Abstract
The gammaproteobacterium Xenorhabdus nematophila is a mutualistic symbiont that colonizes the intestine of the nematode Steinernema carpocapsae. nilB (nematode intestine localization) is essential for X. nematophila colonization of nematodes and is predicted to encode an integral outer membrane beta-barrel protein, but evidence supporting this prediction has not been reported. The function of NilB is not known, but when expressed with two other factors encoded by nilA and nilC, it confers upon noncognate Xenorhabdus spp. the ability to colonize S. carpocapsae nematodes. We present evidence that NilB is a surface-exposed outer membrane protein whose expression is repressed by NilR and growth in nutrient-rich medium. Bioinformatic analyses reveal that NilB is the only characterized member of a family of proteins distinguished by N-terminal region tetratricopeptide repeats (TPR) and a conserved C-terminal domain of unknown function (DUF560). Members of this family occur in diverse bacteria and are prevalent in the genomes of mucosal pathogens. Insertion and deletion mutational analyses support a beta-barrel structure model with an N-terminal globular domain, 14 transmembrane strands, and seven extracellular surface loops and reveal critical roles for the globular domain and surface loop 6 in nematode colonization. Epifluorescence microscopy of these mutants demonstrates that NilB is necessary at early stages of colonization. These findings are an important step in understanding the function of NilB and, by extension, its homologs in mucosal pathogens.
INTRODUCTION
The mutualism between the gammaproteobacterium Xenorhabdus nematophila and the nematode Steinernema carpocapsae is a model to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the initiation and maintenance of long-term beneficial animal-microbe associations (13). The soil-dwelling infective third-stage juvenile nematode (the infective juvenile) is colonized by a monoculture of X. nematophila bacteria in a structure, known as the receptacle (previously the vesicle), located at the anterior of the nematode intestine (10, 21, 42, 58). The infective juvenile infects the blood of insect hosts, releases the bacteria from the receptacle, and together with the symbiont rapidly kills the insect host (22, 26, 32). Within the insect cadaver, the nematode reinitiates development and reproduces through adult and juvenile stages that lack the receptacle structure characteristic of the infective juvenile stage. When nutrients derived from the insect cadaver are exhausted, progeny juveniles reassociate with the symbiotic bacteria and develop into the infective juvenile stage, which exits the insect cadaver to search for a new host (reviewed in reference 50). X. nematophila's contributions to mutualism are that it is essential for both insect host killing and S. carpocapsae nematode growth. In turn, X. nematophila uses its nematode host as a vector into insects and as a protected environment between infections (39, 43, 44).
Bacterial colonization of the infective juvenile nematode host takes place in at least three stages: (i) entry of a few bacterial cells into the receptacle, (ii) outgrowth of the initiating population to 30 to 200 bacterial cells, entirely filling the receptacle (37), and (iii) persistence of the colonizing bacteria until the bacteria are released into an insect host by a recovering infective juvenile (21, 25). The process by which X. nematophila cells initially gain entry into the infective juvenile receptacle and the point at which other species are excluded have not been elucidated. Transposon screens for colonization-defective X. nematophila mutants revealed genes involved in both entry and outgrowth (30, 37). Outgrowth mutants, including those with defects in methionine and threonine biosynthesis, localize to the receptacle but do not replicate to fill it (21, 38) and ultimately disappear from within the nematode population (38). In contrast, mutants that are defective in early stages of colonization are never apparent within the receptacle, either because they fail to enter or because they fail to survive immediately after entering. Mutations in any of three genes, nilA, -B, and -C (nematode intestine localization), carried on a 3.5-kb locus (called SR1), cause entry defects. nilA mutants colonize nematodes to approximately 2.5% of the level of the wild type, while nilB and nilC mutants do not colonize above the level of detection (0.005 CFU/infective juvenile) (30). Microscopic analysis demonstrated that the partial colonization phenotype of a nilA mutant occurs because a few nematodes are partially colonized, while the rest are devoid of bacteria. This indicates that nilA mutants are defective primarily in entry but also have outgrowth defects (17). However, it remains unclear whether nilA mutations cause a defect in adherence to specific tissues or in survival during colonization initiation.
An early observation regarding the nil locus was that it is absent from other species of Xenorhabdus (17, 30), suggesting that it may be specifically required for colonization of S. carpocapsae nematodes. Indeed, when nilA, -B, and -C were introduced into the chromosome of Xenorhabdus poinarii or Xenorhabdus bovienii, these strains colonized the receptacles of S. carpocapsae nematodes, but the corresponding control strains lacking the nil locus did not (17). Therefore, the nil locus not only is necessary for S. carpocapsae nematode colonization by X. nematophila (30) but also functions as a specificity determinant.
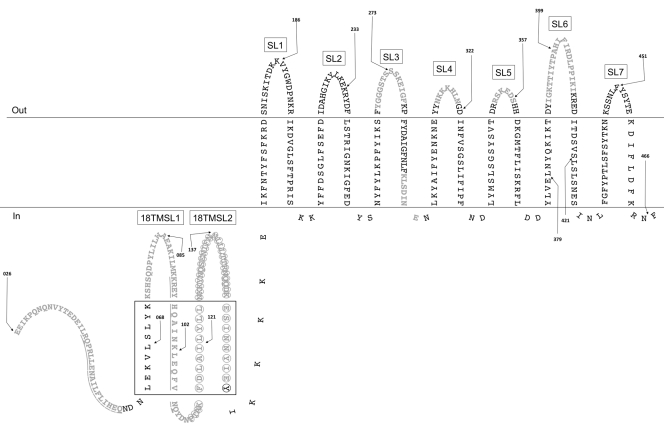
Online databases lack nil gene homologs of known function, and understanding nil gene function therefore requires fundamental genetic and biochemical characterization. NilC is a 282-amino-acid (aa) outer membrane-localized lipoprotein that is predominantly oriented toward the periplasm (based on its resistance to degradation by proteinase K in whole cells) (15). NilA is predicted to be a small 90-aa inner membrane protein (30), and NilB is predicted to encode a 466-aa protein that adopts a beta-barrel structure in the outer membrane (Fig. 1) (30). The predicted localization of NilB to the outer membrane suggests that it may interact directly with host surfaces or molecules, for example, by binding to nematode surface structures or by transporting a nutrient provided to the bacteria from the host.
Fig 1.
NilB topology predicted by the PROFtmb (9) hidden Markov model. The model presented is similar to the model predicted by B2TMR-HMM (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material and reference 36). While the PROFtmb model predicts that the ∼130 N-terminal amino acids are periplasmic, TMBB-PRED predicts that ∼100 of these amino acids form four additional TM domains (5, 6) (drawn in the periplasm in the same manner as TM domains and surface loops; the black box denotes this region). Only mature NilB is pictured (as predicted by SignalP 3.0 [8]), and numbering is according to that of immature NilB. Black arrows, FLAG tag insertions (before indicated amino acid); gray text, deletions (underlining distinguishes adjacent deletions); circles, the predicted TPR domain; SL, surface loop; 18TMSL, surface loop unique to the 18-TM strand model.
To investigate the topology and function of NilB, we assessed the colonization phenotypes of nilB mutants created by FLAG tag insertions and domain deletions. These data reveal certain domains critical for NilB function in colonization. Also, coupled with in vivo imaging of colonizing bacteria within the nematode host, our data suggest that NilB functions solely at entry into the nematode receptacle. Unlike with another specificity factor, nilA, we found no indication that nilB is necessary for outgrowth or persistence within the nematode receptacle.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains, plasmids, media, and growth conditions.
