Abstract
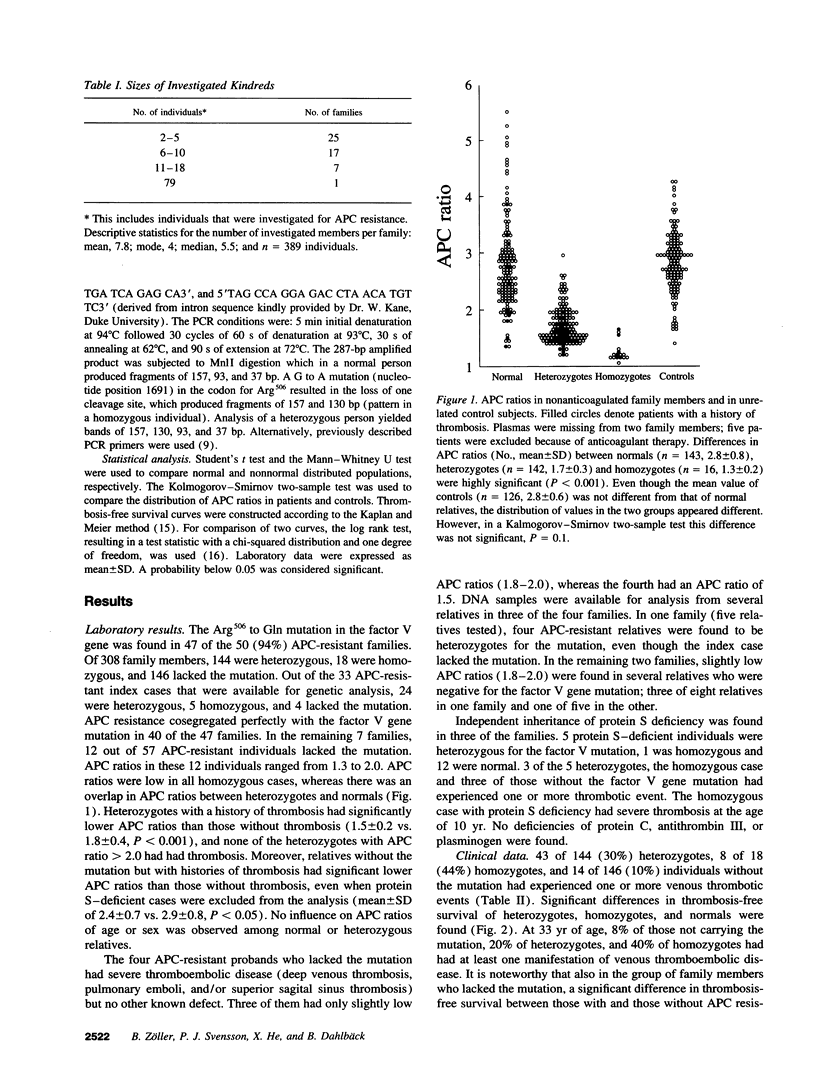
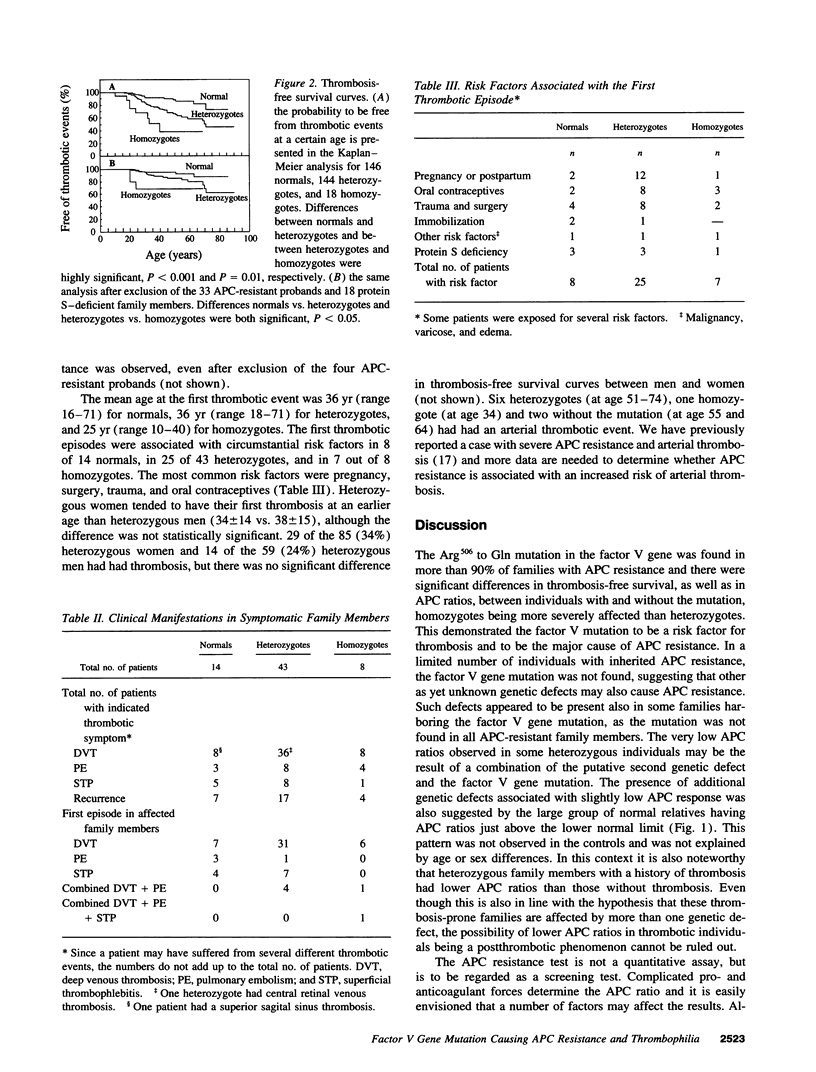
Resistance to activated protein C (APC) is the most prevalent inherited cause of venous thrombosis. The APC resistance phenotype is associated with a single point mutation in the factor V gene, changing Arg506 in the APC cleavage site to a Gln. We have investigated 50 Swedish families with inherited APC resistance for this mutation and found it to be present in 47 of them. Perfect cosegregation between a low APC ratio and the presence of mutation was seen in 40 families. In seven families, the co-segregation was not perfect as 12 out of 57 APC-resistant family members were found to lack the mutation. Moreover, in three families with APC resistance, the factor V gene mutation was not found, suggesting another still unidentified cause of inherited APC resistance. Of 308 investigated families members, 146 were normal, 144 heterozygotes, and 18 homozygotes for the factor V gene mutation and there were significant differences in thrombosis-free survival curves between these groups. By age 33 yr, 8% of normals, 20% of heterozygotes, and 40% of homozygotes had had manifestation of venous thrombosis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertina R. M., Koeleman B. P., Koster T., Rosendaal F. R., Dirven R. J., de Ronde H., van der Velden P. A., Reitsma P. H. Mutation in blood coagulation factor V associated with resistance to activated protein C. Nature. 1994 May 5;369(6475):64–67. doi: 10.1038/369064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Carlsson M., Svensson P. J. Familial thrombophilia due to a previously unrecognized mechanism characterized by poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C: prediction of a cofactor to activated protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hildebrand B. Inherited resistance to activated protein C is corrected by anticoagulant cofactor activity found to be a property of factor V. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faioni E. M., Franchi F., Asti D., Sacchi E., Bernardi F., Mannucci P. M. Resistance to activated protein C in nine thrombophilic families: interference in a protein S functional assay. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Dec 20;70(6):1067–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard J. S., Sun X., Xu X., Fernandez J. A., Griffin J. H., Evatt B. Activated protein C resistance caused by Arg506Gln mutation in factor Va. Lancet. 1994 May 28;343(8909):1361–1362. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92497-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Evatt B., Wideman C., Fernández J. A. Anticoagulant protein C pathway defective in majority of thrombophilic patients. Blood. 1993 Oct 1;82(7):1989–1993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster T., Rosendaal F. R., de Ronde H., Briët E., Vandenbroucke J. P., Bertina R. M. Venous thrombosis due to poor anticoagulant response to activated protein C: Leiden Thrombophilia Study. Lancet. 1993 Dec 18;342(8886-8887):1503–1506. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)80081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad B., Svensson P. J., Dahlbäck B. Arterial and venous thromboembolism with fatal outcome and resistance to activated protein C. Lancet. 1994 Apr 9;343(8902):917–917. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantel N. Evaluation of survival data and two new rank order statistics arising in its consideration. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1966 Mar;50(3):163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlar R. A., Neumann A. Neonatal purpura fulminans due to homozygous protein C or protein S deficiencies. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1990 Oct;16(4):299–309. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Dahlbäck B. Factor V and protein S as synergistic cofactors to activated protein C in degradation of factor VIIIa. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18735–18738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Evatt B., Griffin J. H. Blood coagulation factor Va abnormality associated with resistance to activated protein C in venous thrombophilia. Blood. 1994 Jun 1;83(11):3120–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson P. J., Dahlbäck B. Resistance to activated protein C as a basis for venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1994 Feb 24;330(8):517–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199402243300801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorberg J., Roelse J., Koopman R., Büller H., Berends F., ten Cate J. W., Mertens K., van Mourik J. A. Association of idiopathic venous thromboembolism with single point-mutation at Arg506 of factor V. Lancet. 1994 Jun 18;343(8912):1535–1536. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92939-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zöller B., Dahlbäck B. Linkage between inherited resistance to activated protein C and factor V gene mutation in venous thrombosis. Lancet. 1994 Jun 18;343(8912):1536–1538. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92940-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



