Abstract
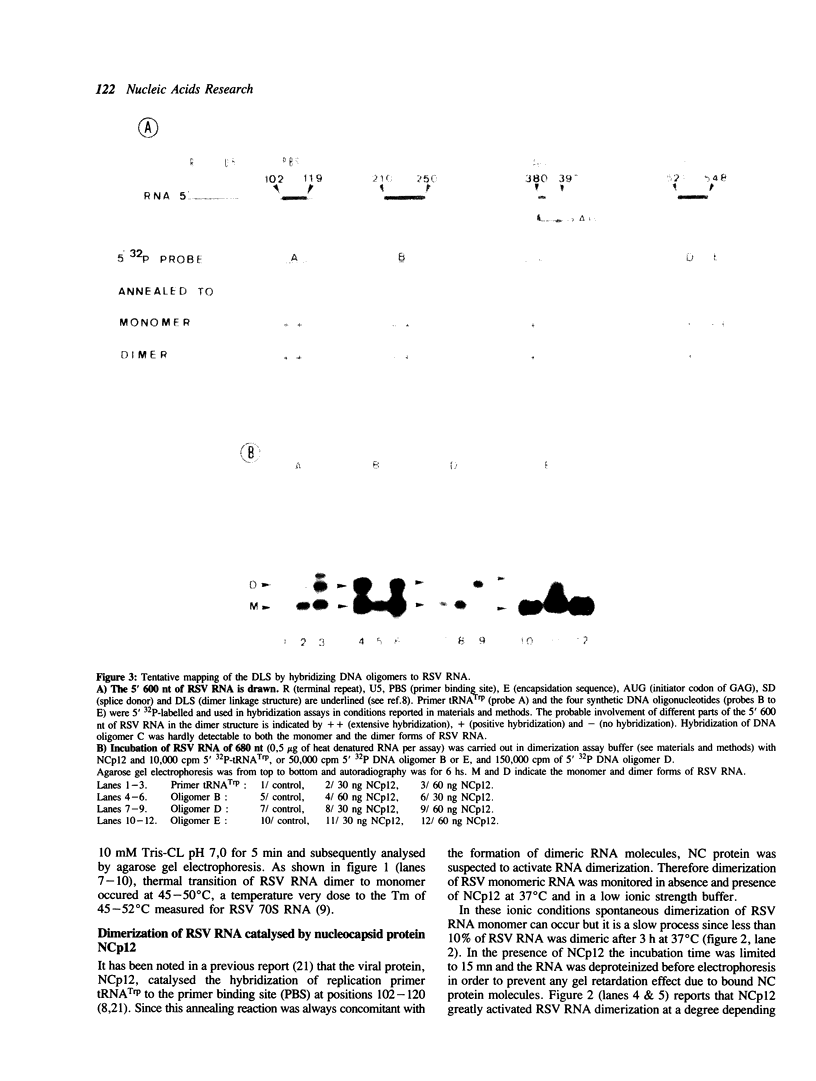
The genetic material of all retroviruses examined so far is an RNA dimer where two identical RNA subunits are joined at their 5' ends by a structure named dimer linkage structure (DLS). Since the precise location and structure of the DLS as well as the mechanism and role(s) of RNA dimerization remain unclear, we analysed the dimerization process of Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) RNA. For this purpose we set up an in vitro model for RSV RNA dimerization. Using this model RSV RNA was shown to form dimeric molecules and this dimerization process was greatly activated by nucleocapsid protein (NCp12) of RSV. Furthermore, RSV RNA dimerization was performed in the presence of complementary 5'32P-DNA oligomers in order to probe the monomer and dimer forms of RSV RNA. Data indicated that the DLS of RSV RNA probably maps between positions 544-564 from the 5' end. In an attempt to define sequences needed for the dimerization of RSV RNA, deletion mutageneses were generated in the 5' 600 nt. The results showed that the dimer promoting sequences probably are located within positions 208-270 and 400-600 from the 5' end and hence possibly encompassing the cis-acting elements needed for the specific encapsidation of RSV genomic RNA. Also it is reported that synthesis of the polyprotein precursor Pr76gag is inhibited upon dimerization of RSV RNA. These results suggest that dimerization and encapsidation of genome length RSV RNA might be linked in the course of virion formation since they appear to be under the control of the same cis elements, E and DLS, and the trans-acting factor nucleocapsid protein NCp12.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender W., Chien Y. H., Chattopadhyay S., Vogt P. K., Gardner M. B., Davidson N. High-molecular-weight RNAs of AKR, NZB, and wild mouse viruses and avian reticuloendotheliosis virus all have similar dimer structures. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):888–896. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.888-896.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Davidson N. Mapping of poly(A) sequences in the electron microscope reveals unusual structure of type C oncornavirus RNA molecules. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):595–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone L. R., Skalka A. M. Viral DNA synthesized in vitro by avian retrovirus particles permeabilized with melittin. I. Kinetics of synthesis and size of minus- and plus-strand transcripts. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):109–116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.109-116.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Stoltzfus C. M. Cloning and nucleotide sequences of cDNAs spanning the splice junctions of Rous sarcoma virus mRNAs. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):969–972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.969-972.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Garon C. F., Papas T. S. Native ribonucleoprotein is an efficient transcriptional complex of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1296–1300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N. Amino acid sequence homology in gag region of reverse transcribing elements and the coat protein gene of cauliflower mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):623–633. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L. Control of Rous sarcoma virus RNA translation and packaging by the 5' and 3' untranslated sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 5;189(3):421–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90314-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Schwager M., Spahr P. F., Bromley P. A. Analysis of the secondary and tertiary structures of Rous sarcoma virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3335–3354. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Spahr P. F. Binding sites of viral protein P19 onto Rous sarcoma virus RNA and possible controls of viral functions. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):147–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Spahr P. F., Bromley P. A. Analysis of Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) RNA structure by means of specific nucleases. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Spahr P. F., Bromley P. A., Jaton J. C. In vitro, the major ribosome binding site on Rous sarcoma virus RNA does not contain the nucleotide sequence coding for the N-terminal amino acids of the gag gene product. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):597–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.597-611.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Zuker M., Spahr P. F. Structure-function relationship of Rous sarcoma virus leader RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5183–5196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Baltimore D. RNA metabolism of murine leukemia virus: detection of virus-specific RNA sequences in infected and uninfected cells and identification of virus-specific messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 15;80(1):93–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier M., Dorizzi M., Sarger C., Labouresse J. Purification of tRNATrp, tRNAVal, and partial purification of tRNAIle and tRNAMfet from beef liver. Biochimie. 