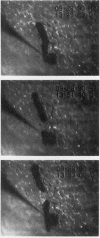
Abstract
We determined the effect of sera enriched with the soluble complex of complement (SC5b-9), on hydraulic conductivity (Lp) of single pulmonary venules (diameter 20-30 microns). Sera free of anticoagulants and blood cells were prepared from rat and human blood. Lp were determined by our split drop technique in isolated, blood-perfused lungs prepared from anesthetized rats (2% halothane; Sprague Dawley, 500 g; n = 73). Zymosan-activated (ZAS) and control sera were used for Lp determinations. In ZAS prepared from human serum, SC5b-9 concentration was > 300 micrograms/ml (control: < 1 microgram/ml) as determined by ELISA. At baseline, Lp averaged 3.4 +/- .4 x 10(-7) ml/(cm2.s.cm H2O), but it increased by 217 +/- 32% with undiluted ZAS (P < 0.05). The Lp increase correlated significantly with different ZAS dilutions for rat serum and with SC5b-9 concentration for human serum. Lp did not increase significantly with ZAS prepared from heat-treated sera, C6- and C8-deficient sera; or with ZAS in which SC5b-9 had been depleted by immunoprecipitation. The ZAS-induced increase of Lp was blocked completely by venular preinfusion with the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) tripeptide (1 mg/ml, 10 min). We report for the first time that: (a) SC5b-9 increases lung endothelial Lp; and (b) the increase of Lp is attributable to an integrin-dependent mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albelda S. M., Buck C. A. Integrins and other cell adhesion molecules. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2868–2880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Lint T. F., McLeod B. C., Behrends C. L., Gewurz H. Studies on the inhibition of C56-induced lysis (reactive lysis). VI. Modulation of C56-induced lysis polyanions and polycations. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):554–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bariety J., Hinglais N., Bhakdi S., Mandet C., Rouchon M., Kazatchkine M. D. Immunohistochemical study of complement S protein (Vitronectin) in normal and diseased human kidneys: relationship to neoantigens of the C5b-9 terminal complex. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Jan;75(1):76–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Hugo F., Tranum-Jensen J. Functions and relevance of the terminal complement sequence. Blut. 1990 Jun;60(6):309–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01737843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya J., Gropper M. A., Staub N. C. Interstitial fluid pressure gradient measured by micropuncture in excised dog lung. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Feb;56(2):271–277. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya J. Hydraulic conductivity of lung venules determined by split-drop technique. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jun;64(6):2562–2567. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.6.2562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G. The complement SC5b-9 complex mediates cell adhesion through a vitronectin receptor. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Caldwell P. R., Andres G., Brentjens J. R. Lung injury mediated by antibodies to endothelium. II. Study of the effect of repeated antigen-antibody interactions in rabbits tolerant to heterologous antibody. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):216–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenais F., Virella G., Patrick C. C., Fudenberg H. H. Isolation of soluble immune complexes by affinity chromatography using staphylococcal protein A--Sepharose as substrate. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(1-2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A. Human endothelial cells synthesize and express an Arg-Gly-Asp-directed adhesion receptor involved in attachment to fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6471–6475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI CARLO F. J., FIORE J. V. On the composition of zymosan. Science. 1958 Apr 4;127(3301):756–757. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3301.756-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Colella S., Conforti G., Abbadini M., Gaboli M., Marchisio P. C. Fibronectin and vitronectin regulate the organization of their respective Arg-Gly-Asp adhesion receptors in cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1215–1223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doumas B. T., Bayse D. D., Carter R. J., Peters T., Jr, Schaffer R. A candidate reference method for determination of total protein in serum. I. Development and validation. Clin Chem. 1981 Oct;27(10):1642–1650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Podack E., Dalmasso A. P., Jennette J. C. Localization of S protein and its relationship to the membrane attack complex of complement in renal tissue. Am J Pathol. 1987 Apr;127(1):182–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawryl M. S., Simon M. T., Eatman J. L., Lint T. F. An enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay for the quantitation of the terminal complement complex from cell membranes or in activated human sera. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 24;95(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg J. C. Neutrophil kinetics and lung injury. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1249–1295. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Hamdoch T., Mathey D., Schäfer H., Bhakdi S. Quantitative measurement of SC5b-9 and C5b-9(m) in infarcted areas of human myocardium. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jul;81(1):132–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Krämer S., Bhakdi S. Sensitive ELISA for quantitating the terminal membrane C5b-9 and fluid-phase SC5b-9 complex of human complement. J Immunol Methods. 1987 May 20;99(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampugnani M. G., Resnati M., Dejana E., Marchisio P. C. The role of integrins in the maintenance of endothelial monolayer integrity. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):479–490. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois P. F., Gawryl M. S. Accentuated formation of the terminal C5b-9 complement complex in patient plasma precedes development of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Aug;138(2):368–375. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.2.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack complex of complement. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:503–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons P. E., Giclas P. C. The terminal complement complex (sC5b-9) is not specifically associated with the development of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Jan;141(1):98–103. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Purification of the sixth and seventh component of human complement without loss of hemolytic activity. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T., Anders E., Grulich-Henn J., Müller-Berghaus G. Attachment of cultured human endothelial cells is promoted by specific association with S protein (vitronectin) as well as with the ternary S protein-thrombin-antithrombin III complex. Blood. 1988 Jun;71(6):1581–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preissner K. T. Structure and biological role of vitronectin. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:275–310. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiao R. L., Bhattacharya J. Segmental barrier properties of the pulmonary microvascular bed. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Dec;71(6):2152–2159. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.71.6.2152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Hartmann R., Neuhoff H., Bhakdi S. Local complement activation, thromboxane-mediated vasoconstriction, and vascular leakage in isolated lungs. Role of the terminal complement sequence. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jan;139(1):88–99. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Pierschbacher M. D., Hayman E. G., Nguyen K., Ohgren Y., Ruoslahti E. Domain structure of vitronectin. Alignment of active sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15307–15314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till G. O., Johnson K. J., Kunkel R., Ward P. A. Intravascular activation of complement and acute lung injury. Dependency on neutrophils and toxic oxygen metabolites. J Clin Invest. 1982 May;69(5):1126–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI110548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson P. D. Effect of plasma and red blood cells on water permeability in cat hindlimb. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):H818–H823. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1984.246.6.H818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]