anatomy of gallstones. Ann Surg. 1963 May;157:670–686. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196305000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Capes S. E., Mantsch H. H. Hydrogen bonding between anhydrous cholesterol and phosphatidylcholines: an infrared spectroscopic study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 27;980(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]