Abstract
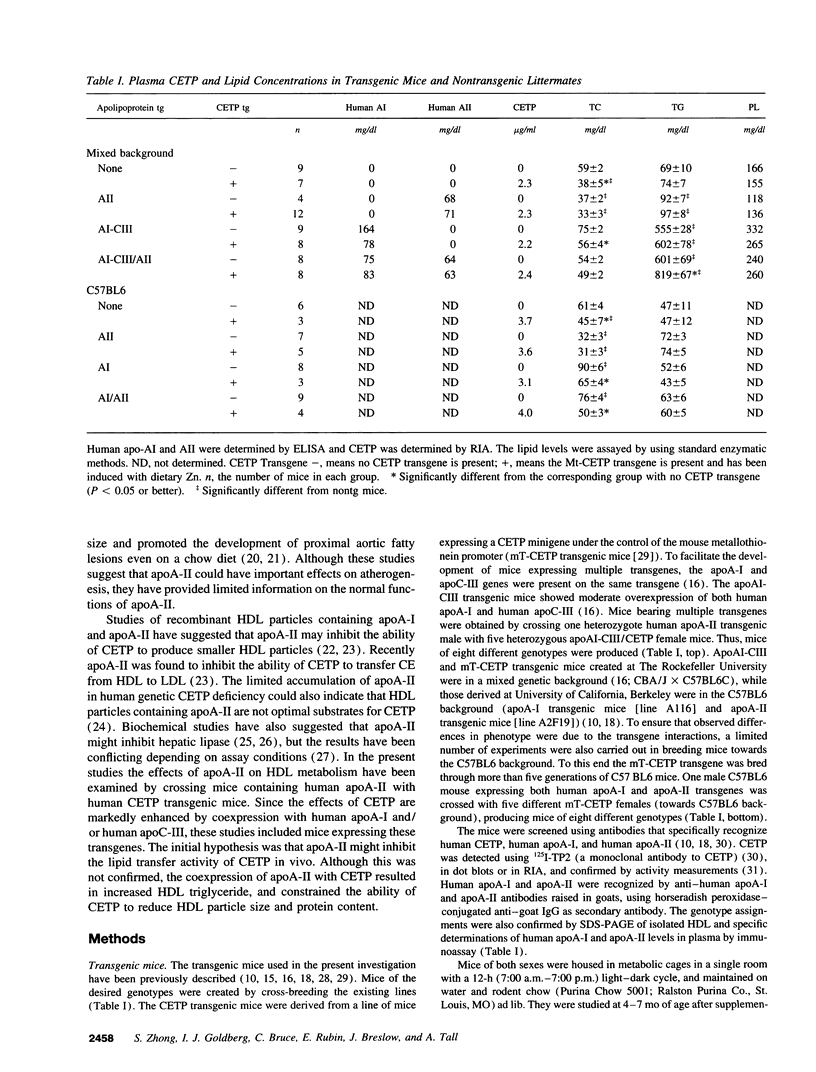
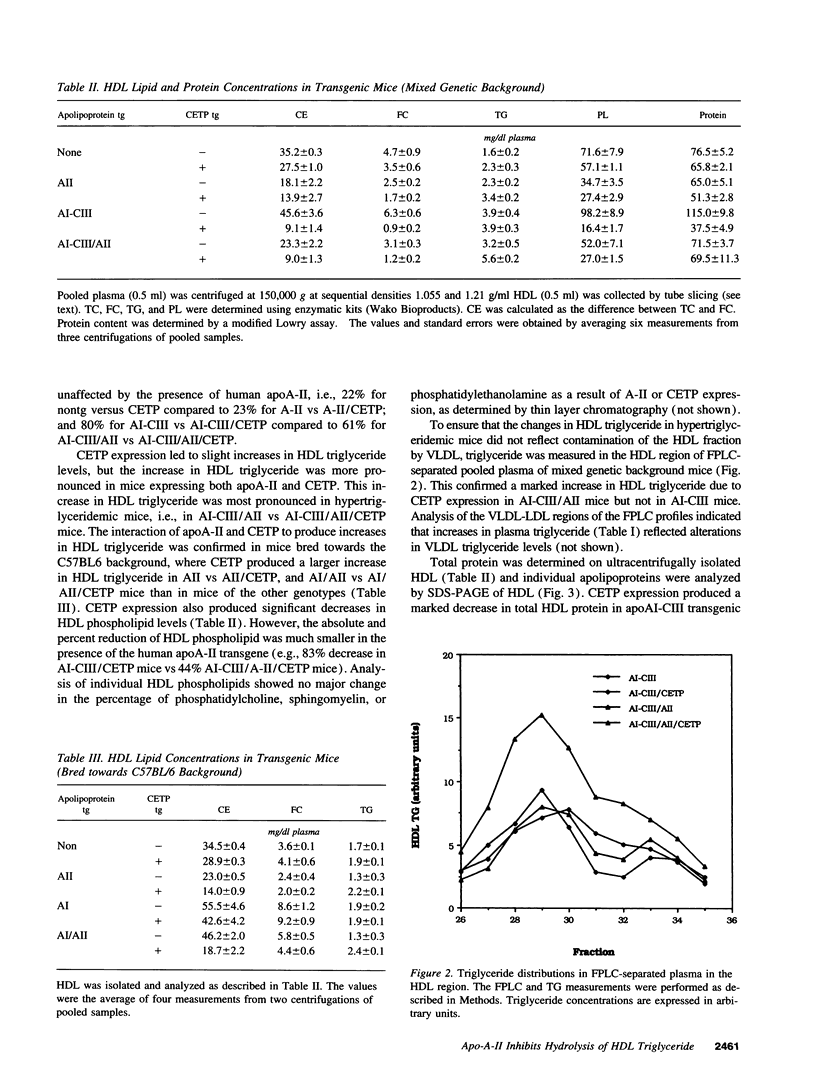
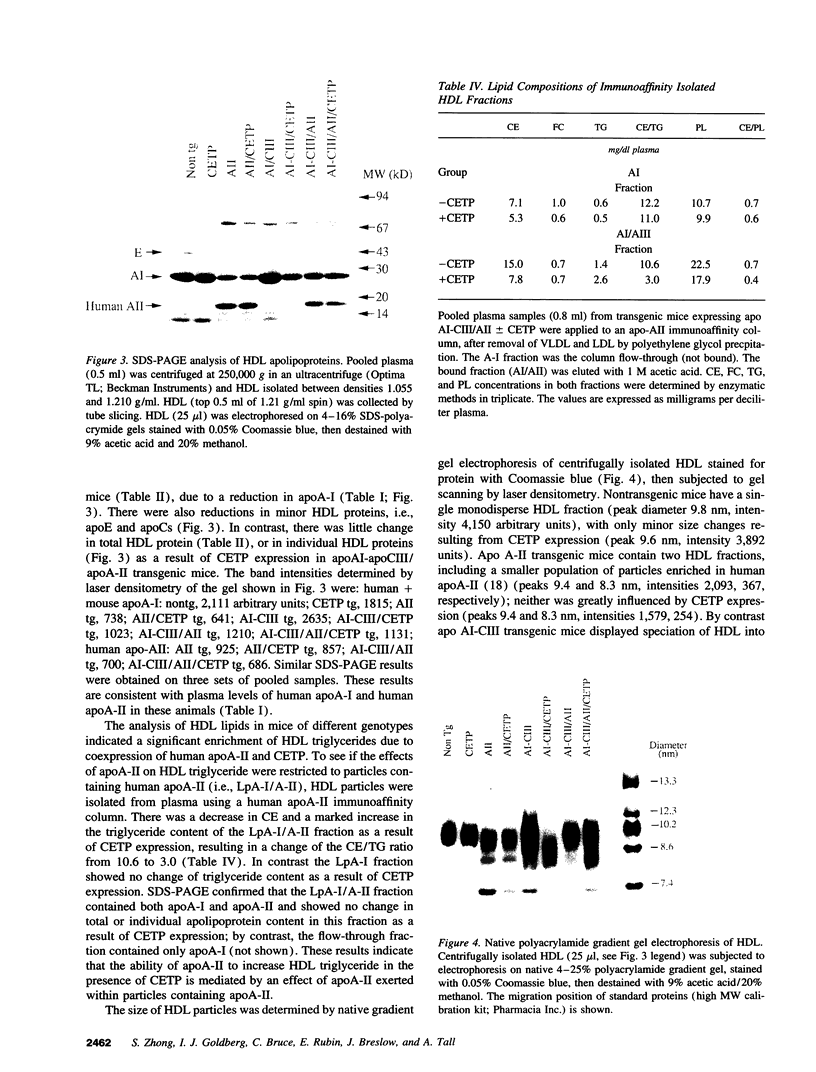
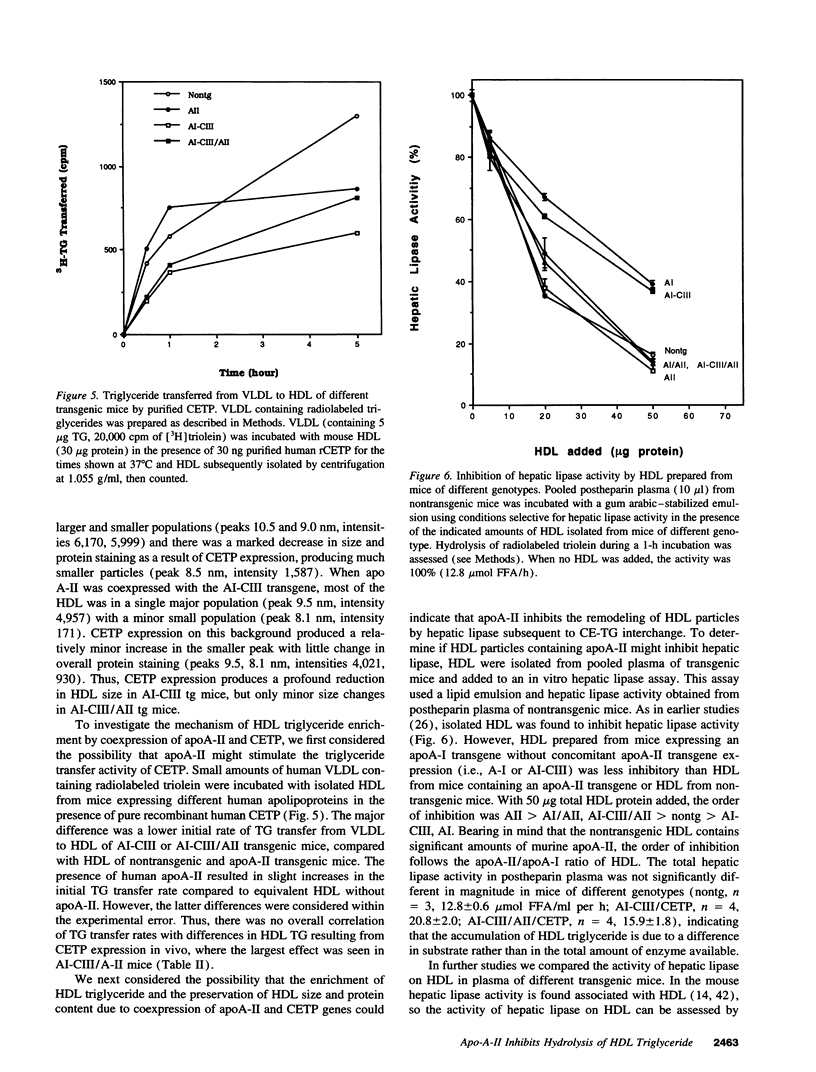
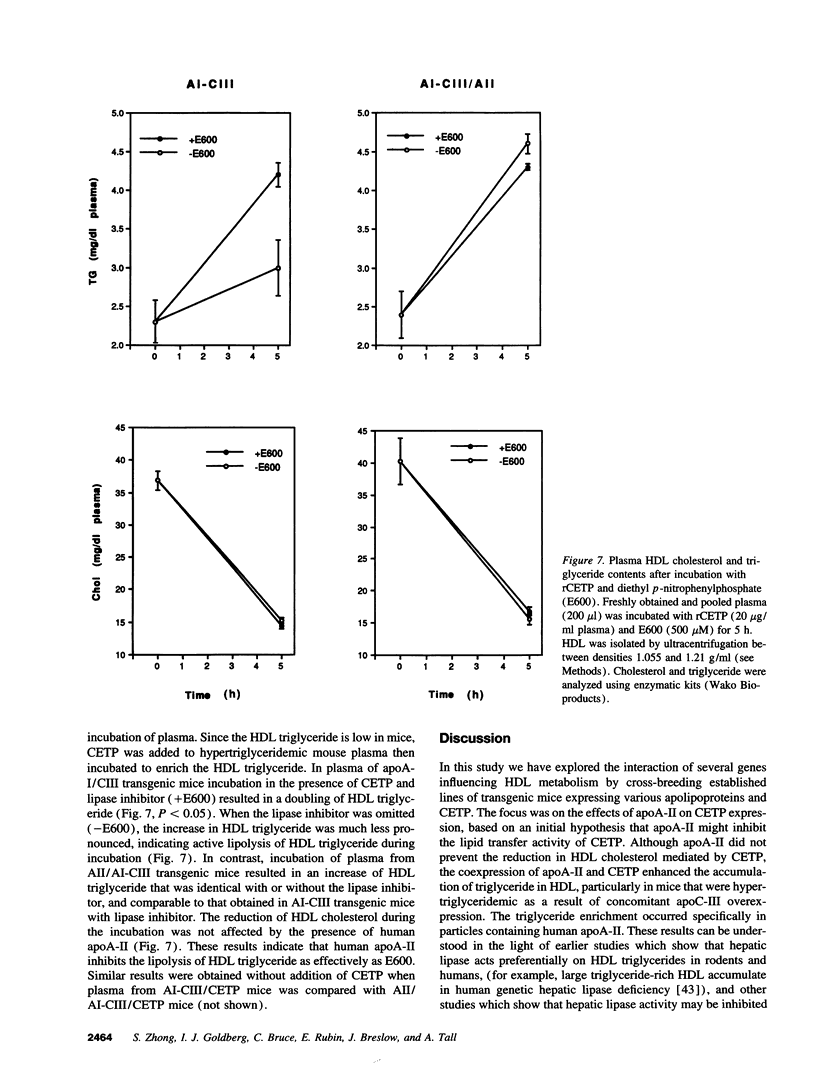
The plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) mediates the exchange of HDL cholesteryl esters with triglycerides of other lipoproteins. Subsequent lipolysis of the triglyceride-enriched HDL by hepatic lipase leads to reductions of HDL size and apoA-I content. To investigate a possible modulation of the effects of CETP by apoA-II, human CETP transgenic mice were cross-bred with transgenic mice expressing human apoA-II and, in some cases, human apoA-I and apoC-III (with human-like HDL and hypertriglyceridemia). CETP expression resulted in reductions of HDL and increases in VLDL cholesteryl ester in mice expressing human apoA-II, alone or in combination with apoA-I and apoC-III, indicating that apoA-II does not inhibit the cholesteryl ester transfer activity of CETP. However, CETP expression resulted in more prominent increases in HDL triglyceride in mice expressing both apoA-II and CETP, especially in CETP/apoA-II/apoAI-CIII transgenic mice. CETP expression caused dramatic reductions in HDL size and apoA-I content in apoAI-CIII transgenic mice, but not in apoA-II/AI-CIII transgenic mice. HDL prepared from mice of various genotypes showed inhibition of emulsion-based hepatic lipase activity in proportion to the apoA-II/apoA-I ratio of HDL. The presence of human apoA-II also inhibited mouse plasma hepatic lipase activity on HDL triglyceride. Thus, apoA-II does not inhibit the lipid transfer activity of CETP in vivo. However, coexpression of apoA-II with CETP results in HDL particles that are more triglyceride enriched and resistant to reductions in size and apoA-I content, reflecting inhibition of hepatic lipase by apoA-II. The inhibition of HDL remodeling by apoA-II could explain the relatively constant levels of HDL containing both apoA-I and apoA-II in human populations.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agellon L. B., Walsh A., Hayek T., Moulin P., Jiang X. C., Shelanski S. A., Breslow J. L., Tall A. R. Reduced high density lipoprotein cholesterol in human cholesteryl ester transfer protein transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10796–10801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allain C. C., Poon L. S., Chan C. S., Richmond W., Fu P. C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baginsky M. L., Brown W. V. A new method for