Abstract
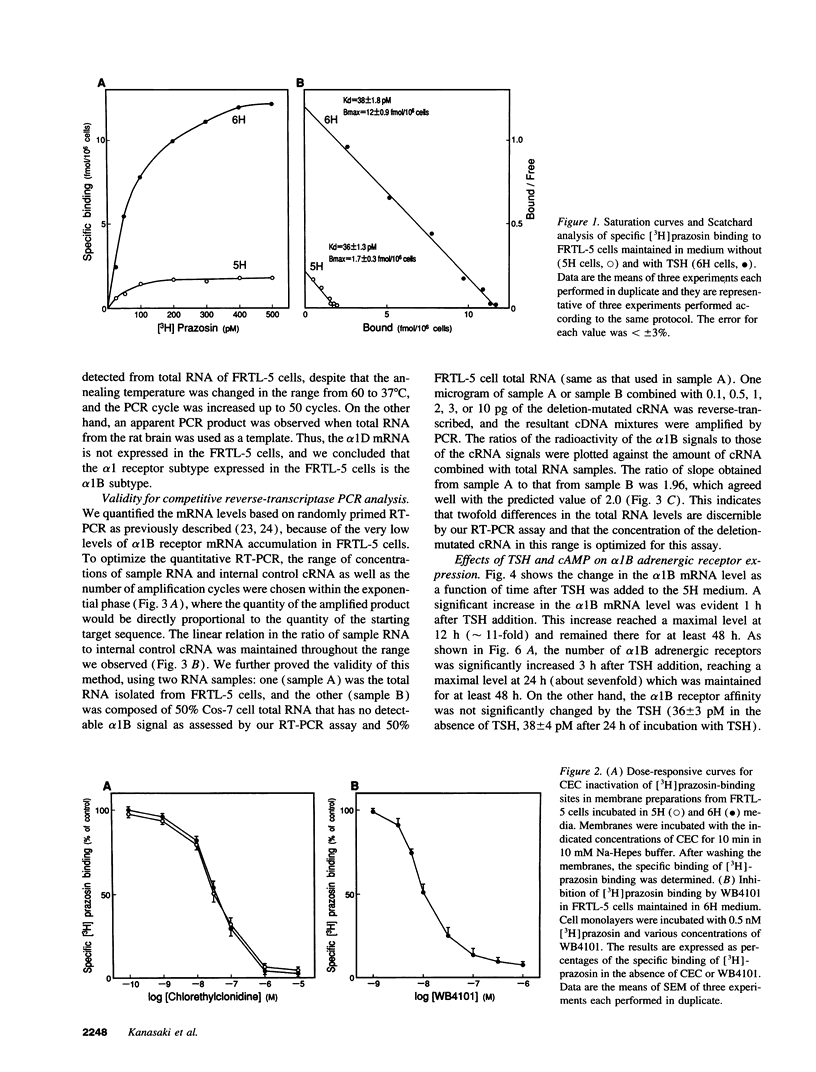
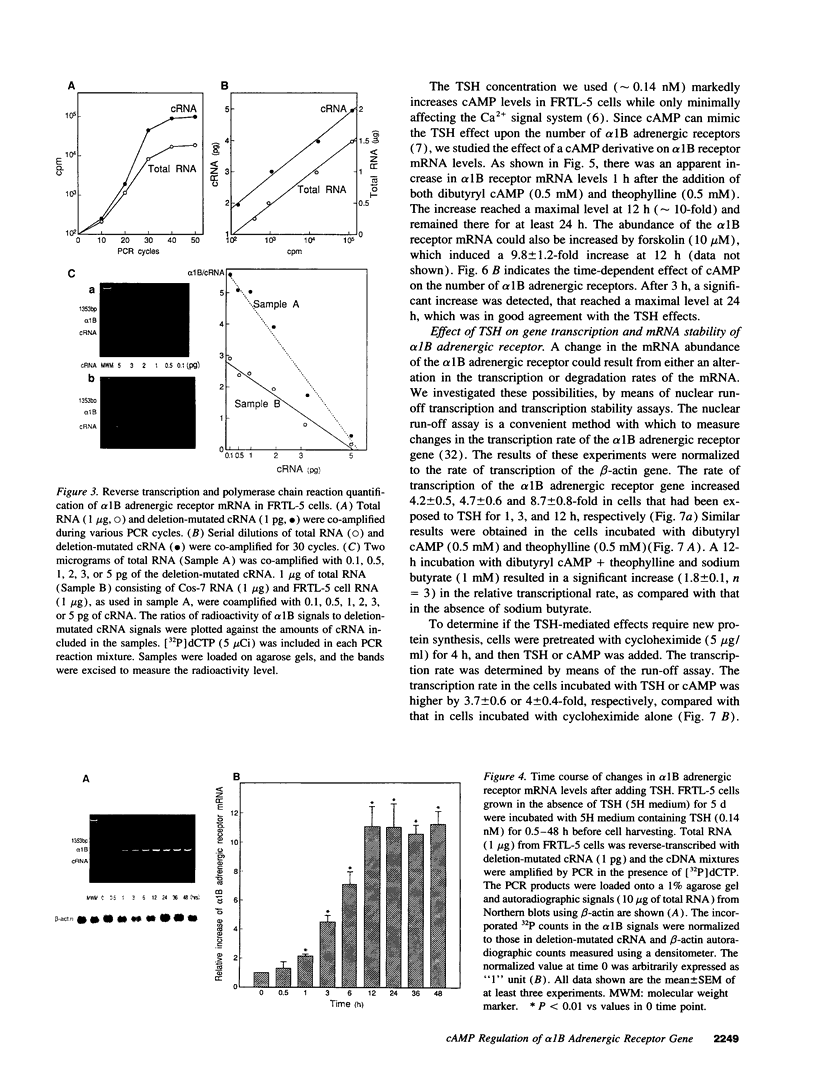
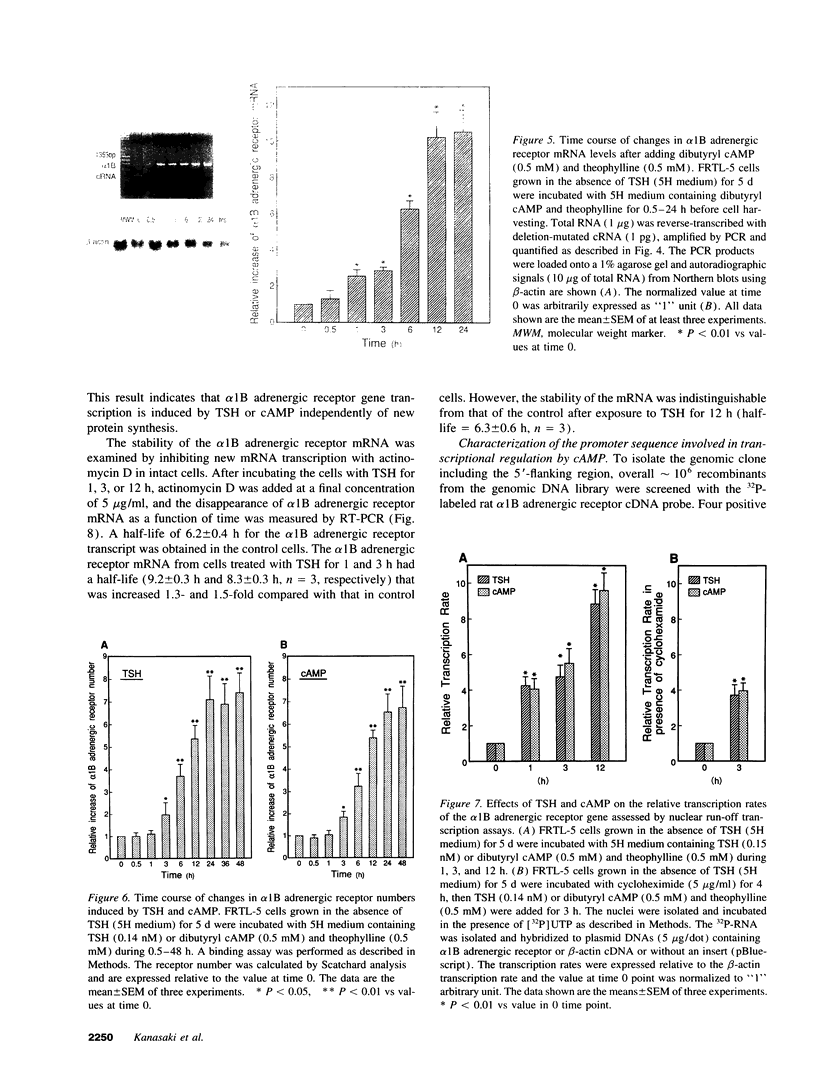
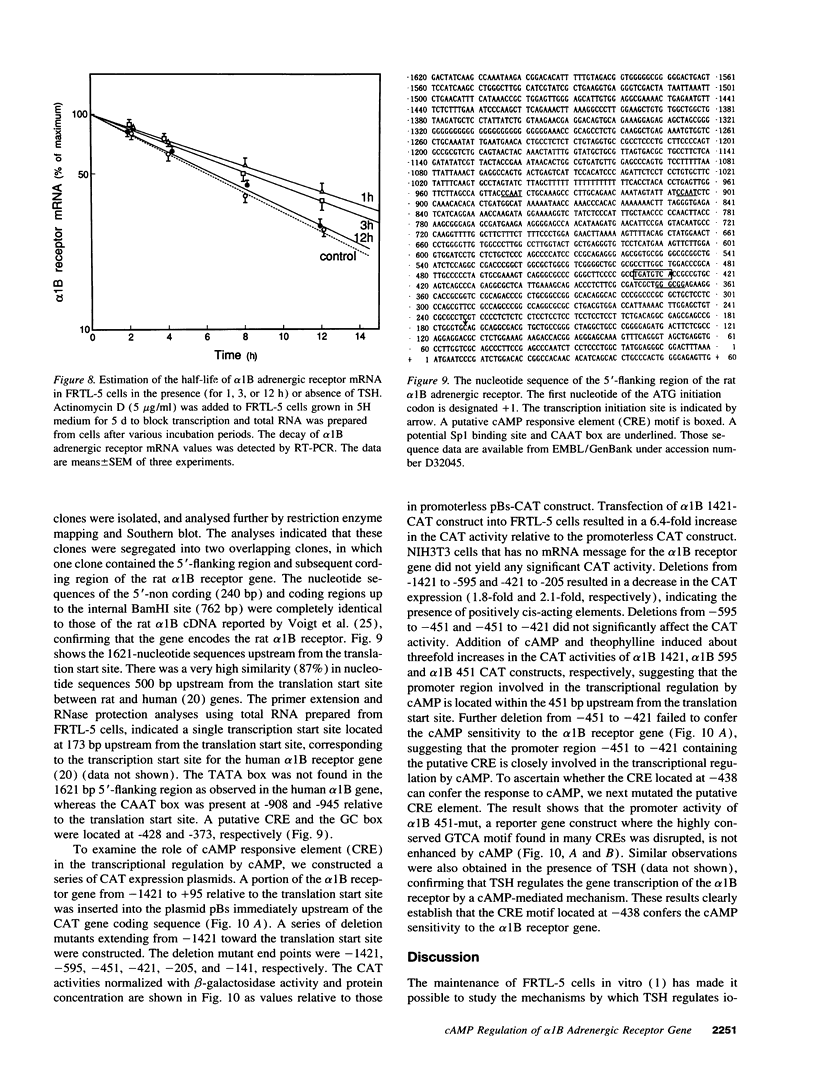
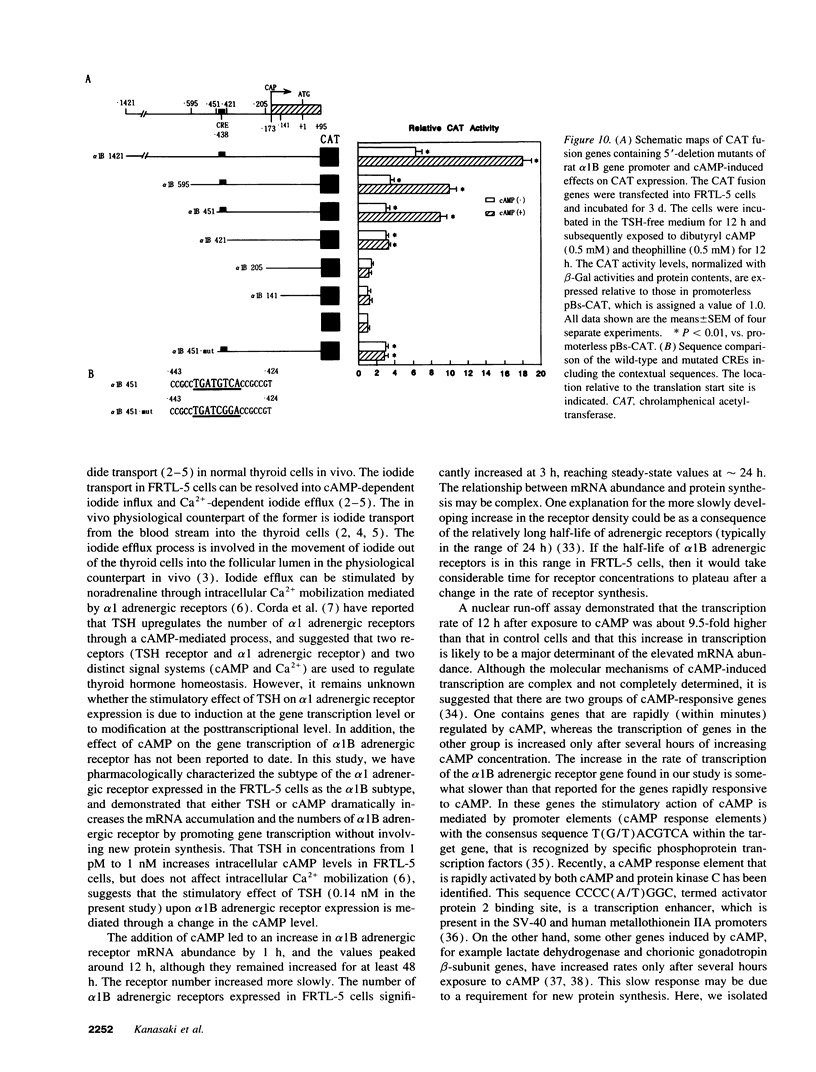
To elucidate the molecular mechanism of the stimulatory effect of thyrotropin on the gene regulation of alpha 1B adrenergic receptor in functioning rat thyroid (FRTL-5) cells, we established a competitive reverse-transcriptase (RT) polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and nuclear run-off assay to quantify changes in mRNA levels and transcription rates. A binding assay showed that FRTL-5 cells predominantly expressed alpha 1B adrenergic receptor and that thyrotropin increased its expression sevenfold. By means of RT-PCR, we found that thyrotropin induced an 11-fold increase in alpha 1B receptor mRNA abundance. The nuclear run-off assay demonstrated that thyrotropin caused a ninefold increase at the gene transcriptional level, which occurred in the presence of the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide. The half-life of the alpha 1B receptor mRNA in cells incubated with thyrotropin for 1 h increased 1.5-fold but returned to the original value after 12 h. Dibutyryl cAMP and forskolin mimicked the stimulatory effects of thyrotropin on the gene transcriptional level. The 5'-flanking region of the rat alpha 1B receptor gene contained a putative cAMP responsive element (CRE) at nucleotide -438 relative to the translation start site. The promoter analysis using the reporter gene indicated that the CRE motif confers the cAMP sensitivity to the transcription of the rat alpha 1B receptor gene. These results demonstrated that a CRE-mediated mechanism is involved in the transcriptional regulation of the alpha 1B receptor gene by thyrotropin without requiring new protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambesi-Impiombato F. S., Parks L. A., Coon H. G. Culture of hormone-dependent functional epithelial cells from rat thyroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Bouvier M., Bolanowski