X. nematophila strains (Table 1) were grown aerobically at 30°C on LB agar plates containing 0.1% pyruvate or in the dark in LB broth in the presence of appropriate antibiotics, unless stated otherwise. Final antibiotic concentrations used were ampicillin at 100 μg/ml, chloramphenicol at 30 (for E. coli) or 15 (X. nematophila) μg/ml, erythromycin at 200 μg/ml, kanamycin at 50 μg/ml, and streptomycin at 25 (E. coli) or 12.5 (X. nematophila) μg/ml. Defined medium was made as described previously (41) except that agar and amino acids were omitted and 0.68 g MgCl2(H2O)6 liter−1 and 0.91% glucose were added after the autoclaving.
Table 1.
Xenorhabdus strains used in this study
| Strain type | Strain | Parent strain | Relevant characteristic(s) | Source or reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insertionlessa | HGB007 | NAb | Sequenced ATCC 19061 X. nematophila wild type | ATCC |
| HGB777 | HGB007 | Δ(nilA-nilC)7::Km (ΔSR1) | 15 | |
| HGB1251 | HGB777 | Δ(nilA-nilC)7::Km (ΔSR1) ΔnilR16::Sm | This study | |
| HGB1430 | HGB777 | Δ(nilA-nilC)7::Km lacZp-GFP (from pJMC001) | This study | |
| HGB1429 | HGB1251 | Δ(nilA-nilC)7::Km ΔnilR16::Sm lacZp-GFP (from pJMC001) | This study | |
| Non-GFP-expressing nilB FLAG insertion mutants | HGB778 | HGB777 | SR1 | 15 |
| HGB1256 | HGB777 | SR1/nilB26-FLAG aa026 (nilB-FLAG26) | This study | |
| HGB1200 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB26-FLAG aa026 (nilB-FLAG26) | This study | |
| HGB1805 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB27-FLAG aa068 | This study | |
| HGB1201 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB28-FLAG aa085 | This study | |
| HGB1806 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB29-FLAG aa102 | This study | |
| HGB1807 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB30-FLAG aa121 | This study | |
| HGB1203 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB31-FLAG aa137 | This study | |
| HGB1254 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB32-FLAG aa186 | This study | |
| HGB1204 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB33-FLAG aa233 | This study | |
| HGB1253 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB34-FLAG aa273 | This study | |
| HGB1206 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB35-FLAG aa322 | This study | |
| HGB1260 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB36-FLAG aa357 | This study | |
| HGB1808 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB37-FLAG aa379 | This study | |
| HGB1207 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB38-FLAG aa399 | This study | |
| HGB1809 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB39-FLAG aa421 | This study | |
| HGB1208 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB40-FLAG aa451 | This study | |
| HGB1324 | HGB1251 | SR1/nilB41-FLAG aa466 | This study | |
| HGB1255 | HGB1251 | SR1 | This study | |
| GFP-expressing nilB FLAG insertion mutants | HGB1502 | HGB1430 | SR1/nilB34-FLAG aa270 | This study |
| HGB1495 | HGB1429 | Empty | This study | |
| HGB1496 | HGB1429 | SR1 (wild type nilB without FLAG) | This study | |
| HGB1484 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB26-FLAG aa026 (nilB-FLAG26) | This study | |
| HGB1487 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB32-FLAG aa186 | This study | |
| HGB1489 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB34-FLAG aa273 | This study | |
| HGB1490 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB35-FLAG aa322 | This study | |
| HGB1492 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB38-FLAG aa399 | This study | |
| GFP-expressing nilB-FLAG26 deletion mutants | HGB1460 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB42-Δ026–042 | This study |
| HGB1461 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB43-Δ043–059 | This study | |
| HGB1462 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB44-Δ026–059 | This study | |
| HGB1463 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB45-Δ076–091 | This study | |
| HGB1464 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB46-Δ092–108 | This study | |
| HGB1465 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB47-Δ026–108 | This study | |
| HGB1510 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB48-Δ109–156 | This study | |
| HGB1511 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB49-Δ026–156 | This study | |
| HGB1466 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB50-Δ266–279 | This study | |
| HGB1467 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB51-Δ292–298 | This study | |
| HGB1468 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB52-Δ314–320 | This study | |
| HGB1469 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB53-Δ352–357 | This study | |
| HGB1470 | HGB1429 | SR1/nilB54-Δ389-410 | This study |
All strains except HGB007, HGB777, HGB1251, HGB1430, and HGB1429 had att Tn7 insertions.
NA, not applicable.
An X. nematophila strain (HGB1251) that lacks nilR (encoding a repressor of the nil locus) as well as the locus carrying nilA, nilB, and nilC, symbiosis region 1 (SR1), was created by conjugating strain HGB1141 (E. coli S17 λ pir containing pΔnilR16::Sm [16]) into the recipient strain HGB777 (ΔSR1-7::Kan) (15). To facilitate in vivo visualization of strains colonizing nematodes, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression plasmid JMC001 was created. Plasmid pURR25 was digested with SacI and BglII (Promega) to isolate the 2.5-kb cat-lacZp-GFP fragment. pECM20 (37) was also digested with SacI and BglII to remove the aphAp-GFP region. The resulting 5-kb pECM20 fragment was ligated to the 2.5-kb cat-lacZp-GFP fragment using T4 DNA ligase (Promega) and electroporated into E. coli S17-1 λ pir cells. A colony with green coloration, visible by the naked eye, was frozen and used as a donor to transfer pECM20-lacZp-GFP into HGB1251 to create X. nematophila ΔnilR16::Sm ΔSR1-7::Km lacZp-GFP (HGB1429) or into HGB777 to create X. nematophila ΔSR1-7::Km lacZp-GFP (HGB1430).
NilB-FLAG insertion mutants were created by PCR amplification (with Platinum PFX DNA polymerase; Invitrogen) of the entire pTn7/SR1 plasmid (15) with primers flanking the mutation site (see Table S1 in the supplemental material). One primer contained an nilB-complementary sequence, the FLAG sequence (nucleotides, GATTACAAGGATGACGACGATAAG; amino acids, DYKDDDDK) and the NheI restriction site, while the other primer contained an nilB-complementary sequence and the NheI restriction site. PCR products were cleaned using the QIAquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen), digested with the restriction enzyme NheI at 37°C, ligated with T4 DNA ligase (Promega), and electroporated into E. coli S17-1 λ pir cells.