the measurement of lipoprotein lipase in postheparin plasma using sodium dodecyl sulfate for the inactivation of hepatic triglyceride lipase. J Lipid Res. 1979 May;20(4):548–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberger M., Lund-Katz S., Phillips M. C., Rothblat G. H. Mechanism of the hepatic lipase induced accumulation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by cells in culture. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3693–3701. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfrage P., Vaughan M. Simple liquid-liquid partition system for isolation of labeled oleic acid from mixtures with glycerides. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanche P. J., Gong E. L., Forte T. M., Nichols A. V. Characterization of human high-density lipoproteins by gradient gel electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 24;665(3):408–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L. Transgenic mouse models of lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8314–8318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. L., Inazu A., Hesler C. B., Agellon L. B., Mann C., Whitlock M. E., Marcel Y. L., Milne R. W., Koizumi J., Mabuchi H. Molecular basis of lipid transfer protein deficiency in a family with increased high-density lipoproteins. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):448–451. doi: 10.1038/342448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucolo G., David H. Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clin Chem. 1973 May;19(5):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch S. J., Barnhart R. L., Martin G. A., Fitzgerald M. C., Yates M. T., Mao S. J., Thomas C. E., Jackson R. L. Human hepatic triglyceride lipase expression reduces high density lipoprotein and aortic cholesterol in cholesterol-fed transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16376–16382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabresi L., Banfi C., Sirtori C. R., Franceschini G. Apolipoprotein A-II modulates HDL remodeling in plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 4;1124(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90098-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro G. R., Fielding C. J. Early incorporation of cell-derived cholesterol into pre-beta-migrating high-density lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):25–29. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay M. A., Newnham H. H., Barter P. J. Hepatic lipase promotes a loss of apolipoprotein A-I from triglyceride-enriched human high density lipoproteins during incubation in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Mar-Apr;11(2):415–422. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.2.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckelbaum R. J., Ramakrishnan R., Eisenberg S., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Triacylglycerol and phospholipid hydrolysis in human plasma lipoproteins: role of lipoprotein and hepatic lipase. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 15;31(36):8544–8551. doi: 10.1021/bi00151a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. High density lipoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1984 Oct;25(10):1017–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. J., Blaner W. S., Vanni T. M., Moukides M., Ramakrishnan R. Role of lipoprotein lipase in the regulation of high density lipoprotein apolipoprotein metabolism. Studies in normal and lipoprotein lipase-inhibited monkeys. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):463–473. doi: 10.1172/JCI114732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T., Castelli W. P., Hjortland M. C., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am J Med. 1977 May;62(5):707–714. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90874-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayek T., Azrolan N., Verdery R. B., Walsh A., Chajek-Shaul T., Agellon L. B., Tall A. R., Breslow J. L. Hypertriglyceridemia and cholesteryl ester transfer protein interact to dramatically alter high density lipoprotein levels, particle sizes, and metabolism. Studies in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1143–1152. doi: 10.1172/JCI116683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayek T., Chajek-Shaul T., Walsh A., Agellon L. B., Moulin P., Tall A. R., Breslow J. L. An interaction between the human cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) and apolipoprotein A-I genes in transgenic mice results in a profound CETP-mediated depression of high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):505–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI115887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick C. C., Castellani L. W., Warden C. H., Puppione D. L., Lusis A. J. Influence of mouse apolipoprotein A-II on plasma lipoproteins in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20676–20682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegele R. A., Little J. A., Vezina C., Maguire G. F., Tu L., Wolever T. S., Jenkins D. J., Connelly P. W. Hepatic lipase deficiency. Clinical, biochemical, and molecular genetic characteristics. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 May;13(5):720–728. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.5.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikewaki K., Rader D. J., Sakamoto T., Nishiwaki M., Wakimoto N., Schaefer J. R., Ishikawa T., Fairwell T., Zech L. A., Nakamura H. Delayed catabolism of high density lipoprotein apolipoproteins A-I and A-II in human cholesteryl ester transfer protein deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1650–1658. doi: 10.1172/JCI116750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Azrolan N., O'Connell A., Walsh A., Breslow J. L. Hypertriglyceridemia as a result of human apo CIII gene expression in transgenic mice. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):790–793. doi: 10.1126/science.2167514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. E., Osborne J. C., Jr, Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Activation of the enzymic activity of hepatic lipase by apolipoprotein A-II. Characterization of a major component of high density lipoprotein as the activating plasma component in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):25–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Z. S., Fazio S., Lee Y. L., Mahley R. W. Secretion-capture role for apolipoprotein E in remnant lipoprotein metabolism involving cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2764–2772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X. C., Agellon L. B., Walsh A., Breslow J. L., Tall A. Dietary cholesterol increases transcription of the human cholesteryl ester transfer protein gene in transgenic mice. Dependence on natural flanking sequences. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1290–1295. doi: 10.1172/JCI115993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X. C., Masucci-Magoulas L., Mar J., Lin M., Walsh A., Breslow J. L., Tall A. Down-regulation of mRNA for the low density lipoprotein receptor in transgenic mice containing the gene for human cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Mechanism to explain accumulation of lipoprotein B particles. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 25;268(36):27406–27412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiao S., Cole T. G., Kitchens R. T., Pfleger B., Schonfeld G. Genetic heterogeneity of lipoproteins in inbred strains of mice: analysis by gel-permeation chromatography. Metabolism. 