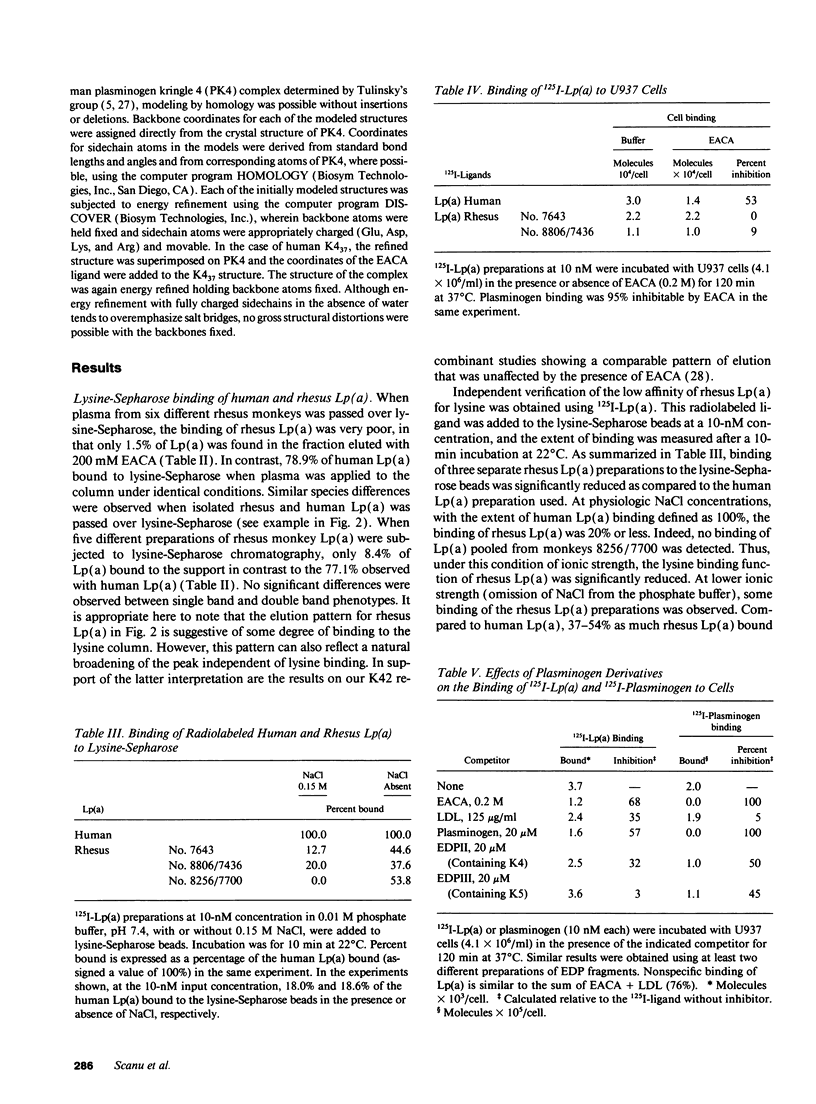
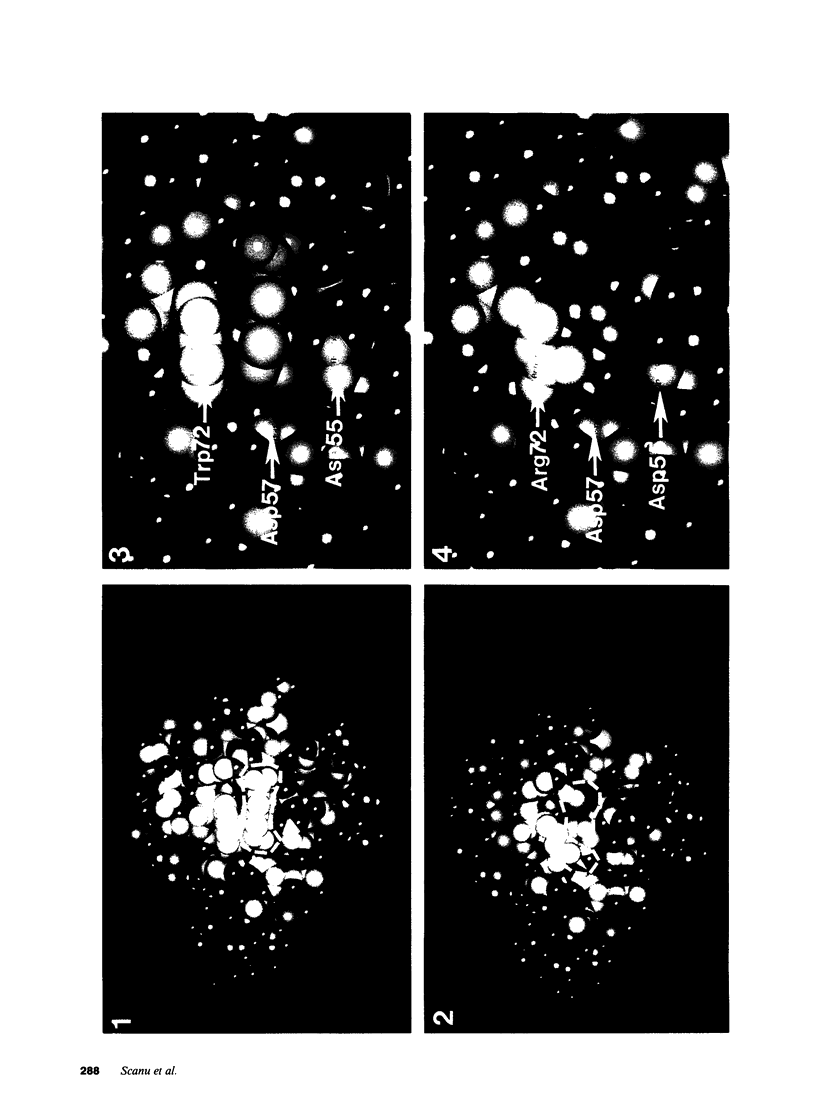
Abstract
Rhesus lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]) binds less efficiently than human Lp(a) to lysine-Sepharose and to cultured U937 cells. Studies using elastase-derived plasminogen fragments indicated that neither kringle 5 nor the protease domain of Lp(a) are required in these interactions pointing at an involvement of the K4 region. Comparative structural analyses of both the human and simian apo(a) K4 domain, together with molecular modeling studies, supported the conclusion that K4(37) plays a dominant role in the lysine binding function of apo(a) and that the presence of arginine 72 rather than tryptophan in this kringle can account for the functional deficiency observed with rhesus Lp(a). These in vitro results suggest that rhesus Lp(a) may be less thrombogenic than human Lp(a).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beisiegel U., Niendorf A., Wolf K., Reblin T., Rath M. Lipoprotein(a) in the arterial wall. Eur Heart J. 1990 Aug;11 (Suppl E):174–183. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/11.suppl_e.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Serrano V. S., Castellino F. J. Role of tryptophan-74 of the recombinant kringle 2 domain of tissue-type plasminogen activator in its omega-amino acid binding properties. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 7;31(13):3326–3335. doi: 10.1021/bi00128a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., Rolih C. A., Scanu A. M. Heterogeneity of human plasma lipoprotein (a). Isolation and characterization of the lipoprotein subspecies and their apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11470–11478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., Snyder M. L., Scanu A. M. Enzyme-linked immunoassay for Lp[a]. J Lipid Res. 1989 May;30(5):651–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., ZumMallen M. E., Scanu A. M. Physicochemical properties of apolipoprotein(a) and lipoprotein(a-) derived from the dissociation of human plasma lipoprotein (a). J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8712–8718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gronow M., Edelberg J. M., Pizzo S. V. Further characterization of the cellular plasminogen binding site: evidence that plasminogen 2 and lipoprotein a compete for the same site. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2374–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschwender S. M., Laursen R. A. The lysine binding sites of human plasminogen. Evidence for a critical tryptophan in the binding site of kringle 4. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11172–11176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Li Z. G., Pfaffinger D., Neven L., Scanu A. M. Familial hypercholesterolemia in a rhesus monkey pedigree: molecular basis of low density lipoprotein receptor deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3122–3126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z., Gambino R., Fless G. M., Copeland R. A., Halfpenny A. J., Scanu A. M. Expression and purification of kringle 4-type 2 of human apolipoprotein (a) in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 1992 Jun;3(3):212–222. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(92)90017-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo J. Lipoprotein(a). A unique risk factor for atherothrombotic disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Sep-Oct;10(5):672–679. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.5.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Scanu A. M. Lipoprotein(a): nonhuman primate models. Lipids. 1991 Sep;26(9):679–683. doi: 10.1007/BF02535613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lawn R. M. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):132–137. doi: 10.1038/330132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Plow E. F. Lp(a): an interloper into the fibrinolytic system? Thromb Haemost. 1990 Jun 28;63(3):331–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulichak A. M., Tulinsky A., Ravichandran K. G. Crystal and molecular structure of human plasminogen kringle 4 refined at 1.9-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10576–10588. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulichak A. M., Tulinsky A. Structure of the lysine-fibrin binding subsite of human plasminogen kringle 4. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1990 Dec;1(6):673–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Gavish D., Azrolan N., Clarkson T. B. Lipoprotein(a) in diet-induced atherosclerosis in nonhuman primates. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Jan-Feb;11(1):32–38. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neven L., Khalil A., Pfaffinger D., Fless G. M., Jackson E., Scanu A. M. Rhesus monkey model of familial hypercholesterolemia: relation between plasma Lp[a] levels, apo[a] isoforms, and LDL-receptor function. J Lipid Res. 1990 Apr;31(4):633–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh V., Petros A. M., Llinás M., Tulinsky A., Park C. H. Proton magnetic resonance study of lysine-binding to the kringle 4 domain of human plasminogen. The structure of the binding site. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):481–498. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90295-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouy D., Laplaud P. M., Saboureau M., Anglés-Cano E. Hedgehog lipoprotein(a) is a modulator of activation of plasminogen at the fibrin surface. An in vitro study. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Feb;12(2):146–154. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.2.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Fless G. M. Lipoprotein (a). Heterogeneity and biological relevance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1709–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI114625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M., Khalil A., Neven L., Tidore M., Dawson G., Pfaffinger D., Jackson E., Carey K. D., McGill H. C., Fless G. M. Genetically determined hypercholesterolemia in a rhesus monkey family due to a deficiency of the LDL receptor. J Lipid Res. 1988 Dec;29(12):1671–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B., Cochran S. Factors influencing the accumulation in fibrous plaques of lipid derived from low density lipoprotein. II. Preferential immobilization of lipoprotein (a) (Lp(a)). Atherosclerosis. 1990 Oct;84(2-3):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(90)90088-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. L., Polacek D., Scanu A. M., Fless G. M. Comparative binding and degradation of lipoprotein(a) and low density lipoprotein by human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):339–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson J. E., McLean J. W., Lawn R. M. Rhesus monkey apolipoprotein(a). Sequence, evolution, and sites of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5957–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trexler M., Váli Z., Patthy L. Structure of the omega-aminocarboxylic acid-binding sites of human plasminogen. Arginine 70 and aspartic acid 56 are essential for binding of ligand by kringle 4. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7401–7406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulinsky A., Park C. H., Skrzypczak-Jankun E. Structure of prothrombin fragment 1 refined at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):885–901. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90565-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. P., Padmanabhan K., Tulinsky A., Mulichak A. M. The refined structure of the epsilon-aminocaproic acid complex of human plasminogen kringle 4. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10589–10594. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]