With one exception, nilB in-frame deletion constructs were created by PCR by amplifying the entire pAB001 plasmid (containing nilB26-FLAG26), with primers oriented in the direction opposite to that of the desired deletion site and containing 9 bp of the sequence upstream and 18 bp of the sequence downstream of the desired deletion site (see Table S1 in the supplemental material), using Takara PrimeStar polymerase per the manufacturer's instructions and annealing at 55°C for 5 to 10 s. PCR products were cleaned using a Zyppy PCR purification kit (Zymo Research), digested with DpnI, reverse dialyzed on a 0.025-μm VSWP membrane (Millipore) for 15 min, and electroporated into E. coli S17-1 λ pir cells. The exception was that the nilB construct with a deletion of aa 26 to 156 (nilBΔ26–156 construct) could not be created using this approach, so the NheI restriction site approach utilized for creating FLAG insertions was adopted, resulting in insertion of duplicate NheI sites flanking the FLAG26 insertion (AS-DYKDDDDK-AS). Enzymes used for creating deletions were also used to create the nilBΔ26-156 construct and the constructs nilB-FLAG aa068 (in which the FLAG tag is inserted before aa 68), nilB-FLAG aa102, nilB-FLAG aa121, nilB-FLAG aa379, and nilB-FLAG aa421. The complete SR1 region of each Tn7-nilB mutant construct (plasmids are listed in Table 2) was sequenced to ensure that additional mutations did not arise during PCR. Constructs were incorporated into the att Tn7 site of X. nematophila ATCC 19061 ΔSR1 ΔnilR (HGB1251), ΔSR1 (HGB777), ΔSR1 lacZp-GFP (HGB1430), or ΔSR1 ΔnilR lacZp-GFP (HGB1429) by triparental mating as described previously (7). Verification of insertion of each Tn7/nilB-FLAG or deletion construct at the att Tn7 site was verified by PCR as described previously (15). Since insertion or deletion mutations were created in the context of the SR1 genomic region, the mutant nilB alleles were expressed from the native nilB promoter and regulatory regions. Constructs were introduced into a strain lacking SR1 so that no SR1 DNA sequence was present in duplicate. Therefore, HGB777, -1251, -1429, and -1430 complemented with Tn7/SR1 lacking any modifications to SR1 are considered wild-type controls in this study.
Table 2.
Plasmids used in this study
| Type of construct | Plasmid | Relevant properties | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|---|
| pEVS107 | oriR6K mobRP4; mobilizable suicide miniTn7-Erm delivery vector; Ermr Kmr | 52 | |
| pUX-BF13 | Mobilizable Tn7 transposition helper plasmid that expresses Tn7 transposase in trans; Apr | 7 | |
| pTn7/SR1 | Delivers miniTn7-Erm/SR1; used as a template for creation of the NilB-FLAG insertion and deletion mutations | 15 | |
| pJMC001 | Plasmid pECM20 with cat-lacZp-GFP from pURR25 cloned into the SacI and BglII sites, replacing the original gene encoding GFP on this plasmid | This study | |
| pECM20 | GFP plasmid that contains a 614-bp chromosomal sequence of X. nematophila ATCC 19061 that facilitates plasmid integration at a site that does not interfere with nematode colonization | 37 | |
| pURR25 | Tn7 PA1/03/04gfpmut3; cat-lacZp-GFP source for pJMC001 | D. Lies and D. Newmann via T. Ciche | |
| pTn7/SR1nilB-FLAG insertion mutant constructs | pAB001 | pTn7/SR1/nilB26-FLAG aa026 (nilB-FLAG26) | This study |
| pAB002 | pTn7/SR1/nilB28-FLAG aa085 | This study | |
| pAB003 | pTn7/SR1/nilB31-FLAG aa137 | This study | |
| pAB004 | pTn7/SR1/nilB32-FLAG aa186 | This study | |
| pAB005 | pTn7/SR1/nilB33-FLAG aa233 | This study | |
| pAB006 | pTn7/SR1/nilB34-FLAG aa273 | This study | |
| pAB007 | pTn7/SR1/nilB35-FLAG aa322 | This study | |
| pAB008 | pTn7/SR1/nilB36-FLAG aa357 | This study | |
| pAB009 | pTn7/SR1/nilB38-FLAG aa399 | This study | |
| pAB010 | pTn7/SR1/nilB40-FLAG aa451 | This study | |
| pAB011 | pTn7/SR1/nilB41-FLAG aa466 | This study | |
| pJMC016 | pTn7/SR1/nilB27-FLAG aa068 | This study | |
| pJMC017 | pTn7/SR1/nilB29-FLAG aa102 | This study | |
| pJMC018 | pTn7/SR1/nilB30-FLAG aa121 | This study | |
| pJMC019 | pTn7/SR1/nilB37-FLAG aa379 | This study | |
| pJMC020 | pTn7/SR1/nilB39-FLAG aa421 | This study | |
| pAB001 nilB-FLAG26 deletion mutant constructs | pJMC002 | pTn7/SR1/nilB42-Δ026–042 | This study |
| pJMC003 | pTn7/SR1/nilB43-Δ043–059 | This study | |
| pJMC004 | pTn7/SR1/nilB44-Δ026–059 | This study | |
| pJMC005 | pTn7/SR1/nilB45-Δ076–091 | This study | |
| pJMC006 | pTn7/SR1/nilB46-Δ092–108 | This study | |
| pJMC007 | pTn7/SR1/nilB47-Δ026–108 | This study | |
| pJMC014 | pTn7/SR1/nilB48-Δ109–156 | This study | |
| pJMC015 | pTn7/SR1/nilB49-Δ026–156 | This study | |
| pJMC008 | pTn7/SR1/nilB50-Δ266-279 | This study | |
| pJMC009 | pTn7/SR1/nilB51-Δ292–298 | This study | |
| pJMC010 | pTn7/SR1/nilB52-Δ314–320 | This study | |
| pJMC011 | pTn7/SR1/nilB53-Δ352–357 | This study | |
| pJMC012 | pTn7/SR1/nilB54-Δ389–410 | This study |
Fractionation, NilB detection by Western blotting, and glycosylation.
Two Western blotting methods were used in this study. In method 1, used for all experiments except where stated otherwise, strains were grown as described above prior to harvesting of cell pellets. Pellets were washed and resuspended in cold 1× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and sonicated on ice using a Sonic Dismembrator with 5 bursts of 3 s each or until the cells lysed. Lysed cells were spun at 13,000 rpm in a microcentrifuge to remove cell debris. The total protein concentration of the cleared lysates was determined by the Bradford assay (Bio-Rad), and equal amounts of protein were heated for 10 min at 95°C in 1× SDS-PAGE loading dye prior to being loaded onto 12% SDS-PAGE gels. In other cases, the cleared lysate was spun at 434,513 × g in a Beckman TLA 100.2 rotor for 30 min at 4°C for separation of the membrane and soluble fractions. The membrane fraction was solubilized in 1× PBS plus 0.5% Sarkosyl by stirring for 30 min. Fractions were heated for 10 min at 95°C in 1× SDS-PAGE loading dye prior to being loaded onto 12% SDS-PAGE gels. After transfer to polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Bio-Rad), membranes were blocked for 1 h with 5% dry milk in 1× Tris-buffered saline with Tween 20 (TBS-T) at room temperature, washed, and incubated with 1:1,000-diluted anti-FLAG antibody (Cell Signaling) in 1× TBS-T plus 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) overnight at 4°C. The next day, membranes were washed, incubated with 1:10,000-diluted horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-linked anti-rabbit IgG (Cell Signaling) for 1 h at room temperature, and washed again prior to detection using the Amersham ECL Plus Western blotting detection system (GE Healthcare) and the Storm/Typhoon scanner or the LAS4010 biomolecular imager (ImageQuant) according to the manufacturers' instructions.
