Abstract
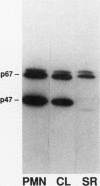
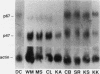
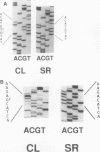
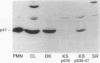
Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphocytes generate superoxide in response to various agonists in an enzymatic reaction similar to that which occurs in stimulated phagocytes. We generated transformed B lymphoblast cell lines from controls, from four patients with p47-phox-deficient chronic granulomatous disease, and from three parents. The cells from controls and from the parents generated 7.0-35 nmol of O2-/10(7) cells per 30 min in response to phorbol myristate acetate. None of the patient cell lines generated any detectable superoxide. Both p47-phox and p67-phox were detected by immunoblot in the cytosol of control and parent cell lines and, as in neutrophils, these proteins had affinity for GTP-agarose. The patients' cell lines contained no detectable p47-phox by immunoblot. mRNA for both cytosolic proteins was detected in all cell lines. We generated cDNA and obtained multiple clones from two patients by polymerase chain reaction. One patient was a compound heterozygote with each allele resulting in an early stop codon. Clones derived from the other patient demonstrated only a GT deletion at base 75. The cDNA for p47-phox was inserted into an EBV-expression vector and stably transfected cell lines were obtained using hygromycin B selection. Transfected cell lines from a p47-phox-deficient patient generated normal levels of superoxide and had readily detectable cytosolic p47-phox. Thus, B lymphoblasts provide an excellent model system for studies of the NADPH oxidase, for expression of functional recombinant forms of oxidase components, and for initial experimental approaches to genetic reconstitution in CGD.
Full text
PDF

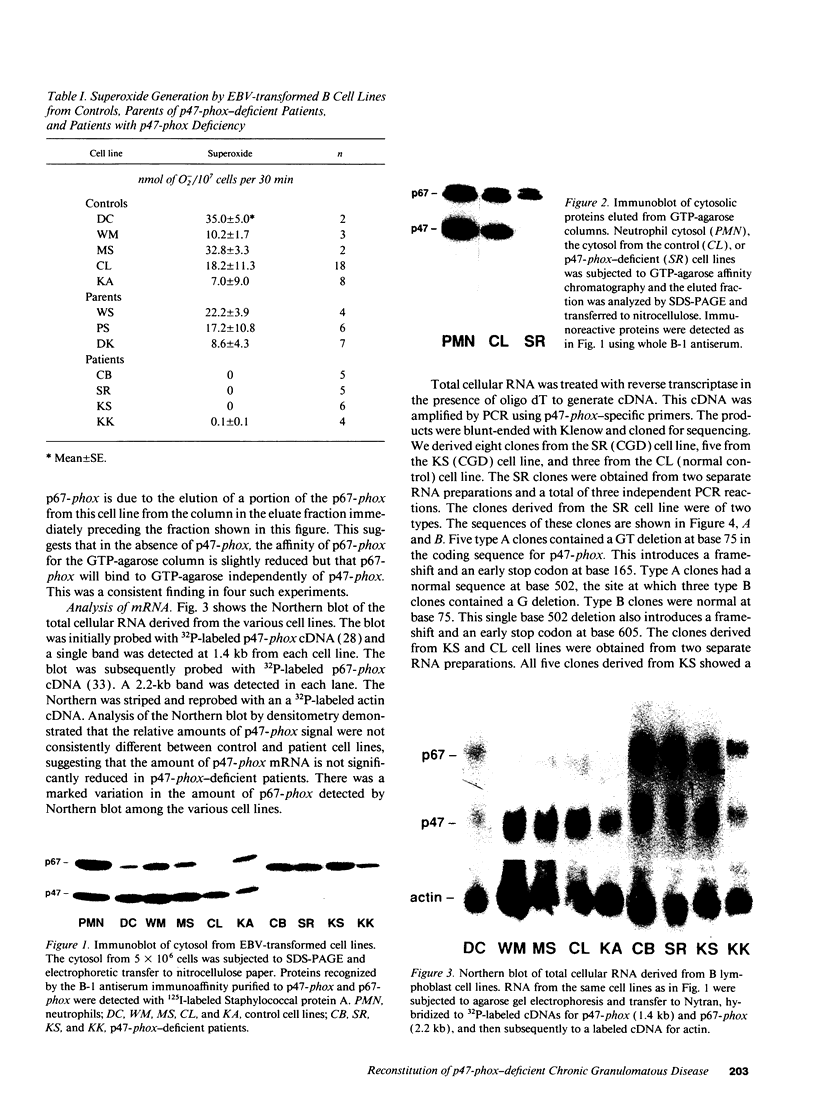
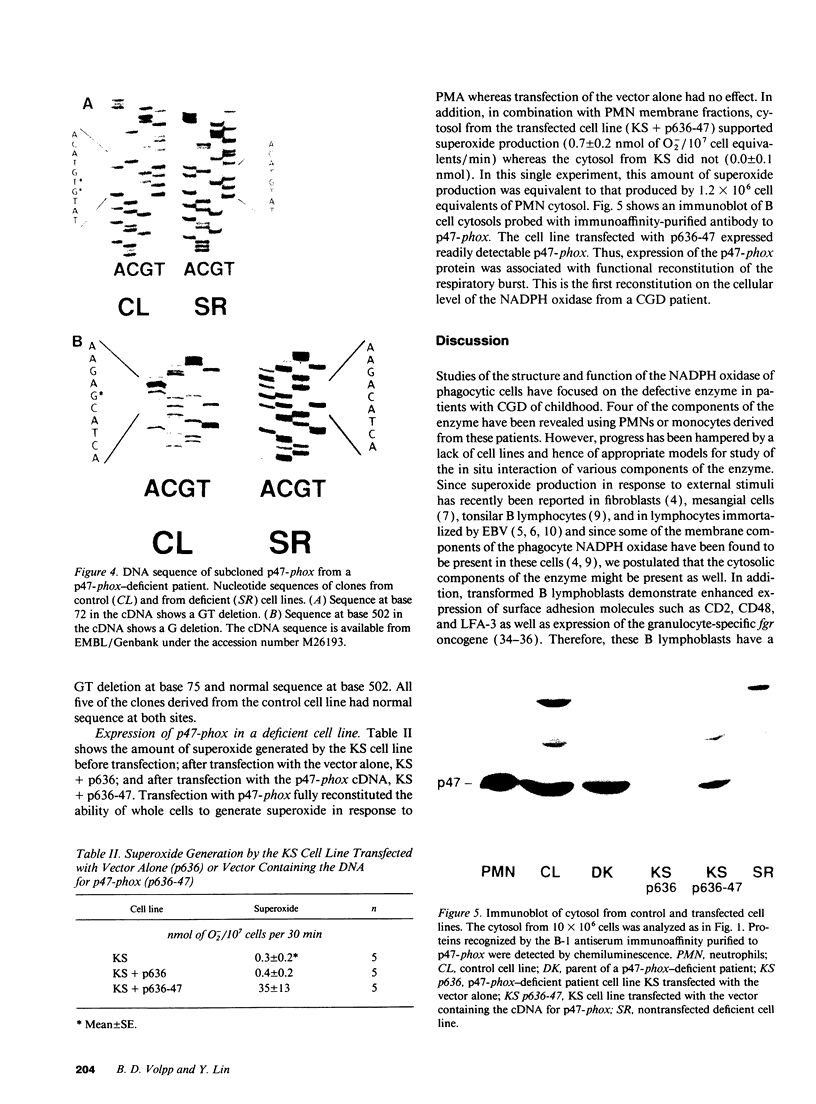



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo A., Pick E., Hall A., Totty N., Teahan C. G., Segal A. W. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):668–670. doi: 10.1038/353668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo A., Pick E. Purification and characterization of a third cytosolic component of the superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23577–23585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 30;298(13):721–725. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803302981305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. The respiratory burst oxidase and the molecular basis of chronic granulomatous disease. Am J Hematol. 1991 Aug;37(4):263–266. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830370410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebenek K., Kunkel T. A. Frameshift errors initiated by nucleotide misincorporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4946–4950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Quilliam L. A., Bohl B. P., Jesaitis A. J., Quinn M. T. Inhibition of Rap1A binding to cytochrome b558 of NADPH oxidase by phosphorylation of Rap1A. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1794–1796. doi: 10.1126/science.1763330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolscher B. G., de Boer M., de Klein A., Weening R. S., Roos D. Point mutations in the beta-subunit of cytochrome b558 leading to X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1991 Jun 1;77(11):2482–2487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casimir C. M., Bu-Ghanim H. N., Rodaway A. R., Bentley D. L., Rowe P., Segal A. W. Autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease caused by deletion at a dinucleotide repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2753–2757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. A., Klebanoff S. J. Chronic granulomatous disease: studies of a family with impaired neutrophil chemotactic, metabolic and bactericidal function. Am J Med. 1978 Dec;65(6):941–948. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90745-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Leidal K. G., Pearson D. W., Nauseef W. M. NADPH oxidase of human neutrophils. Subcellular localization and characterization of an arachidonate-activatable superoxide-generating system. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4065–4074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Malech H. L., Gallin J. I., Nunoi H., Volpp B. D., Pearson D. W., Nauseef W. M., Curnutte J. T. Genetic variants of chronic granulomatous disease: prevalence of deficiencies of two cytosolic components of the NADPH oxidase system. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 7;321(10):647–652. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909073211005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A. The human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1140–1147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Volpp B. D., Leidal K. G., Nauseef W. M. Two cytosolic components of the human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase translocate to the plasma membrane during cell activation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI114496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Tanugi L., Morel F., Pilloud-Dagher M. C., Seigneurin J. M., Francois P., Bost M., Vignais P. V. Activation of O2(-)-generating oxidase in an heterologous cell-free system derived from Epstein-Barr-virus-transformed human B lymphocytes and bovine neutrophils. Application to the study of defects in cytosolic factors in chronic granulomatous disease. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 5;202(2):649–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Scott P. J., Mayo L. A. Cytosolic components of the respiratory burst oxidase: resolution of four components, two of which are missing in complementing types of chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Curnutte J. T., Rosen H., Orkin S. H. A missense mutation in the neutrophil cytochrome b heavy chain in cytochrome-positive X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):2012–2016. doi: 10.1172/JCI114393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Pierce E. A., Bruns G. A., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Human neutrophil cytochrome b light chain (p22-phox). Gene structure, chromosomal location, and mutations in cytochrome-negative autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1729–1737. doi: 10.1172/JCI114898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund E. A., Marshall M., Gibbs J. B., Crean C. D., Gabig T. G. Resolution of a low molecular weight G protein in neutrophil cytosol required for NADPH oxidase activation and reconstitution by recombinant Krev-1 protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13964–13970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. A., Nguyen P. N., Edwards A., Civitello A. B., Caskey C. T. Multiplex DNA deletion detection and exon sequencing of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene in Lesch-Nyhan families. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90545-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Link D. C., Katamine S., Lacal P., Miki T., Ley T. J., Robbins K. C. A novel c-fgr exon utilized in Epstein-Barr virus-infected B lymphocytes but not in normal monocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1500–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. T., Henderson L. M., Jones O. T. Superoxide generation by EBV-transformed B lymphocytes. Activation by IL-1 beta, TNF-alpha and receptor independent stimuli. Immunology. 1990 Oct;71(2):213–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. L., Wardlaw A. J., Stacker S. A., Anderson D. C., Lee A., Roberts T. M., Springer T. A. Transfection of cells from patients with leukocyte adhesion deficiency with an integrin beta subunit (CD18) restores lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 expression and function. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):674–681. doi: 10.1172/JCI114491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Oxygen metabolism and the toxic properties of phagocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Sep;93(3):480–489. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-3-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczak M., Cooper D. N. Gene deletions causing human genetic disease: mechanisms of mutagenesis and the role of the local DNA sequence environment. Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;86(5):425–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00194629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Misalignment-mediated DNA synthesis errors. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 4;29(35):8003–8011. doi: 10.1021/bi00487a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leca G., Benichou G., Bensussan A., Mitenne F., Galanaud P., Vazquez A. Respiratory burst in human B lymphocytes. Triggering of surface Ig receptors induces modulation of chemiluminescence signal. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3542–3549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leto T. L., Garrett M. C., Fujii H., Nunoi H. Characterization of neutrophil NADPH oxidase factors p47-phox and p67-phox from recombinant baculoviruses. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19812–19818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maly F. E., Cross A. R., Jones O. T., Wolf-Vorbeck G., Walker C., Dahinden C. A., De Weck A. L. The superoxide generating system of B cell lines. Structural homology with the phagocytic oxidase and triggering via surface Ig. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2334–2339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maly F. E., Nakamura M., Gauchat J. F., Urwyler A., Walker C., Dahinden C. A., Cross A. R., Jones O. T., de Weck A. L. Superoxide-dependent nitroblue tetrazolium reduction and expression of cytochrome b-245 components by human tonsillar B lymphocytes and B cell lines. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1260–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier B., Cross A. R., Hancock J. T., Kaup F. J., Jones O. T. Identification of a superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase system in human fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 1;275(Pt 1):241–245. doi: 10.1042/bj2750241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs H. D., Igo R. P. The NBT slide test: a simple screening method for detecting chronic granulomatous disease and female carriers. J Pediatr. 1973 Jul;83(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Molecular genetics of chronic granulomatous disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M., Faulkner L., Katz D. R., Brickell P. M. The c-fgr proto-oncogene: expression in Epstein-Barr-virus-infected B lymphocytes and in cells of the myelomonocytic and granulocytic lineages. Pathobiology. 1991;59(4):289–292. doi: 10.1159/000163665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Gadba R. Certain lymphoid cells contain the membrane-associated component of the phagocyte-specific NADPH oxidase. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1611–1617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Kroizman T., Abo A. Activation of the superoxide-forming NADPH oxidase of macrophages requires two cytosolic components--one of them is also present in certain nonphagocytic cells. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4180–4187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn M. T., Parkos C. A., Walker L., Orkin S. H., Dinauer M. C., Jesaitis A. J. Association of a Ras-related protein with cytochrome b of human neutrophils. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):198–200. doi: 10.1038/342198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radeke H. H., Cross A. R., Hancock J. T., Jones O. T., Nakamura M., Kaever V., Resch K. Functional expression of NADPH oxidase components (alpha- and beta-subunits of cytochrome b558 and 45-kDa flavoprotein) by intrinsic human glomerular mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21025–21029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Marsh K., Yates J. A vector that replicates as a plasmid and can be efficiently selected in B-lymphoblasts transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):410–413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umei T., Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T., Smith R. M. Identification of the NADPH-binding subunit of the respiratory burst oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6019–6022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpp B. D., Nauseef W. M., Clark R. A. Two cytosolic neutrophil oxidase components absent in autosomal chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1295–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.2848318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpp B. D., Nauseef W. M., Donelson J. E., Moser D. R., Clark R. A. Cloning of the cDNA and functional expression of the 47-kilodalton cytosolic component of human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7195–7199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. T., DePamphilis M. L. Specific sequences in native DNA that arrest synthesis by DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2075–2086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]