1990 Feb;39(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90069-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo M., Matsuzawa Y., Yokoyama S., Tajima S., Ishikawa K., Yamamoto A., Tarui S. Mechanism of inhibition of hepatic triglyceride lipase from human postheparin plasma by apolipoproteins A-I and A-II. J Biochem. 1982 Sep;92(3):865–870. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrost L., Perségol L., Lallemant C., Gambert P. Influence of apolipoprotein composition of high density lipoprotein particles on cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity. Particles containing various proportions of apolipoproteins AI and AII. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3189–3197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcel Y. L., McPherson R., Hogue M., Czarnecka H., Zawadzki Z., Weech P. K., Whitlock M. E., Tall A. R., Milne R. W. Distribution and concentration of cholesteryl ester transfer protein in plasma of normolipemic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):10–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI114397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Tolbert N. E., Bieber L. L. Protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples: manual and automated procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:296–303. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotti K. R., Castle C. K., Boyle T. P., Lin A. H., Murray R. W., Melchior G. W. Severe atherosclerosis in transgenic mice expressing simian cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):73–75. doi: 10.1038/364073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotti K. R., Castle C. K., Murray R. W., Rehberg E. F., Polites H. G., Melchior G. W. The role of cholesteryl ester transfer protein in primate apolipoprotein A-I metabolism. Insights from studies with transgenic mice. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Jun;12(6):736–744. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.6.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior G. W., Castle C. K., Murray R. W., Blake W. L., Dinh D. M., Marotti K. R. Apolipoprotein A-I metabolism in cholesteryl ester transfer protein transgenic mice. Insights into the mechanisms responsible for low plasma high density lipoprotein levels. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8044–8051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. J., Miller N. E. Plasma-high-density-lipoprotein concentration and development of ischaemic heart-disease. Lancet. 