Western blotting method 2 was used for the experiments from which results are shown in Fig. 4 and for which data are not shown. In this method, strains were subcultured from LB at a 1:100 dilution into defined medium for ∼24 h prior to harvesting of cell pellets. Pellets were washed in an equal volume of PBS, concentrated 4-fold in PBS, and normalized to their optical density at 600 nm (OD600) prior to being mixed with 2× SDS-PAGE loading dye, heated to 95°C for 10 min, and run at 100 V on a 7.5% SDS-PAGE gel. Gels were transferred to a PVDF membrane (Bio-Rad) by a Trans-Blot SD semidry electrophoretic transfer cell (Bio-Rad) set to transfer at 22 V for at least 15 min. Membranes were blocked overnight in PBS plus 5% dry milk prior to being sequentially washed and incubated with a 1:10,000 or 1:5,000 dilution of anti-FLAG antibody (Sigma F7425) and HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Pierce catalog number 32260) according to the manufacturers' instructions. Blots were detected using the ECL Plus Western blotting substrate (Pierce catalog number 32209) and XAR film (Kodak XAR catalog number 165-1454). Adobe Photoshop CS3 was used to alter the intensity and contrast of scanned images of films, with all samples within an individual panel (including the controls) manipulated in the same way.
The glycosylation state of NilB was determined using the GelCode glycoprotein staining kit (Pierce). X. nematophila crude protein was extracted from all nilB-FLAG insertion mutants in the ΔSR1 ΔnilR background and electrophoresed as described above, except that transfer was onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad) rather than a PVDF membrane. Positive (horseradish peroxidase) and negative (soybean trypsin inhibitor) control proteins were also loaded on the protein gel. Upon transfer, the membrane was washed with acetic acid, oxidizing solution, staining reagent, and reducing agent according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Proteinase K assay.
Strain HGB1200 (ΔSR1 ΔnilR Tn7/SR1nilB-FLAG26) was grown at 30°C overnight in LB broth. Cells were pelleted and then washed and resuspended in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8, 1 mM CaCl2. The resuspended whole cells were split into two aliquots. One aliquot was treated with 0.1% Triton X-100 (final concentration) to break open the cells. Both aliquots were treated with 38.4 μg/ml proteinase K (final concentration; Fermentas) for 0 to 30 min at 37°C. At various time points, samples were removed and reactions were stopped with the addition of 5 mM PMSF (Sigma catalog number P-7626) and kept on ice. SDS-PAGE loading dye was added to all the reaction mixtures, which were heated at 95°C for 10 min, sonicated for 8 s to shear the DNA, and electrophoresed on 12% SDS-PAGE gels. NilB and NilC (as a control) were detected in Western blots using anti-FLAG and anti-NilC antibody (15), respectively.
Growth curves and time courses of NilB protein levels.
Strains HGB1200 (ΔSR1 ΔnilR Tn7/SR1 nilB-FLAG26) and HGB1256 (ΔSR1 Tn7/SR1 nilB-FLAG26) were streaked from −80°C onto LB pyruvate plates with antibiotics. Colonies from these plates were inoculated into liquid LB with antibiotics and grown at 30°C overnight in a shaking water bath. Overnight cultures were subcultured 1:100 into 1 ml LB or defined medium (no antibiotics) in the wells of a 24-well plate. Absorbance at 600 nm was measured at 1-h intervals using the SpectraMax M5e plate reader (Molecular Devices). At 6, 12, 24, 36, 54, and 77 h, 0.5 ml of each strain in either LB or defined medium was removed, microcentrifuged to remove the medium, washed with 1× cold PBS, resuspended in 1× PBS, and sonicated at approximately 14 W for 10 s. Sample protein concentrations were assessed by the Bradford assay (Bio-Rad), and all samples were normalized to each other. Samples at later time points were diluted in more PBS than earlier time points (PBS resuspension volumes ranged from 37.5 to 150 μl). After resuspension, 4× SDS-PAGE loading dye was added and the samples were stored at −20°C until Western blotting was performed. Quantitation of blots was performed using the ImageQuant TL program (GE Healthcare).
Nematode-bacterium cocultivations.
The effect of FLAG insertions in NilB on nematode colonization was tested by growing each mutant on lipid agar (54) and inoculating greater than 200 sterile nematode eggs (55) or surface-sterilized axenic infective juveniles onto each plate. The latter were prepared by inoculating sterile nematode eggs onto a GFP-expressing strain of X. nematophila (HGB1430 ΔSR1::Km lacZp-GFP) defective in nematode colonization. Infective juveniles were harvested from White traps and stored at 25°C until they were surface sterilized for 3 min in 0.5% NaOCl (30), and then they were inoculated onto bacterial lawns. Infective juveniles that developed on the FLAG-tagged mutant bacteria were harvested in White traps (56), and bacterial colonization of the nematode host was assessed either by dilution plating surface-sterilized nematode sonicates to calculate average numbers of CFU per infective juvenile (15) or by analyzing nematode carriage of GFP-labeled bacteria by epifluorescence microscopy as described previously (37). For microscopy, nematodes were analyzed at a 100× magnification and scored as either colonized (bacteria were localized to the receptacle) or uncolonized (no bacteria were observed within the receptacle). If greater than 30 in 500 nematodes in the population were colonized, nematodes were scored individually. If fewer than 30 nematodes in 500 were colonized, samples of nematode populations were scanned for colonized nematodes in 24-well plates. The number of colonized nematodes in each well was determined, and the entire nematode population in each well was enumerated by dilution counting. Organisms in additional wells were counted until either 30 colonized nematodes or all nematode progeny from the inoculated plate were counted (whichever occurred first). Data are reported as the percentages of total nematodes that carried GFP-labeled bacteria.
For data presented in Fig. 5, sterile nematode eggs were added to each lawn of bacteria and nematode sonications were performed on samples from at least five different experiments performed at different times. For Fig. 4, surface-sterilized axenic infective juveniles were added to each lawn of bacteria. Nematode sonications were performed on samples from two experiments performed at different times. For the first experiment, two otherwise isogenic exconjugants were inoculated, and three replicate experiments were performed for each (six replicate experiments, total) (data not shown). Colonization results for each exconjugant pair were the same, so for the second experiment (data shown), the results of two replicate samples for each of three isogenic cultures of a single representative exconjugant were assessed. The results of replicate samples were averaged to give biological-replicate (i.e., isogenic strain) values, and averages and standard deviations among biological-replicate values for the second experiment are presented in Fig. 4. A linear mixed-effects model was applied to each experiment individually, and similar statistical trends were observed between the two experiments. For all other colonization tests, surface-sterilized axenic infective juveniles were used to inoculate bacterial lawns. Assays were performed as two experiments at different times with two replicate samples for each of three biological replicates of each strain. For graphical presentation, the results of replicate samples were averaged to give biological-replicate values, and averages and standard deviations among biological-replicate values for a single representative experiment are presented. A linear mixed-effects model or a generalized linear mixed-effects model was applied to raw values or data after combination of the results of both experiments.
Statistical analysis.
Statistical differences in Fig. 5 were assessed in Microsoft Excel using a two-tailed heteroscedastic Student t test. Otherwise, differences between sonicated samples were performed using a linear mixed-effects model, and differences between samples analyzed by microscopy were assessed using a generalized linear mixed-effects model. Statistical tests were performed in R (48). All collected data points were included in the analyses unless otherwise indicated, and the P value cutoffs are at least <0.05.
RESULTS
nilB represents a family of proteins found within symbionts of animals.