1976;58(10):1159–1165. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Kofoid E. C., Marlière P., Louis B. G. Potential secondary structure at translation-initiation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):345–360. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick R. J., Henderson L. E., Hanser J. P., Rein A. Point mutants of Moloney murine leukemia virus that fail to package viral RNA: evidence for specific RNA recognition by a "zinc finger-like" protein sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8420–8424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Terry R. W., Skalka A. M. A conserved cis-acting sequence in the 5' leader of avian sarcoma virus RNA is required for packaging. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):163–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.163-167.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. J., Hu S., Bender W., Bailey J. M., Davidson N., Nicolson M. O., McAllister R. M. RD-114, baboon, and woolly monkey viral RNA's compared in size and structure. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):609–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J., Jentoft J. Characteristics and regulation of interaction of avian retrovirus pp12 protein with viral RNA. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.361-369.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. A., Garapin A. C., Jackson N., Fanshier L., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid in cells producing rous sarcoma virus: detection and characterization. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):891–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.891-902.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moelling K., Sykora K. W., Dittmar K. E., Scott A., Watson K. F. The isolation of avian viral RNA and polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3738–3742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe S. H., Duthie R. S. Splice site consensus sequences are preferentially accessible to nucleases in isolated adenovirus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8447–8465. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murti K. G., Bondurant M., Tereba A. Secondary structural features in the 70S RNAs of Moloney murine leukemia and Rous sarcoma viruses as observed by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.411-419.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méric C., Darlix J. L., Spahr P. F. It is Rous sarcoma virus protein P12 and not P19 that binds tightly to Rous sarcoma virus RNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 15;173(4):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90396-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méric C., Goff S. P. Characterization of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants with single-amino-acid substitutions in the Cys-His box of the nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1558–1568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1558-1568.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méric C., Spahr P. F. Rous sarcoma virus nucleic acid-binding protein p12 is necessary for viral 70S RNA dimer formation and packaging. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):450–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.450-459.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Fiore D. Ordered interstrand and intrastrand DNA transfer during reverse transcription. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1064–1069. doi: 10.1126/science.2457948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., Sarih L., Gabus C., Litvak S., Keith G., Darlix J. L. Small finger protein of avian and murine retroviruses has nucleic acid annealing activity and positions the replication primer tRNA onto genomic RNA. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1777–1783. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugatsch T., Stacey D. W. Identification of a sequence likely to be required for avian retroviral packaging. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):505–511. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. J., Bailey J. M. The binding of an avian myeloblastosis virus basic 12,000 dalton protein to nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):2055–2072. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.2055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Snyder P. N. Structure of B77 sarcoma virus RNA: stabilization of RNA after packaging. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1161–1170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1161-1170.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykora K. W., Moelling K. Properties of the avian viral protein p12. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):379–391. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]