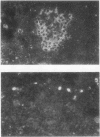
Abstract
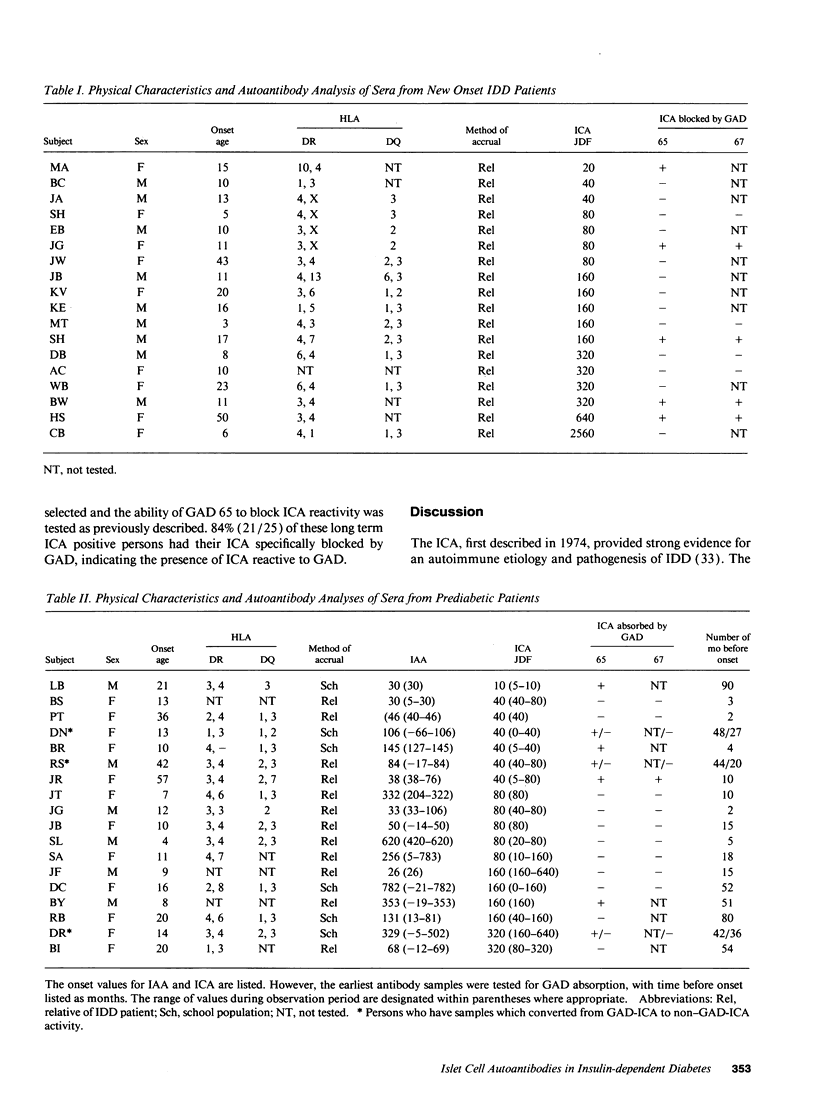
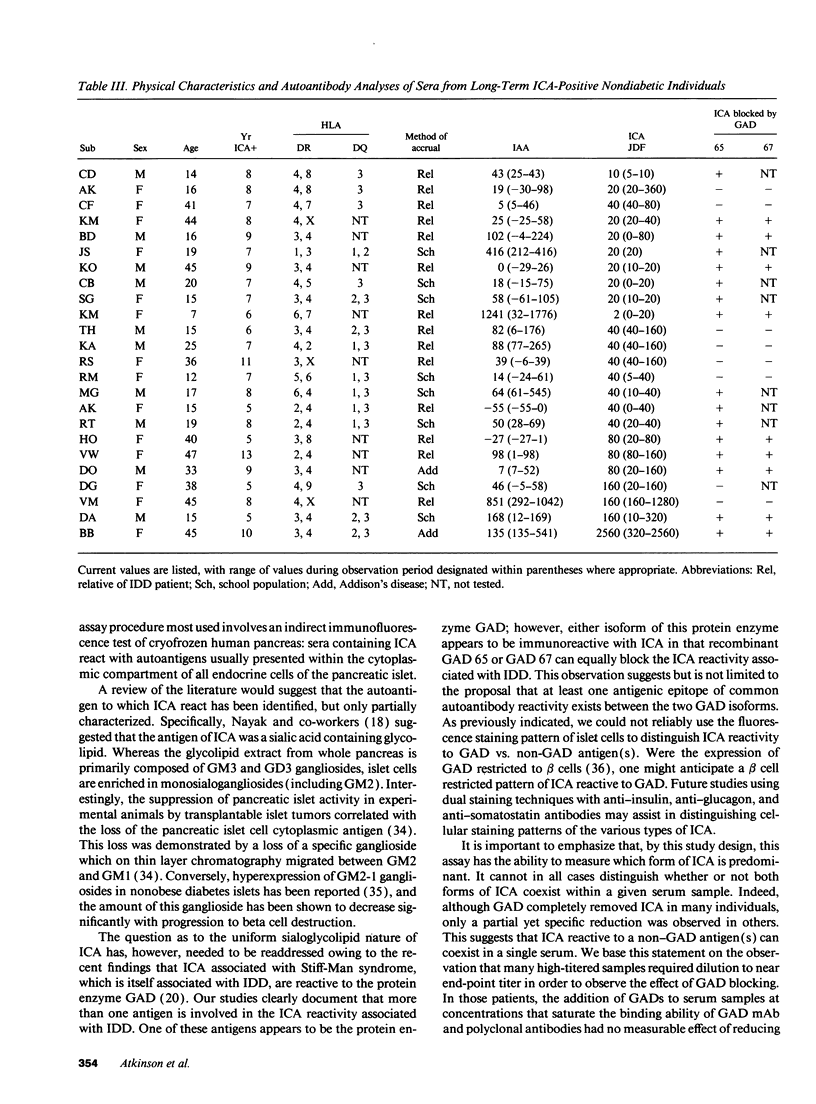
Individuals with or at risk for insulin-dependent diabetes (IDD) frequently have autoantibodies against an islet cell cytoplasmic (ICA) antigen thought to be a sialoglycolipid. However, we now report that preabsorption of ICA-positive sera with recombinant glutamate decarboxylase (human GAD 65 and/or GAD 67) reduced or blocked the ICA reactivity of 5/18 (27%) new-onset IDD patients and 7/18 (39%) prediabetics. Interestingly, nondiabetic subjects with ICA of > or = 5 yr in duration had GAD-reactive ICA significantly more often (16/24, 67%, P < 0.04) than the diabetic groups. ICA reactivity to GAD was not related to serum ICA titer nor the age of the individual, and in all cases tested was blocked by GAD 65 or GAD 67 with equivalent efficiency. The ICA observed in 21/25 (84%) IDD patients with ICA long after clinical onset of disease (9-42 yr) was reactive to GAD. A natural history analysis of three individuals showed conversions from ICA which was reactive to GAD to a non-GAD-reactive ICA nearer to their clinical onsets of IDD. This study further defines the autoantigens reactive to ICA, and suggests that, whereas ICA that are not reactive to GAD may identify an advanced and more prognostic lesion, GAD-reactive ICA may typify the early or inductive lesion that may or may not progress to clinically significant beta cell injury.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Kaufman D. L., Campbell L., Gibbs K. A., Shah S. C., Bu D. F., Erlander M. G., Tobin A. J., Maclaren N. K. Response of peripheral-blood mononuclear cells to glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1992 Feb 22;339(8791):458–459. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91061-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Riley W. J., Winter W. E., Fisk D. D., Spillar R. P. Are insulin autoantibodies markers for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus? Diabetes. 1986 Aug;35(8):894–898. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.8.894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Scharp D. W., Lacy P. E., Riley W. J. 64,000 Mr autoantibodies as predictors of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990 Jun 9;335(8702):1357–1360. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K. What causes diabetes? Sci Am. 1990 Jul;263(1):62-3, 66-71. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0790-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Nielsen J. H., Marner B., Bilde T., Ludvigsson J., Lernmark A. Autoantibodies in newly diagnosed diabetic children immunoprecipitate human pancreatic islet cell proteins. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):167–169. doi: 10.1038/298167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betterle C., Presotto F., Pedini B., Moro L., Slack R. S., Zanette F., Zanchetta R. Islet cell and insulin autoantibodies in organ-specific autoimmune patients. Their behaviour and predictive value for the development of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. A 10-year follow-up study. Diabetologia. 1987 May;30(5):292–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00299020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacio E., Boitard C., Gleichmann H., Shattock M. A., Molenaar J. L., Bottazzo G. F. Assessment of precision, concordance, specificity, and sensitivity of islet cell antibody measurement in 41 assays. Diabetologia. 1990 Dec;33(12):731–736. doi: 10.1007/BF00400345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacio E., Lernmark A., Dawkins R. L. Serum exchange and use of dilutions have improved precision of measurement of islet cell antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Jan 21;106(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90274-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Florin-Christensen A., Doniach D. Islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. Lancet. 