In 2002, it was reported that, while X. nematophila nilB is absent from other Xenorhabdus species tested to date, it has ∼18 to 25% full-length sequence similarity (BLASTp) to proteins of unknown function encoded by Neisseria meningitidis, Pasteurella multocida, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis (2, 30). A more recent BLASTX analysis probing the NCBI database (December 2011) revealed additional proteins with 18 to 26% sequence identity to NilB (cutoff E value of 10−5) (see Table S2 in the supplemental material). All BLASTX hits were encoded by harmful or beneficial animal symbionts, including many Neisseria and Actinobacillus spp., and isolates revealed by the Human Microbiome Project. Two species of Psychrobacter, normally found in cold-adapted environments, appear on this list, and both are also host associated. Psychrobacter sp. strain PRwf-1 is found on fish skin and gills and was isolated in Puerto Rico (see http://genome.jgi-psf.org/psy_p/psy_p.home.html); Psychrobacter sp. strain 1510 was isolated from blood as part of the Human Microbiome Project (NCBI accession number AFHU00000000). In the enterobacteriaceae, which are well represented with sequenced isolates, NilB homologs have been identified in only three species: X. nematophila, Salmonella enterica subsp. arizonae, a reptile pathogen, and Edwardsiella tarda, a vertebrate symbiont and fish pathogen.
NilB has not been found in any Xenorhabdus species tested to date other than X. nematophila (17, 30). We also did not observe any Xenorhabdus proteins in our nilB BLASTX analysis. However, we did identify a protein in the X. nematophila genome (14) with sequence similarity to NilB homologs (this protein was identified by reciprocally comparing low-scoring NilB homologs against the X. nematophila genome [cutoff E value of 10−5]). This X. nematophila protein (XNC1_0074, YP_003710424) is found in the same genomic context in X. nematophila, X. bovienii, Photorhabdus luminescens, and Photorhabdus asymbiotica (close relatives of Xenorhabdus spp.) (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material) (12, 26). We distinguish NilB homologs from NilB-like proteins based on their identification by BLASTX: NilB homologs are classified as those retrieved by nilB BLASTX (E value of <10−5; 109 hits); NilB-like proteins are those identified using XNC1_0074 BLASTX (E value of <10−5; 326 hits). There is substantial overlap between these protein groups, since 80 proteins are identified by both nilB and XNC1_0074 BLASTX queries.
NilB is predicted to be an outer membrane protein with 7 or 9 surface-exposed loops and two conserved domains.
Prediction programs indicate that NilB homologs and NilB-like proteins localize to the outer membrane and adopt beta-barrel structures (5, 6, 9) (Fig. 1 and data not shown). The N-terminal 25 amino acids of X. nematophila NilB are predicted to encode a sec secretion signal sequence that is cleaved prior to outer membrane localization (8, 30). Of the online programs available for predicting the structure of beta-barrels, hidden Markov models (HMM) have the highest accuracy (4). Two HMM programs (PROFtmb [9] and B2TMR-HMM [36]) each predict that NilB adopts an outer membrane structure with 14 transmembrane (TM) strands, 7 surface loops (SLs), and a 138- or 140-aa (postcleavage) N-terminal periplasmic domain, respectively (Fig. 1). These structures differ from the model predicted by the HMM program PRED-TMBB (6), which predicts that the 350 C-terminal amino acids of NilB comprise 18 TM strands and 9 SLs and that the N terminus is a 38-aa periplasmic domain (Fig. 1). All three programs predict similar locations for the seven extracellular SLs (Fig. 1), but the PROFtmb and B2TMR-HMM models predict that the two additional SLs in the PRED-TMBB model make up a longer N-terminal periplasmic domain.
The family of NilB/NilB-like proteins shares two conserved domains, neither of which is unique to this family. At least one copy of a 34-aa tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR)-like domain, predicted to fold into two packed α-helices (1, 3, 11), is found within the N-terminal one-third of the proteins. TPR motifs are widely distributed and occur within proteins involved in diverse functions, including transcription, cell cycle control, and protein transport complexes (19). The TPR domain is thought to mediate protein-protein interactions (11). In NilB, a TPR domain was not identified by a TPR prediction program (TPRpred; http://toolkit.tuebingen.mpg.de/tprpred) using standard maximum cutoffs (1e−4), but a single TPR domain (aa 112 to 145) was identified by lowering the stringency of the cutoff value (P value 1.2e−03). Several NilB homologs tested (e.g., those of Aggregatibacter aphrophilus, Actinobacillus minor, and Haemophilus parasuis) had multiple consecutive TPR domains, while some NilB homologs had only a single copy (e.g., that of Mannheimia haemolytica). The X. nematophila NilB-like protein XNC1_0074 contains four consecutive predicted TPR domains (data not shown). The second conserved domain, DUF560/pfam04575 (35), spans the C-terminal two-thirds of NilB homologs, essentially constituting the barrel domain predicted by the 14-TM strand model. This domain of unknown function is present in over 900 proteins, including all NilB homologs evaluated. In some cases, the TPR and DUF560 domains overlap. No structure or function has been assigned to the DUF560 domain.
NilB protein levels are elevated by nilR mutation and nutrient-limiting conditions.
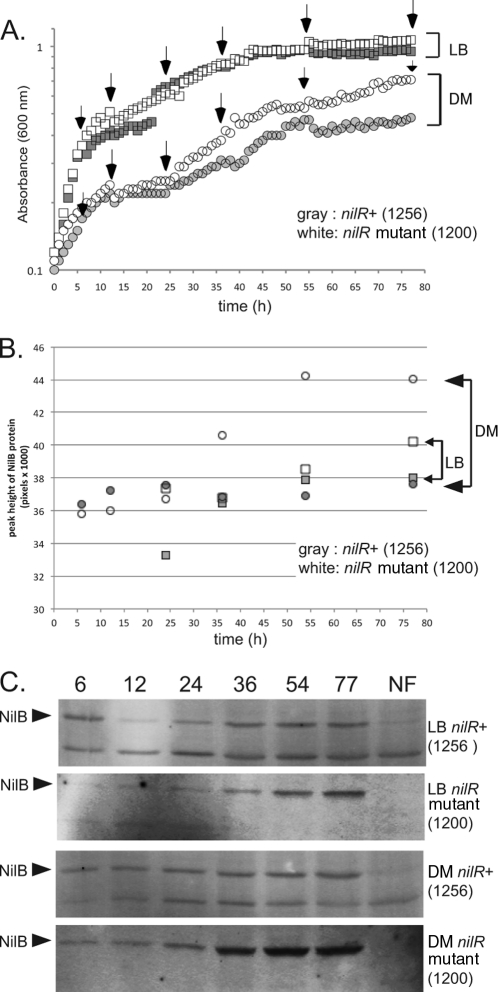
The current working model for Xenorhabdus-Steinernema symbiosis is that nutrient limitation in the insect cadaver is the signal for Xenorhabdus to colonize the nematode intestine. This idea, combined with previous data demonstrating that nilC transcription is upregulated during stationary phase, led us to investigate whether NilB production is also growth phase dependent (15). To monitor NilB protein levels, we attempted to generate polyclonal antibodies against NilB but were unsuccessful. Instead, we engineered a FLAG (DYKDDDDK)-tagged version of NilB, in which the tag amino acids were inserted immediately preceding amino acid 26 (predicted to be the first amino acid in the mature protein after signal sequence cleavage). FLAG-tagged nilB was provided in trans at the att Tn7 site of an X. nematophila strain lacking wild-type nilB. Since under laboratory growth conditions NilR suppresses transcription of the nil genes (16), we also tested NilB production in the presence and absence of nilR. Neither the nilR mutation (16) nor the FLAG insertion in NilB (see below; also, data not shown) negatively affects nematode colonization (i.e., NilB function). To determine the effect of the nilR mutation and growth phase on NilB protein levels, we monitored growth and NilB-FLAG26 levels of nilR+ (HGB1256) and nilR mutant (HGB1200) strains in LB broth and defined medium. nilR+ and nilR mutant strains have similar growth curves in LB. In defined medium, both strains grow similarly until a plateau is reached at ∼25 h (A600 ≈ 0.22), after which nilR mutant cells continue to grow at a higher rate and ultimately reach a higher A600 (∼0.7) than do nilR+ cells (A600, ∼0.5) (Fig. 2A). The difference in the maximum levels of absorbance of the two strains was not due to differences in viability (both strains yielded 1 × 109 CFU/ml at 77 h), differences in absorbance of the culture supernatant, or gross differences in cell size (monitored by microscopy) (data not shown).
