Abstract
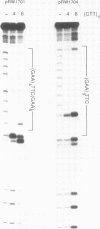
The ability of oligopyrimidines to inhibit, through triple helix formation, the specific protein-DNA interactions of the EcoRI restriction and modification enzymes (EcoRI and MEcoRI) with their recognition sequence (GAATTC) was studied. The oligonucleotides (CTT)4 and (CTT)8 formed triplexes in plasmids at (GAA)n repeats containing EcoRI sites. Cleavage and methylation of EcoRI sites within these sequences were specifically inhibited by the oligonucleotides, whereas an EcoRI site adjacent to a (GAA)n sequence was inhibited much less. Also, other EcoRI sites within the plasmid, or in exogenously added lambda DNA, were not inhibited. These results demonstrate the potential of using triplex-forming oligonucleotides to block protein-DNA interactions at specific sites, and thus this technique may be useful in chromosome mapping and in the modulation of gene expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Selsing E. Structures for the polynucleotide complexes poly(dA) with poly (dT) and poly(dT) with poly(dA) with poly (dT). J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90498-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasty A. M., Behe M. J. An oligopurine sequence bias occurs in eukaryotic viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1517–1528. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M. J. The DNA sequence of the human beta-globin region is strongly biased in favor of long strings of contiguous purine or pyrimidine residues. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7870–7875. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Sederoff R. R., Paterson M. C. Distribution of polypyrimidine . polypurine segments in DNA from diverse organisms. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):301–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broitman S. L., Im D. D., Fresco J. R. Formation of the triple-stranded polynucleotide helix, poly(A.A.U). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5120–5124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M., Czernuszewicz G., Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Hogan M. E. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.3293213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Chassignol M., Thuong N. T., Helene C. Sequence-targeted cleavage of single- and double-stranded DNA by oligothymidylates covalently linked to 1,10-phenanthroline. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5891–5898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Klysik J., Wells R. D. Influence of DNA sequence on the formation of non-B right-handed helices in oligopurine.oligopyrimidine inserts in plasmids. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7386–7396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wells R. D. Intramolecular DNA triplexes in supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6292–6296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Htun H., Dahlberg J. E. Single strands, triple strands, and kinks in H-DNA. Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1791–1796. doi: 10.1126/science.3175620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. H. The S1-sensitive form of d(C-T)n.d(A-G)n: chemical evidence for a three-stranded structure in plasmids. Science. 1988 Sep 30;241(4874):1800–1804. doi: 10.1126/science.2845572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi Y., Kohwi-Shigematsu T. Magnesium ion-dependent triple-helix structure formed by homopurine-homopyrimidine sequences in supercoiled plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3781–3785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Doan T., Perrouault L., Praseuth D., Habhoub N., Decout J. L., Thuong N. T., Lhomme J., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition, photocrosslinking and cleavage of the DNA double helix by an oligo-[alpha]-thymidylate covalently linked to an azidoproflavine derivative. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7749–7760. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Johnson D. A., Morgan A. R. Complexes formed by (pyrimidine)n . (purine)n DNAs on lowering the pH are three-stranded. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):3073–3091. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letai A. G., Palladino M. A., Fromm E., Rizzo V., Fresco J. R. Specificity in formation of triple-stranded nucleic acid helical complexes: studies with agarose-linked polyribonucleotide affinity columns. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9108–9112. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Wold B., Dervan P. B. Inhibition of DNA binding proteins by oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):725–730. doi: 10.1126/science.2549631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Massoulié J., Guschlbauer W. Synthetic polynucleotides. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1967;6:83–141. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60525-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkin S. M., Lyamichev V. I., Drushlyak K. N., Dobrynin V. N., Filippov S. A., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. DNA H form requires a homopurine-homopyrimidine mirror repeat. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):495–497. doi: 10.1038/330495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. R., Wells R. D. Specificity of the three-stranded complex formation between double-stranded DNA and single-stranded RNA containing repeating nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Perrouault L., Le Doan T., Chassignol M., Thuong N., Hélène C. Sequence-specific binding and photocrosslinking of alpha and beta oligodeoxynucleotides to the major groove of DNA via triple-helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1349–1353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal P., Feigon J. Triple-strand formation in the homopurine:homopyrimidine DNA oligonucleotides d(G-A)4 and d(T-C)4. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):637–640. doi: 10.1038/339637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen D., Gilbert W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):364–366. doi: 10.1038/334364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Hanvey J. C., Wells R. D. Intramolecular DNA triplexes in supercoiled plasmids. I. Effect of loop size on formation and stability. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5944–5949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Collier D. A., Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wohlrab F. The chemistry and biology of unusual DNA structures adopted by oligopurine.oligopyrimidine sequences. FASEB J. 1988 Nov;2(14):2939–2949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]