M. A., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cAMP stimulates transcription of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor gene in response to short-term agonist exposure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda D., Kohn L. D. Thyrotropin upregulates alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in rat FRTL-5 thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8677–8680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda D., Marcocci C., Kohn L. D., Axelrod J., Luini A. Association of the changes in cytosolic Ca2+ and iodide efflux induced by thyrotropin and by the stimulation of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in cultured rat thyroid cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9230–9236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. D.B.E.: A New Synthetic Oestrogen. Br Med J. 1946 Jan 5;1(4435):9–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C. D., Wilson K. M., Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes and formation of inositol phosphates in dispersed hepatocytes and renal cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;37(6):903–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes linked to different mechanisms for increasing intracellular Ca2+ in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):333–335. doi: 10.1038/329333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Esbenshade T. A., Minneman K. P. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in DDT1 MF-2 and BC3H-1 clonal cell lines. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 5;226(2):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90175-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod Y., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP stabilizes the mRNA for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) against degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7747–7752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann R. A., Kelley D. C., Miles M. F., Milkowski D. M. Cyclic AMP regulation of lactate dehydrogenase. Isoproterenol and N6,O2-dibutyryl cyclic amp increase the rate of transcription and change the stability of lactate dehydrogenase a subunit messenger RNA in rat C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5312–5318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcocci C., Cohen J. L., Grollman E. F. Effect of actinomycin D on iodide transport in FRTL-5 thyroid cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Dec;115(6):2123–2132. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-6-2123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Liman E. R., Hess P., Koren G. Pretranslational mechanisms determine the type of potassium channels expressed in the rat skeletal and cardiac muscles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13324–13328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Suzuki J., Inada M. Shaker-related potassium channel, Kv1.4, mRNA regulation in cultured rat heart myocytes and differential expression of Kv1.4 and Kv1.5 genes in myocardial development and hypertrophy. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1659–1666. doi: 10.1172/JCI116751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Yamamoto J., Hirata Y., Mori Y., Oikawa S., Inada M. Changes of atrial natriuretic peptide and its messenger RNA with development and regression of cardiac hypertrophy in renovascular hypertensive rats. Circ Res. 1990 Jan;66(1):176–184. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.1.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milsted A., Cox R. P., Nilson J. H. Cyclic AMP regulates transcription of the genes encoding human chorionic gonadotropin with different kinetics. DNA. 1987 Jun;6(3):213–219. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Han C., Abel P. W. Comparison of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes distinguished by chlorethylclonidine and WB 4101. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. M., Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Cross-regulation between G-protein-coupled receptors. Activation of beta 2-adrenergic receptors increases alpha 1-adrenergic receptor mRNA levels. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2233–2238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Creese I. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: a reevaluation of [3H]WB4104 and [3H]prazosin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murasawa S., Matsubara H., Urakami M., Inada M. Regulatory elements that mediate expression of the gene for the angiotensin II type 1a receptor for the rat. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 25;268(36):26996–27003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris H., Taouis M., Galitzky J. In vitro study of alpha 2-adrenoceptor turnover and metabolism using the adenocarcinoma cell line HT29. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;32(5):646–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramarao C. S., Denker J. M., Perez D. M., Gaivin R. J., Riek R. P., Graham R. M. Genomic organization and expression of the human alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21936–21945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaue M., Hoffman B. B. cAMP regulates transcription of the alpha 2A adrenergic receptor gene in HT-29 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5743–5749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Szklut P. J., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W. Pharmacologic characterization of cloned alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes: selective antagonists suggest the existence of a fourth subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 1;227(4):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90162-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimura H., Endo T., Tsujimoto G., Watanabe K., Hashimoto K., Onaya T. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes linked to iodide efflux in rat FRTL cells. J Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;124(3):433–441. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1240433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Liu A. Y. Increased turnover of the messenger RNA encoding tyrosine aminotransferase can account for the desensitization and de-induction of tyrosine aminotransferase by 8-bromo-cyclic AMP treatment and removal. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3711–3716. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03254.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki J., Matsubara H., Urakami M., Inada M. Rat angiotensin II (type 1A) receptor mRNA regulation and subtype expression in myocardial growth and hypertrophy. Circ Res. 1993 Sep;73(3):439–447. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda N., Nishikawa M., Horimoto M., Yoshikawa N., Mori Y., Yoshimura M., Masaki H., Tanaka K., Inada M. Synergistic effect of thyroid hormone and thyrotropin on iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase in FRTL-5 rat thyroid cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Sep;127(3):1199–1205. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt M. M., Kispert J., Chin H. M. Sequence of a rat brain cDNA encoding an alpha-1B adrenergic receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1053–1053. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Philp N. J., Ambesi-Impiombato F. S., Grollman E. F. Thyrotropin-stimulated iodide transport mediated by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and dependent on protein synthesis. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1099–1107. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Philp N. J., Grollman E. F. Effect of thyrotropin on iodide efflux in FRTL-5 cells mediated by Ca2+. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1108–1113. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Philp N. J., Grollman E. F. Iodide transport in a continuous line of cultured cells from rat thyroid. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1090–1098. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. M., Minneman K. P. Different pathways of [3H]inositol phosphate formation mediated by alpha 1a- and alpha 1b-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17601–17606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]