Fig 2.
NilB protein expression is highest in stationary phase, repressed by NilR, and elevated by growth in defined medium. (A) Growth curves of X. nematophila nilR+ and nilR mutant strains in defined medium (DM) and LB. White boxes and white circles represent the nilR mutant in LB and defined medium, respectively. Gray boxes and gray circles represent nilR+ in LB and defined medium, respectively. The growth curves of both strains are identical in LB. In defined medium, the curves are similar for the two strains, except that the nilR mutant reaches a higher A600 than the nilR+ strain in stationary phase. (B) Western blots of NilB protein expression. nilR+ and nilR mutant strains were grown in LB or DM as indicated. Crude cell extracts were taken at 6, 12, 24, 36, 54, and 77 h, total protein content was normalized, and samples were loaded onto 12% SDS-PAGE gels for anti-FLAG Western blotting. The arrows indicate NilB, and NF contains extracts from the equivalent X. nematophila strains lacking the FLAG tag. (C) Quantitation of the blots in panel B. White boxes and white circles represent levels of NilB detected in the nilR mutant strain when grown over time in LB and defined medium, respectively. Gray boxes and gray circles represent levels of NilB detected in the nilR+ strain when grown over time in LB and defined medium, respectively. Levels of NilB in LB are similar for the two strains; low levels of NilB are detectable at 6, 12, and 24 h (log phase), and maximal expression is at 54 and 77 h (stationary phase). Levels of NilB in the nilR+ strain grown in defined medium are similar to levels of NilB in LB, except that the amount of NilB expressed is constant over time. Maximum NilB levels are produced in the nilR mutant strain grown in defined medium; low levels of NilB are detectable at 6, 12, and 24 h (log phase), with an increase in expression at 54 and 77 h (stationary phase). Quantitation was done with ImageQuant IQTL 7.0.
At various times during growth in defined medium and LB, crude cell extracts were taken and evaluated for NilB protein production by Western blotting (Fig. 2C). As expected based on previous analyses of nilB-lacZ transcriptional fusions (16), quantification of the Western blot revealed that NilB protein levels were higher in the nilR mutant strain than in the nilR+ strain (Fig. 2B). Maximum levels of NilB production are found in the nilR mutant strain grown in defined medium, with low-but-detectable amounts of NilB produced at 6, 12, and 24 h (log phase), an intermediate amount at 36 h, and maximal amounts at 54 and 77 h (stationary phase) of growth in defined medium. In contrast, the nilR+ strain exhibited low and constant levels of NilB at all time points of growth in defined medium (Fig. 2B and C). In LB medium, NilB levels in both nilR+ and nilR mutant strains increased in stationary phase but never reached the levels observed in the nilR mutant strain during growth in defined medium (Fig. 2B and C). In some samples, another FLAG-reactive band was apparent. This protein is not a variant of NilB, since it is present in the no-FLAG (NF) control (Fig. 2C). The data shown in Fig. 2 indicate that under laboratory growth conditions, NilB levels are highest under stationary-phase and nutrient-limited conditions. Furthermore, NilR negatively impacts NilB levels in all growth phases, perhaps indicating that the signal for NilR derepression is not present in laboratory growth medium. Also, nilB is repressed by other factors (e.g., Lrp [18]) that may contribute to the effects that we observed here.
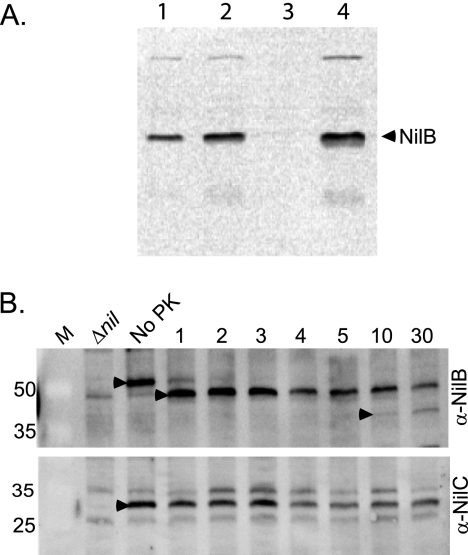
NilB is a surface-exposed outer membrane protein.
To confirm predictions that NilB is localized to the outer membrane, we monitored NilB-FLAG levels in X. nematophila cellular fractions. NilB-FLAG detection by Western blotting was facilitated by preparing extracts from the X. nematophila nilB-FLAG26 strain lacking nilR, which represses nilB transcription (16) and protein levels (Fig. 2). Using anti-FLAG antibody, NilB-FLAG26 (∼53 kDa) was detected in whole cells, crude sonicates, and membrane fractions isolated from X. nematophila but not in soluble, cleared X. nematophila lysates (Fig. 3A), supporting predictions that NilB is localized to the outer membrane and therefore likely adopts a beta-barrel structure (33). To determine if any portion of NilB is surface exposed, we treated whole cells expressing NilB-FLAG26 with proteinase K and then monitored NilB levels over time using anti-FLAG immunoblotting. Levels of full-length NilB-FLAG in whole cells decreased dramatically by 1 min after exposure to proteinase K and were not detectable after 4 min of incubation, indicating that at least some regions of NilB are surface exposed and susceptible to cleavage (Fig. 3B). NilC, which is not sensitive to proteinase K digestion (15), remained detectable over the same time period (Fig. 3B). Both NilB-FLAG and NilC were sensitive to proteinase K digestion in lysed cell extracts (data not shown).
Fig 3.
NilB is a membrane-localized protein and is surface exposed. (A) X. nematophila cells expressing NilB-FLAG26 in a nilR mutant background (HGB1200) were pelleted, resuspended, and sonicated. Soluble and membrane fractions were separated by ultracentrifugation. The crude extract (lane 1), cleared lysate (lane 2), soluble fraction (lane 3), and membrane fraction (lane 4) were electrophoresed on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and transferred to a membrane. NilB protein (arrowhead) was detected using anti-FLAG antibody. (B) Whole X. nematophila nilR mutant cells expressing NilB-FLAG26 (HGB1200) were incubated with 38.4 μg/ml proteinase K (PK) (final concentration) for 1 to 30 min at 37°C. At various time points (indicated in minutes above each lane), samples were removed and reactions were stopped with the addition of 5 mM PMSF (final concentration) and kept on ice. SDS-PAGE loading dye was added to all the reaction mixtures, which were heated at 95°C for 10 min and electrophoresed on 12% SDS-PAGE gels. NilB (top panel) (anti-NilB) or NilC (bottom panel) (anti-NilC) was detected in Western blots using anti-FLAG or anti-NilC (15) antibody, respectively. Full-length NilB-FLAG26 protein (black arrowheads, No PK lanes) was present in the no-proteinase K control but not in cells lacking nilB (Δnil) (HGB1251). This species decreases in intensity after the addition of proteinase K, while smaller-molecular-mass proteins (black arrowheads, lanes 1 and 10) appear. M, Thermo Scientific Pierce prestained protein molecular mass marker (sizes in kDa are noted on the left).