1975 Jan 4;1(7897):16–19. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowri H. O., Patsch W., Smith L. C., Gotto A. M., Jr, Patsch J. R. Different reactivities of high density lipoprotein2 subfractions with hepatic lipase. J Lipid Res. 1992 Sep;33(9):1269–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols A. V., Krauss R. M., Musliner T. A. Nondenaturing polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:417–431. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch J. R., Prasad S., Gotto A. M., Jr, Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Postprandial lipemia. A key for the conversion of high density lipoprotein2 into high density lipoprotein3 by hepatic lipase. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2017–2023. doi: 10.1172/JCI111624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Mouse preheparin plasma contains high levels of hepatic lipase with low affinity for heparin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 14;878(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90344-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips N. R., Havel R. J., Kane J. P. Serum apolipoprotein A-I levels: relationship to lipoprotein lipid levels and selected demographic variables. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Aug;116(2):302–313. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rader D. J., Castro G., Zech L. A., Fruchart J. C., Brewer H. B., Jr In vivo metabolism of apolipoprotein A-I on high density lipoprotein particles LpA-I and LpA-I,A-II. J Lipid Res. 1991 Nov;32(11):1849–1859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond W. Use of cholesterol oxidase for assay of total and free cholesterol in serum by continuous-flow analysis. Clin Chem. 1976 Oct;22(10):1579–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. M., Ishida B. Y., Clift S. M., Krauss R. M. Expression of human apolipoprotein A-I in transgenic mice results in reduced plasma levels of murine apolipoprotein A-I and the appearance of two new high density lipoprotein size subclasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):434–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. M., Krauss R. M., Spangler E. A., Verstuyft J. G., Clift S. M. Inhibition of early atherogenesis in transgenic mice by human apolipoprotein AI. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):265–267. doi: 10.1038/353265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rye K. A., Garrety K. H., Barter P. J. Changes in the size of reconstituted high density lipoproteins during incubation with cholesteryl ester transfer protein: the role of apolipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1992 Feb;33(2):215–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. R., Gong E. L., McCall M. R., Nichols A. V., Clift S. M., Rubin E. M. Expression of human apolipoprotein A-II and its effect on high density lipoproteins in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21630–21636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. R., Verstuyft J. G., Gong E. L., Nichols A. V., Rubin E. M. Protein composition determines the anti-atherogenic properties of HDL in transgenic mice. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):762–764. doi: 10.1038/365762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Jiang X. C., Sakai N., Yamashita S., Hirano K., Bujo H., Yamazaki H., Kusunoki J., Miura T., Kussie P. A missense mutation in the cholesteryl ester transfer protein gene with possible dominant effects on plasma high density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):2060–2064. doi: 10.1172/JCI116802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama M., Itoh S., Nagasaki T., Tanimizu I. A new enzymatic method for determination of serum choline-containing phospholipids. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Aug 15;79(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90465-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R. Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Lipid Res. 1993 Aug;34(8):1255–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R. Plasma high density lipoproteins. Metabolism and relationship to atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):379–384. doi: 10.1172/JCI114722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A., Granot E., Brocia R., Tabas I., Hesler C., Williams K., Denke M. Accelerated transfer of cholesteryl esters in dyslipidemic plasma. Role of cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1217–1225. doi: 10.1172/JCI112940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuren T., Wilcox R. W., Sisson P., Waite M. Hepatic lipase hydrolysis of lipid monolayers. Regulation by apolipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4853–4861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden C. H., Hedrick C. C., Qiao J. H., Castellani L. W., Lusis A. J. Atherosclerosis in transgenic mice overexpressing apolipoprotein A-II. Science. 1993 Jul 23;261(5120):469–472. doi: 10.1126/science.8332912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]