Abstract
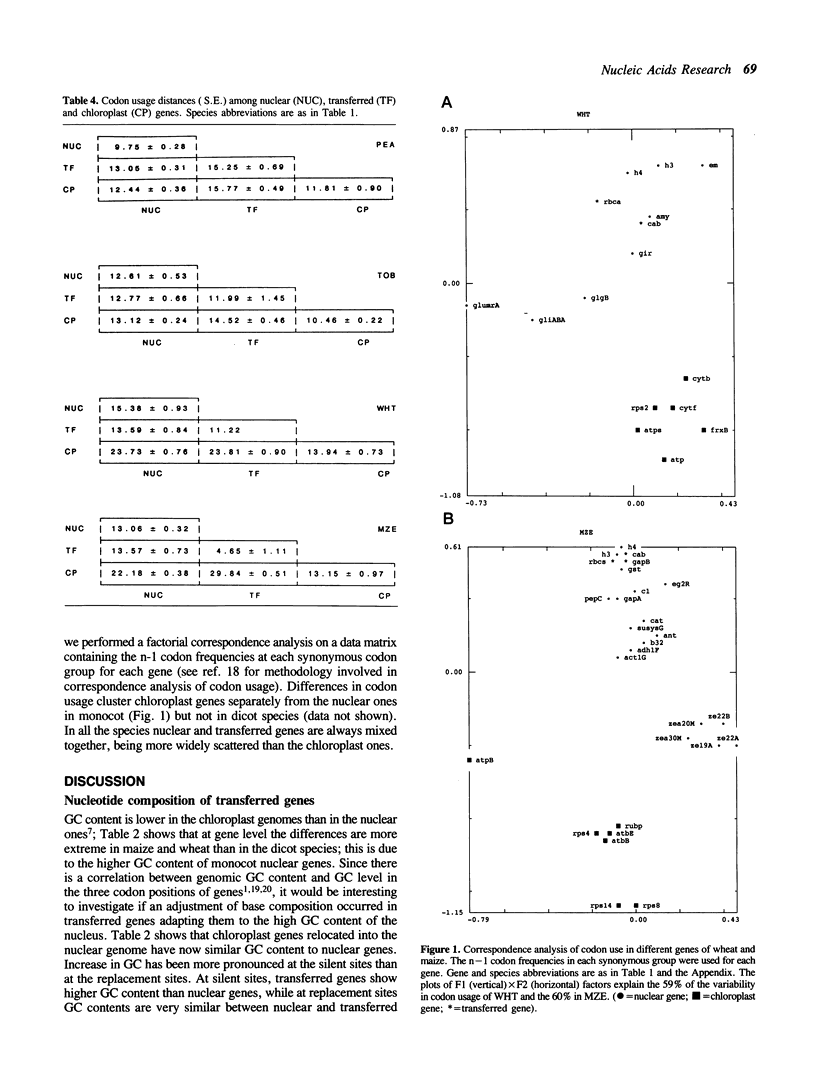
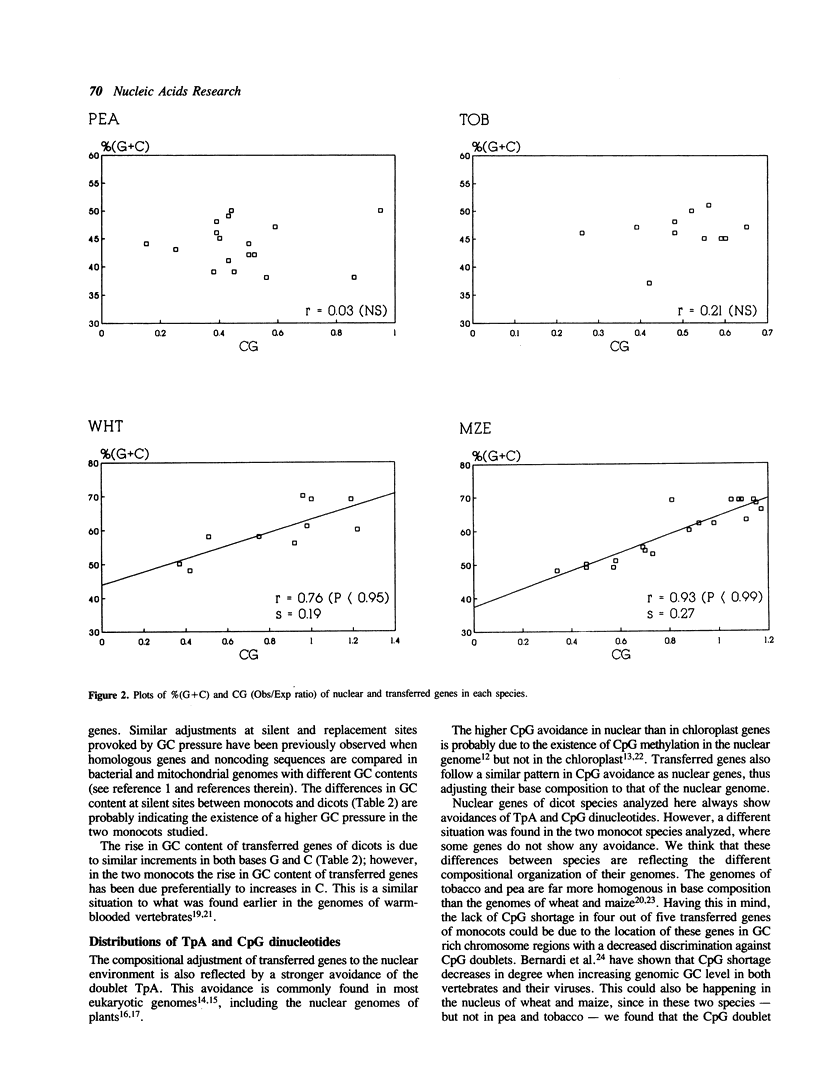
During plant evolution, some plastid genes have been moved to the nuclear genome. These transferred genes are now correctly expressed in the nucleus, their products being transported into the chloroplast. We compared the base compositions, the distributions of some dinucleotides and codon usages of transferred, nuclear and chloroplast genes in two dicots and two monocots plant species. Our results indicate that transferred genes have adjusted to nuclear base composition and codon usage, being now more similar to the nuclear genes than to the chloroplast ones in every species analyzed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aota S., Ikemura T. Diversity in G + C content at the third position of codons in vertebrate genes and its cause. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6345–6355. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Bernardi G. Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF02099946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Olofsson B., Filipski J., Zerial M., Salinas J., Cuny G., Meunier-Rotival M., Rodier F. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):953–958. doi: 10.1126/science.4001930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethards L. A., Skadsen R. W., Scandalios J. G. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the Cat2 gene in maize and its homology with other catalases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6830–6834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilofsky H. S., Burks C., Fickett J. W., Goad W. B., Lewitter F. I., Rindone W. P., Swindell C. D., Tung C. S. The GenBank genetic sequence databank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):1–4. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudraa M., Perrin P. CpG and TpA frequencies in the plant system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5729–5737. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann H., Martinez P., Quigley F., Martin W., Cerff R. Endosymbiotic origin and codon bias of the nuclear gene for chloroplast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from maize. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(4):320–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02101150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann H., Martinez P., Quigley F., Martin W., Cerff R. Endosymbiotic origin and codon bias of the nuclear gene for chloroplast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from maize. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(4):320–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02101150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fonzo N., Hartings H., Brembilla M., Motto M., Soave C., Navarro E., Palau J., Rhode W., Salamini F. The b-32 protein from maize endosperm, an albumin regulated by the O2 locus: nucleic acid (cDNA) and amino acid sequences. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jun;212(3):481–487. doi: 10.1007/BF00330853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. P., Gray J. C. Nucleotide sequence of the frxB gene in wheat chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):348–348. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J. Correlation between molecular clock ticking, codon usage fidelity of DNA repair, chromosome banding and chromatin compactness in germline cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 15;217(2):184–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80660-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Salinas J., Rodier F. Chromosome localization-dependent compositional bias of point mutations in Alu repetitive sequences. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):563–566. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatehouse J. A., Bown D., Gilroy J., Levasseur M., Castleton J., Ellis T. H. Two genes encoding 'minor' legumin polypeptides in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Characterization and complete sequence of the LegJ gene. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):15–24. doi: 10.1042/bj2500015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R. Viral, prokaryote and eukaryote genes contrasted by mRNA sequence indexes. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 1;95(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Naveh-Many T., Cedar H., Razin A. Sequence specificity of methylation in higher plant DNA. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):860–862. doi: 10.1038/292860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm L. Codon usage and gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):3075–3087. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P. Evolution of chromosome bands: molecular ecology of noncoding DNA. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jun;28(6):469–486. doi: 10.1007/BF02602928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höglund A. S., Gray J. C. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for ribosomal protein S2 in wheat chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10590–10590. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jukes T. H., Bhushan V. Silent nucleotide substitutions and G + C content of some mitochondrial and bacterial genes. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):39–44. doi: 10.1007/BF02099949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn D. J., Finnegan E. J., Ellis J. G., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. Structure and expression of an alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene from Pisum sativum (cv. "Greenfeast"). J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90331-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmann-Mulisch U., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence and linkage map position of the genes for ribosomal proteins L14 and S8 in the maize chloroplast genome. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 4;170(3):507–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Cerff R. Prokaryotic features of a nucleus-encoded enzyme. cDNA sequences for chloroplast and cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases from mustard (Sinapis alba). Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):323–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marín A., Bertranpetit J., Oliver J. L., Medina J. R. Variation in G + C-content and codon choice: differences among synonymous codon groups in vertebrate genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6181–6189. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matassi G., Montero L. M., Salinas J., Bernardi G. The isochore organization and the compositional distribution of homologous coding sequences in the nuclear genome of plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5273–5290. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Yamamoto N., Kano-Murakami Y., Tanaka Y., Ozeki Y., Hirano H., Kagawa H., Oshima M., Ohashi Y. Classification and Structural Comparison of Full-Length cDNAs for Pathogenesis-Related Proteins. Plant Physiol. 1987 Dec;85(4):942–946. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.4.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E. E., Lotzer J., Eberle M. Codon usage in plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):477–498. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngernprasirtsiri J., Kobayashi H., Akazawa T. DNA methylation as a mechanism of transcriptional regulation in nonphotosynthetic plastids in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4750–4754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S. Universal rule for coding sequence construction: TA/CG deficiency-TG/CT excess. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9630–9634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. D. Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:325–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ares J., Ghosal D., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3553–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinas J., Matassi G., Montero L. M., Bernardi G. Compositional compartmentalization and compositional patterns in the nuclear genomes of plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4269–4285. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M. C., Lazar G., Goodman H. M. Evidence in favor of the symbiotic origin of chloroplasts: primary structure and evolution of tobacco glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90367-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari K. K., Wildman S. G. Chloroplast DNA from tobacco leaves. Science. 1966 Sep 9;153(3741):1269–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3741.1269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingey S. V., Tsai F. Y., Edwards J. W., Walker E. L., Coruzzi G. M. Chloroplast and cytosolic glutamine synthetase are encoded by homologous nuclear genes which are differentially expressed in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9651–9657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierling E., Nagao R. T., DeRocher A. E., Harris L. M. A heat shock protein localized to chloroplasts is a member of a eukaryotic superfamily of heat shock proteins. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):575–581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierling E., Nagao R. T., DeRocher A. E., Harris L. M. A heat shock protein localized to chloroplasts is a member of a eukaryotic superfamily of heat shock proteins. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):575–581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. D., Lambert N., Delauney A., Yarwood J. N., Croy R. R., Gatehouse J. A., Wright D. J., Boulter D. Isolation and expression of a pea vicilin cDNA in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1988 May 1;251(3):857–864. doi: 10.1042/bj2510857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe K. H., Sharp P. M., Li W. H. Mutation rates differ among regions of the mammalian genome. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):283–285. doi: 10.1038/337283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerkandl E. Polite DNA: functional density and functional compatibility in genomes. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):12–27. doi: 10.1007/BF02099947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