After ∼1 min of incubation with proteinase K, concomitant with the reduction in full-length NilB-FLAG, another band that migrated slightly faster by SDS-PAGE than full-length mature NilB-FLAG appeared (Fig. 3B), and it had an approximate molecular mass of ∼48 kDa. Given that the FLAG tag is encoded at the amino-terminus of the protein, the appearance of these bands is consistent with proteinase K cleavage somewhere in the C-terminal region of the protein. The estimated molecular masses of NilB if it is cleaved in the middle of one of the three SLs at the C-terminal end of the protein are ∼40 (SL5), ∼46 (SL6), and ∼51 (SL7) kDa. Based on this, initial proteinase K cleavage may occur within or near SL6 (aa 387 to 410), the longest predicted surface-exposed loop, which may therefore be particularly susceptible to cleavage. The intensity of the band decreases progressively over time of exposure to proteinase K, while a third band of ∼40 kDa appears by 10 min of incubation with proteinase K, possibly representing another cleavage product (perhaps within SL5).
FLAG tag insertions support a model of NilB with an ∼140-aa periplasmic domain and 7 surface-exposed loops.
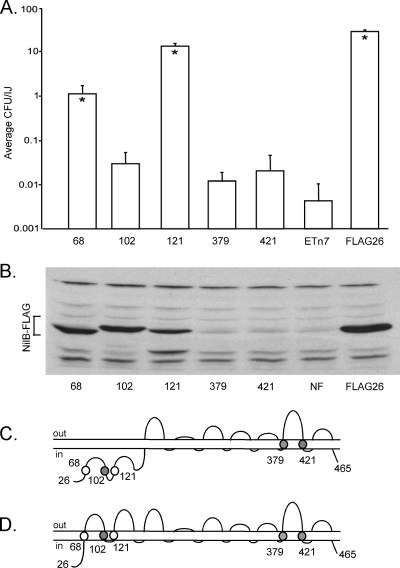
To probe NilB structure and differentiate among bioinformatic topology predictions (Fig. 1), we exploited the fact that insertions within TM strands should destabilize the protein and prevent normal protein localization, while insertions within extracellular or periplasmic domains are more likely to be tolerated (28, 49). Based on HMM models predicted by PRED-TMBB, PROFtmb, and B2TMR-HMM, we created five unique FLAG tag insertion nilB mutants in addition to a nilB-FLAG26 strain to distinguish between the HMM models predicting either 14 (PROFtmb or B2TMR-HMM) or 18 (PRED-TMBB) TM strands (with 7 or 9 SLs, respectively) (Fig. 1).
We inserted FLAG tags into three regions predicted to be transmembrane strands in the 18-strand model but periplasmic strands in the 14-strand model (before aa 68, aa 102, or aa 121). As a control, we also inserted FLAG tags into two domains consistently predicted by all HMM programs to be TMs (before aa 379 and aa 421, flanking SL6). As predicted, X. nematophila expressing NilB FLAG insertions before aa 379 and aa 421 are colonization defective (Fig. 4A) and fail to yield detectable protein (Fig. 4B), indicating that these insertions destabilize the NilB protein. In contrast, X. nematophila carrying NilB-FLAG variants before aa 68 or aa 121 colonize at levels significantly higher than in a strain lacking NilB entirely (Fig. 4A). The difference in colonization phenotype of a strain carrying NilB-FLAG aa102 and a strain lacking nilB entirely was barely significant (P = 0.049) (Fig. 4A) and may indicate that FLAG insertion at aa 102 disrupts NilB function. Regardless, NilB-FLAG protein is detectable in strains expressing NilB-FLAG insertions at aa 68, aa 102, and aa 121 (Fig. 4B), and this is consistent with a periplasmic localization of these domains as predicted in the 14-TM model (Fig. 1 and 4C) but not the 18-TM model (Fig. 4D).
Fig 4.
FLAG tag insertions distinguish whether NilB adopts a predicted 18-TM or 14-TM strand structure. Insertions were made in three N-terminal TM strands (before aa 68, aa 102, and aa 121) predicted only by the 18-TM strand model (D) and in two TM strands predicted by both models (before aa 379 and at aa 421); all mutations were made in nilR mutant cells. The effect of each mutation on nematode colonization (A) and protein production (B) was assessed by nematode sonication and immunoblotting with anti-FLAG, respectively. (A) Insertions before aa 68 or aa 121 reduce nematode colonization below wild-type levels but not to the level observed when nilB is absent (ETn7). Insertions before aa 102, aa 379, and aa 421 cause severe nematode colonization defects. *, P < 0.01, relative to ETn7 values (except with the aa 102 strain, for which P was 0.049). IJ, infective juvenile. (B) When FLAG insertions are in TM strands predicted only by the 18-TM strand model, NilB protein is detectable in whole cells by anti-FLAG Western blotting, but when insertions are in TM strands predicted by both models, NilB is not detectable. (C and D) Schematic of NilB's structure and the relative positions of FLAG tag insertions in the 14-TM (C) and 18-TM (D) strand models. Circles indicate that an insertion mutant colonized better than (white circles) or similarly to (shaded circles) a strain that lacked SR1. NF, Tn7/SR1 without a FLAG26 insertion in NilB; ETn7, Tn7 lacking SR1; FLAG26, Tn7/SR1 with a FLAG26 insertion in NilB (no deletions).
Colonization function of nilB insertion mutants.
We next used FLAG tag insertions to assess which regions of NilB are necessary for colonization, as well as for further verification of the 14-TM strand model shown in Fig. 1, relative to other possible topologies predicted by non-HMM algorithms (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). To this end, we created 10 insertions at regions of NilB predicted to be periplasmic or surface exposed (Fig. 5C) in the 14-TM model (before aa 85, 137, 186, 233, 273, 322, 357, 399, 451, and 466), and at least one of which is within a predicted TM domain in all of the other models that we identified by various prediction programs (Fig. S2).
Fig 5.
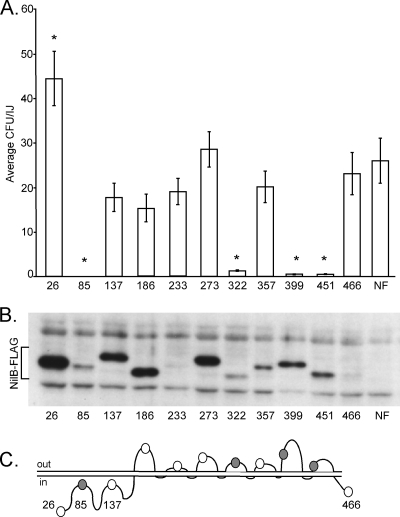
Identification of NilB regions necessary for colonization. FLAG tags were inserted into predicted NilB surface loops, the predicted N-terminal periplasmic domain, and the C terminus. The numbers indicate the amino acid locations of the tag; for example, 26 indicates that the FLAG tag is directly before (N-terminal to) amino acid 26 (Fig. 1). Mutants were made in nilR mutant backgrounds. (A) X. nematophila NilB-FLAG mutants were assessed for S. carpocapsae nematode colonization. Asterisks indicate colonization levels significantly different (P < 0.05) from that of X. nematophila expressing NilB without the FLAG tag (NF). (B) NilB protein production by the NilB-FLAG mutants was assayed on whole cells by Western blotting with anti-FLAG antibody. The abundances and SDS-PAGE migrations of the NilB-FLAG proteins (bracket) are varied. (C) Schematic of NilB structure, including predicted locations of FLAG tag insertions in the 14-TM strand model (Fig. 1). Shaded circles represent insertions that abolished or attenuated nematode colonization, while white circles represent insertions that do not significantly affect colonization.