1974 Nov 30;2(7892):1279–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu D. F., Erlander M. G., Hitz B. C., Tillakaratne N. J., Kaufman D. L., Wagner-McPherson C. B., Evans G. A., Tobin A. J. Two human glutamate decarboxylases, 65-kDa GAD and 67-kDa GAD, are each encoded by a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2115–2119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. C., Gottlieb D. I. Characterization of the proteins purified with monoclonal antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-02123.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christgau S., Schierbeck H., Aanstoot H. J., Aagaard L., Begley K., Kofod H., Hejnaes K., Baekkeskov S. Pancreatic beta cells express two autoantigenic forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase, a 65-kDa hydrophilic form and a 64-kDa amphiphilic form which can be both membrane-bound and soluble. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21257–21264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. G., Nayak R. C., Campbell I. L., Eisenbarth G. S. Binding of cytoplasmic islet cell antibodies is blocked by human pancreatic glycolipid extracts. Diabetes. 1988 May;37(5):645–652. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.5.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorman J. S., Laporte R. E., Kuller L. H., Cruickshanks K. J., Orchard T. J., Wagener D. K., Becker D. J., Cavender D. E., Drash A. L. The Pittsburgh insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) morbidity and mortality study. Mortality results. Diabetes. 1984 Mar;33(3):271–276. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.3.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdö S. L., Wolff J. R. gamma-Aminobutyric acid outside the mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):363–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlander M. G., Tillakaratne N. J., Feldblum S., Patel N., Tobin A. J. Two genes encode distinct glutamate decarboxylases. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90077-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry D. J., Appel N. M., Garry M. G., Sorenson R. L. Cellular and subcellular immunolocalization of L-glutamate decarboxylase in rat pancreatic islets. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Jun;36(6):573–580. doi: 10.1177/36.6.2896676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianani R., Pugliese A., Bonner-Weir S., Shiffrin A. J., Soeldner J. S., Erlich H., Awdeh Z., Alper C. A., Jackson R. A., Eisenbarth G. S. Prognostically significant heterogeneity of cytoplasmic islet cell antibodies in relatives of patients with type I diabetes. Diabetes. 1992 Mar;41(3):347–353. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorsuch A. N., Spencer K. M., Lister J., McNally J. M., Dean B. M., Bottazzo G. F., Cudworth A. G. Evidence for a long prediabetic period in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1981 Dec 19;2(8260-61):1363–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92795-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsen A. E., Hagopian W. A., Grubin C. E., Dube S., Disteche C. M., Adler D. A., Bärmeier H., Mathewes S., Grant F. J., Foster D. Cloning and primary structure of a human islet isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase from chromosome 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8337–8341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Erlander M. G., Clare-Salzler M., Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Tobin A. J. Autoimmunity to two forms of glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):283–292. doi: 10.1172/JCI115573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Houser C. R., Tobin A. J. Two forms of the gamma-aminobutyric acid synthetic enzyme glutamate decarboxylase have distinct intraneuronal distributions and cofactor interactions. J Neurochem. 1991 Feb;56(2):720–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclaren N. K. How, when, and why to predict IDDM. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1591–1594. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis D., Rjasanowski I., Hildmann W., Kohnert K. D., Richter K. V. Validity of WHO criteria for classification of newly diagnosed diabetics. Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1985 Feb;85(1):61–69. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1210420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelsen B. K., Petersen J. S., Boel E., Møldrup A., Dyrberg T., Madsen O. D. Cloning, characterization, and autoimmune recognition of rat islet glutamic acid decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8754–8758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak R. C., Omar M. A., Rabizadeh A., Srikanta S., Eisenbarth G. S. "Cytoplasmic" islet cell antibodies. Evidence that the target antigen is a sialoglycoconjugate. Diabetes. 1985 Jun;34(6):617–619. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.6.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Asplin C. M., Clemons P., Lyen K., Tatpati O., Raghu P. K., Paquette T. L. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science. 1983 Dec 23;222(4630):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6362005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley W. J., Maclaren N. K., Krischer J., Spillar R. P., Silverstein J. H., Schatz D. A., Schwartz S., Malone J., Shah S., Vadheim C. A prospective study of the development of diabetes in relatives of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 25;323(17):1167–1172. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010253231704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley M. J., Mackay I. R., Chen Q. Y., Knowles W. J., Zimmet P. Z. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase discriminate major types of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1992 Apr;41(4):548–551. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solimena M., Folli F., Aparisi R., Pozza G., De Camilli P. Autoantibodies to GABA-ergic neurons and pancreatic beta cells in stiff-man syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 31;322(22):1555–1560. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005313222202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson R. L., Garry D. G., Brelje T. C. Structural and functional considerations of GABA in islets of Langerhans. Beta-cells and nerves. Diabetes. 1991 Nov;40(11):1365–1374. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.11.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikanta S., Ganda O. P., Rabizadeh A., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G. S. First-degree relatives of patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Islet-cell antibodies and abnormal insulin secretion. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 22;313(8):461–464. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508223130801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarn A. C., Thomas J. M., Dean B. M., Ingram D., Schwarz G., Bottazzo G. F., Gale E. A. Predicting insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1988 Apr 16;1(8590):845–850. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91601-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardi P., Dib S. A., Tuttleman M., Connelly J. E., Grinbergs M., Radizabeh A., Riley W. J., Maclaren N. K., Eisenbarth G. S., Soeldner J. S. Competitive insulin autoantibody assay. Prospective evaluation of subjects at high risk for development of type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1987 Nov;36(11):1286–1291. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.11.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rood J. J., van Leeuwen A., Ploem J. S. Simultaneous detection of two cell populations by two-colour fluorescence and application to the recognition of B-cell determinants. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):795–797. doi: 10.1038/262795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]