Abstract
In experimental animals, injection of gram-negative endotoxin (LPS) decreases hepatic cytochrome P450-mediated drug metabolism. To evaluate this phenomenon in a human model of gram-negative sepsis, LPS was administered on two consecutive days to healthy male volunteers during which time a cocktail of antipyrine (AP-250 mg), hexobarbital (HB-500 mg), and theophylline (TH-150 mg) was ingested and the apparent oral clearance of each drug determined. Each subject had a control drug clearance study with saline injections. In the first experiment, six subjects received the drug cocktail 0.5 h after the first dose of LPS. In the second experiment, another six subjects received the drug cocktail 0.5 h after the second dose of LPS. In both experiments, LPS caused the expected physiologic responses of inflammation including fever with increases in serum concentrations of TNF alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and acute phase reactants. In the first experiment, only minor decreases in clearances of the probe drugs were observed (7-12%). However in the second experiment, marked decreases in the clearances of AP (35, 95% CI 18-48%), HB (27, 95% CI 14-34%), and TH (22, 95% CI 12-32%) were seen. The decreases in AP clearance correlated with initial peak values of TNF alpha (r = 0.82) and IL-6 (r = 0.86). These data show that in humans the inflammatory response to even a very low dose of LPS significantly decreases hepatic cytochrome P450-mediated drug metabolism and this effect evolves over a 24-h period. It is likely that septic patients with much higher exposures to LPS have more profound inhibition of drug metabolism.
Full text
PDF
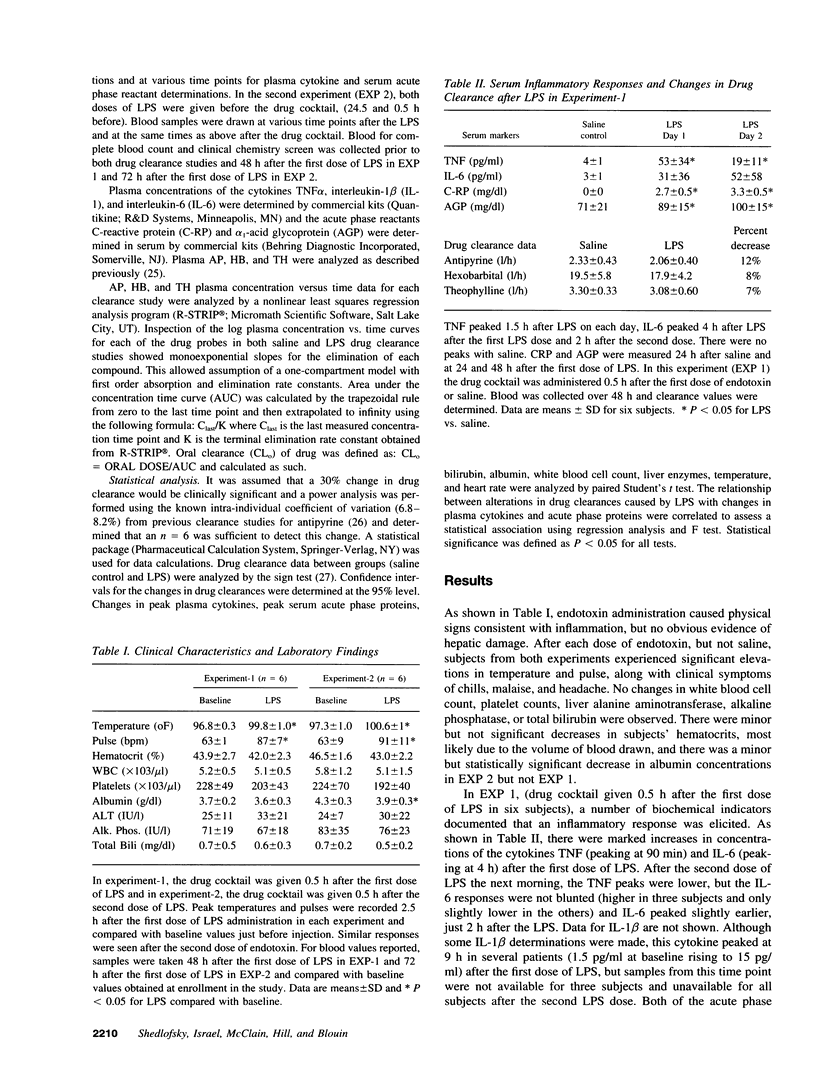
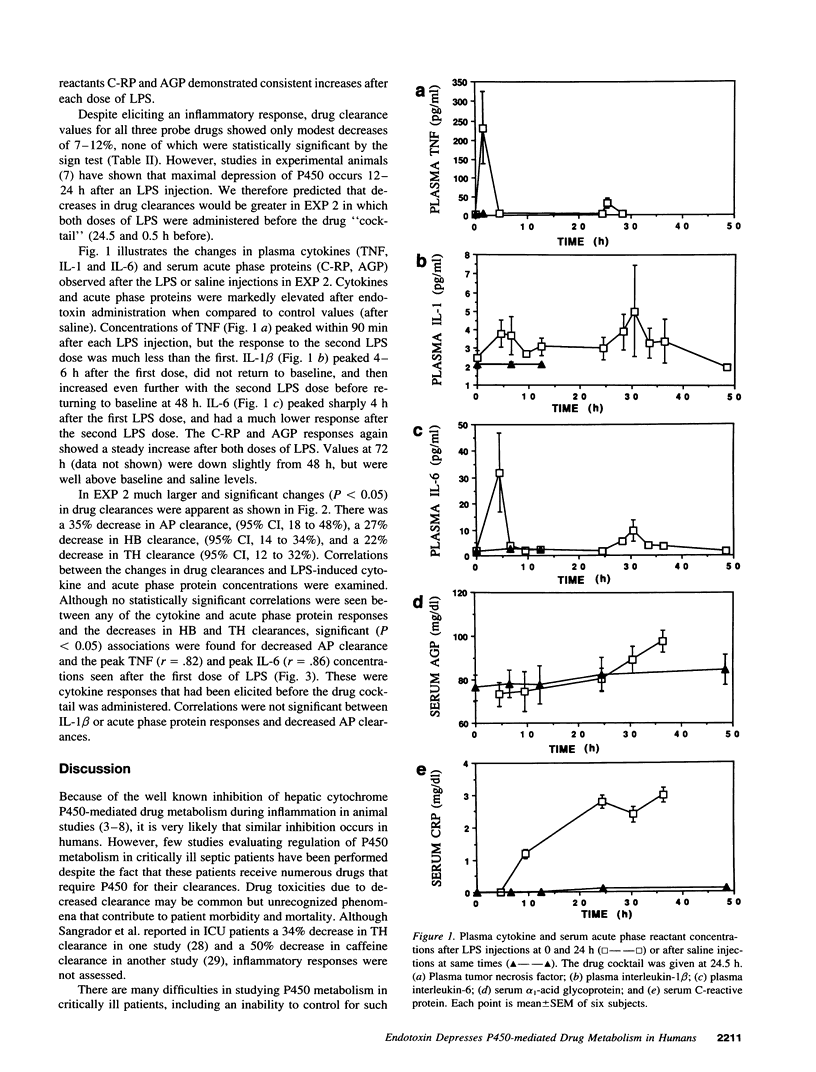
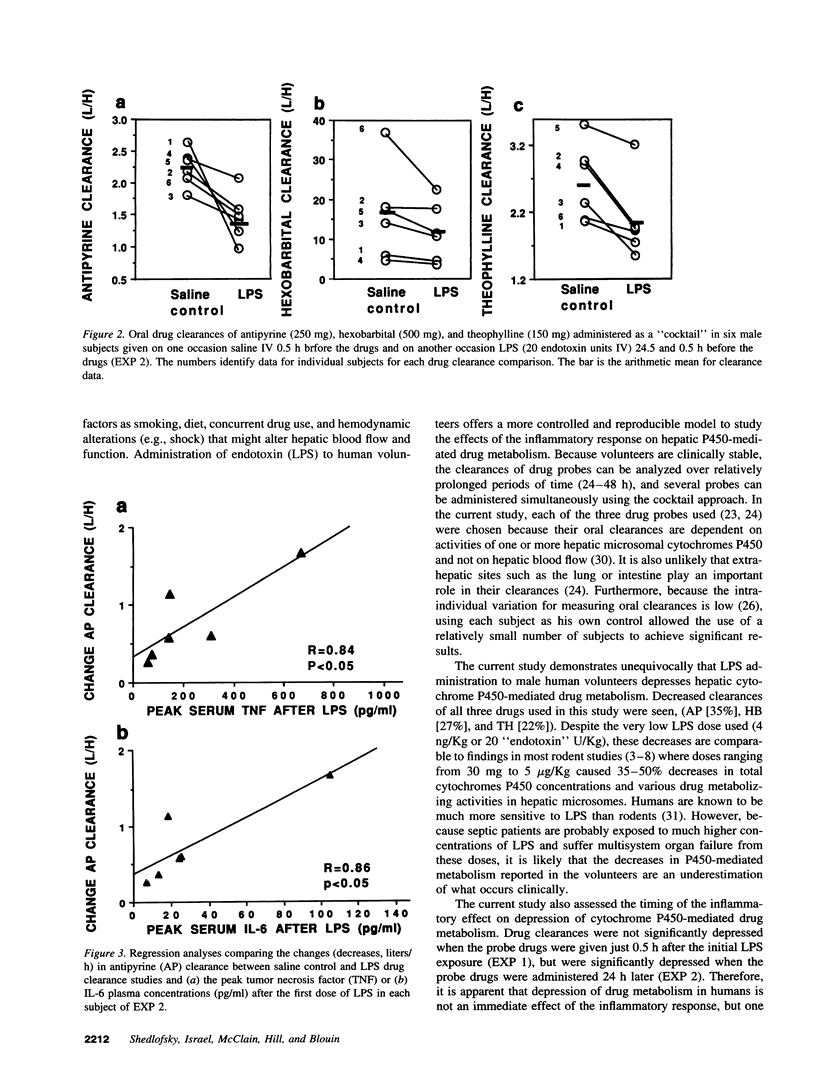


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertini R., Bianchi M., Erroi A., Villa P., Ghezzi P. Dexamethasone modulation of in vivo effects of endotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-1 on liver cytochrome P-450, plasma fibrinogen, and serum iron. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Sep;46(3):254–262. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertini R., Bianchi M., Villa P., Ghezzi P. Depression of liver drug metabolism and increase in plasma fibrinogen by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor: a comparison with lymphotoxin and interferon. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1988;10(5):525–530. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(88)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Fisher C. J., Jr, Clemmer T. P., Slotman G. J., Metz C. A., Balk R. A. A controlled clinical trial of high-dose methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):653–658. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brian W. R., Srivastava P. K., Umbenhauer D. R., Lloyd R. S., Guengerich F. P. Expression of a human liver cytochrome P-450 protein with tolbutamide hydroxylase activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):4993–4999. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. L., Florentin I., Batt A. M., Ferrari L., Giroud J. P., Chauvelot-Moachon L. Effects of interleukin-6 on cytochrome P450-dependent mixed-function oxidases in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;44(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90047-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner R. L., Elin R. J., Hosseini J. M., Wesley R. A., Reilly J. M., Parillo J. E. Endotoxemia in human septic shock. Chest. 1991 Jan;99(1):169–175. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.1.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Vesell E. S., Wolff S. M. Effects of etiocholanolone-induced fever on plasma antipyrine half-lives and metabolic clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Apr;17(4):447–457. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975174447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhr U., Doehmer J., Battula N., Wölfel C., Kudla C., Keita Y., Staib A. H. Biotransformation of caffeine and theophylline in mammalian cell lines genetically engineered for expression of single cytochrome P450 isoforms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 22;43(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90282-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghezzi P., Saccardo B., Bianchi M. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor depresses cytochrome P450-dependent microsomal drug metabolism in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):316–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90912-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghezzi P., Saccardo B., Villa P., Rossi V., Bianchi M., Dinarello C. A. Role of interleukin-1 in the depression of liver drug metabolism by endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):837–840. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.837-840.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorodischer F., Krasner J., McDevitt J. J., Nolan J. P., Yaffe S. J. Hepatic microsomal drug metabolism after administration of endotoxin in rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Feb 1;25(3):351–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granowitz E. V., Porat R., Mier J. W., Orencole S. F., Kaplanski G., Lynch E. A., Ye K., Vannier E., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Intravenous endotoxin suppresses the cytokine response of peripheral blood mononuclear cells of healthy humans. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1637–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse D. G., Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Manogue K. R., Palladino M. A., Jr, Cerami A., Shires G. T., Lowry S. F. Cytokine appearance in human endotoxemia and primate bacteremia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Feb;166(2):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel B. C., Blouin R. A., McIntyre W., Shedlofsky S. I. Effects of interferon-alpha monotherapy on hepatic drug metabolism in cancer patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;36(3):229–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1993.tb04222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappas A., Anderson K. E., Conney A. H., Alvares A. P. Influence of dietary protein and carbohydrate on antipyrine and theophylline metabolism in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Dec;20(6):643–653. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976206643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knodell R. G., Dubey R. K., Wilkinson G. R., Guengerich F. P. Oxidative metabolism of hexobarbital in human liver: relationship to polymorphic S-mephenytoin 4-hydroxylation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jun;245(3):845–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loft S. Metronidazole and antipyrine as probes for the study of foreign compound metabolism. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;66 (Suppl 6):1–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1990.tb01611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall C. E., Grosso-Wilmoth L. M., LaRue K., Guzman R. N., Cousart S. L. Tolerance to endotoxin-induced expression of the interleukin-1 beta gene in blood neutrophils of humans with the sepsis syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):853–861. doi: 10.1172/JCI116306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. D., Jr, Moss N. A., Revhaug A., Wilmore D., Mannick J. A., Rodrick M. L. A single dose of endotoxin activates neutrophils without activating complement. Surgery. 1987 Aug;102(2):200–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. T. Down-regulation of multiple cytochrome P450 gene products by inflammatory mediators in vivo. Independence from the hypothalamo-pituitary axis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 26;45(2):415–419. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90078-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. T. Suppression of constitutive cytochrome P-450 gene expression in livers of rats undergoing an acute phase response to endotoxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;36(5):699–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz C., Carlet J., Fitting C., Misset B., Blériot J. P., Cavaillon J. M. Dysregulation of in vitro cytokine production by monocytes during sepsis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1747–1754. doi: 10.1172/JCI115493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. A., Miners J. O., Matthews A. P., Stupans I., Meller D., McManus M. E., Birkett D. J. Characterisation of theophylline metabolism by human liver microsomes. Inhibition and immunochemical studies. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 May 1;37(9):1651–1659. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangrador G., Sánchez-Alcaraz A., Ubeda R., Ibañez P. Theophylline plasma clearance in critically ill geriatric patients receiving total parenteral nutrition and in control patients. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1990 Aug;15(4):273–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.1990.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar M. A., Hunt C., Guzelian P. S., Karnes H. T. Characterization of human liver cytochromes P-450 involved in theophylline metabolism. Drug Metab Dispos. 1992 Jan-Feb;20(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellens J. H., Janssens A. R., van der Wart J. H., van der Velde E. A., Breimer D. D. Relationship between the metabolism of antipyrine, hexobarbital and theophylline in patients with liver disease as assessed by a 'cocktail' approach. Eur J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;19(5):472–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1989.tb00262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellens J. H., van der Wart J. H., Danhof M., van der Velde E. A., Breimer D. D. Relationship between the metabolism of antipyrine, hexobarbitone and theophylline in man as assessed by a 'cocktail' approach. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;26(4):373–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedlofsky S. I., Swim A. T., Robinson J. M., Gallicchio V. S., Cohen D. A., McClain C. J. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) depresses cytochrome P450 levels and activities in mice. Life Sci. 1987 Jun 15;40(24):2331–2336. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90506-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Keller U., Brockhaus M. Release of soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in relation to circulating TNF during experimental endotoxinemia. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):533–536. doi: 10.1172/JCI115891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley L. A., Adams D. J., Lindsay R., Meehan R. R., Liao W., Wolf C. R. Potentiation and suppression of mouse liver cytochrome P-450 isozymes during the acute-phase response induced by bacterial endotoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 16;174(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffredini A. F., Fromm R. E., Parker M. M., Brenner M., Kovacs J. A., Wesley R. A., Parrillo J. E. The cardiovascular response of normal humans to the administration of endotoxin. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 3;321(5):280–287. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908033210503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Alcaraz A., Ibáez P., Sangrador G. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous caffeine in critically ill patients. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1991 Aug;16(4):285–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.1991.tb00316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vähäkangas K., Pelkonen O., Sotaniemi E. Cigarette smoking and drug metabolism. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Mar;33(3):375–380. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R., Shand D. G. Commentary: a physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):377–390. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F. Induction of tolerance in mice and rats to the effect of endotoxin to decrease the hepatic microsomal mixed-function oxidase system. Evidence for a possible macrophage-derived factor in the endotoxin effect. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(4):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(85)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F., Lowitt S., Szentivanyi A. Endotoxin depression of hepatic mixed function oxidase system in C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeN mice. Immunopharmacology. 1980 Dec;2(4):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(80)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright K., Morgan E. T. Regulation of cytochrome P450IIC12 expression by interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-6, and dexamethasone. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;39(4):468–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