Nematode colonization phenotypes varied among the insertion mutants. The insertion at aa 84 in the predicted periplasmic domain completely abolishes colonization, measured as the average number of CFU/infective juvenile determined by nematode sonication and dilution plating (Fig. 5A). Colonization by strains carrying insertions at aa 322 (SL4), aa 399 (SL6), and aa 451 (SL7) was detectable but significantly attenuated relative to that by a non-FLAG-tagged wild-type strain, while strains carrying insertions at aa 137, 186, 233, 273, 357, and 466 colonized at levels not significantly different from that of the wild-type nilB control (Fig. 5A). To determine if the colonization defects of the insertion mutants are due to a lack of NilB protein production, Western blotting with anti-FLAG antibody was performed on whole-cell extracts from all mutants. NilB protein was detected at various amounts and levels of mobility in X. nematophila strains expressing each nilB variant. The amount of NilB produced during laboratory growth did not correlate with nematode colonization, since two strains with barely detectable levels of NilB (those with FLAG inserted before aa 233 and aa 466) displayed colonization proficiency (Fig. 5B). The migration distance of each mutant protein also did not correlate with colonization proficiency or deficiency. For example, NilB proteins with insertions at aa 137 and 186 migrated differently than NilB protein with an insertion at aa 26, but both strains carrying these nilB variants colonized the nematode receptacle at levels not different from that of the wild type. The cause of variability in NilB protein mobility is unknown, but a similar phenomenon has been reported previously in some insertion (including FLAG tag) mutagenesis studies (28, 49) but not others (40). In studies where migration variability was observed, differences were attributed to heat-modifiable stability (27). NilB-FLAG mutants were analyzed for heat modifiability by either boiling crude extracts for 15 min at 97°C or not boiling them; samples were then electrophoresed by SDS-PAGE in a 4°C cold room and Western blotted. No heat-dependent changes in mobility were observed (data not shown). Alternatively, insertion mutants may display differential detergent binding as a reflection of variable protein-lipid or intraprotein interactions (46). When we tested if the protein migration differences were due to variable NilB glycosylation, results showed that in glycoprotein stains of whole-cell X. nematophila extracts, no X. nematophila proteins were found to be glycosylated (data not shown). Despite mobility differences, the presence of NilB protein in the colonization-defective strains with a FLAG insertion before aa 85, aa 322, aa 399, and aa 451 supports the conclusion that these regions are critical for the function of NilB.
nilB mutants are defective in the entry stage of nematode colonization.
To gain further insight into the effect of nilB-FLAG mutations on nematode colonization, we assessed nematode colonization phenotypes in vivo using GFP-expressing nilB-FLAG mutants and epifluorescence microscopy. We expected that partial-colonization mutants would fall into one of two classes: outgrowth mutants, with nearly all nematodes carrying one or a few bacteria in each receptacle, or entry or persistence mutants, with a mixture of nematodes with fully colonized or completely empty receptacles. We chose FLAG tag insertion constructs that cause normal to high (with FLAG before aa 26 and aa 273), low (with FLAG before aa 322 and aa 399), and intermediate (with FLAG before aa 186) levels of colonization and incorporated them into the att Tn7 site of a GFP-expressing ΔSR1 strain (HGB1430). The percentage of nematodes within each population where the GFP-labeled bacteria were observed in the receptacle was determined. An oligo-colonization phenotype, in which a receptacle contained one or a few bacterial cells (29, 38), was not observed for any of the 5 NilB FLAG tag mutants tested in this experiment (data not shown). Further, nematode receptacles qualitatively appeared to be full of bacteria or were empty (e.g., Fig. 6A), suggesting that these nilB mutations affect entry, not outgrowth. This idea was further addressed by quantifying the average bacterial load per nematode through surface sterilization and sonication of 10,000 nematodes. Sonication (average bacterial load) and microscopy (colonization frequency) data are presented normalized against a strain carrying wild-type nilB without a FLAG insertion (Table 3). Fold differences reveal good correlation between the outputs of the two tests, suggesting that bacteria that gained access to the receptacle fully colonized it and that the colonization defect of a nilB mutant occurs prior to its gaining access to the receptacle. This finding was not necessarily expected, since a similar comparison of sonication and microscopy data for a nilA mutant revealed a >25-fold difference between nematode colonization frequency (65% of nematodes) and bacterial load (2.5% of wild-type cells) (17). Thus, the partial colonization defects observed for nilA and nilB mutants are distinct. These findings raise the possibility that the nil genes, which are together sufficient for nematode colonization, may act at distinct stages of nematode colonization.
Fig 6.
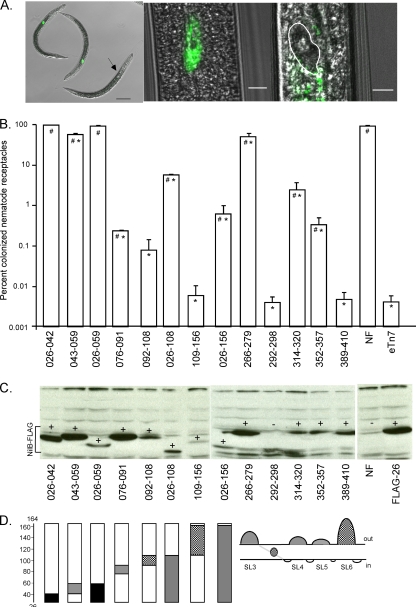
In-frame amino acid deletions identify structurally and functionally required domains of NilB. (A) Partial nematode colonization mutants fully colonize few nematodes instead of partially colonizing many nematodes in the population. Representative images of nematodes grown on colonization mutants are shown. Images from left to right are as follows: a 40× magnification of 2 colonized (HGB1502) nematodes (the green dot is an epifluorescent overlay) and 1 uncolonized nematode (the black arrow points to the location of an empty receptacle), a zoomed image of a colonized nematode (HGB1502) with an epifluorescent overlay on a DIC image, and a zoomed image of an uncolonized nematode (HGB1429) with an epifluorescent overlay on a DIC image, with the empty nematode receptacle highlighted (white outlining). Scale bars from left to right: 50 μm, 5 μm, and 5 μm. (B) Small regions in the N-terminal periplasmic domain were individually sequentially deleted (Δ026–042, Δ043–059, Δ076–091, Δ092–108, Δ109–156), along with larger regions of this domain (Δ026–059, Δ026–108, Δ026–156). Amino acids were also deleted from SL3, SL4, SL5, or SL6, as well as a region within the predicted TM domain between SL3 and SL4 (as a negative control). Each of these deletions was created in the plasmid pTn7/SR1/nilB-FLAG26, and Tn7 integration at the att Tn7 site of GFP-expressing X. nematophila ATCC 19061 ΔSR1 ΔnilR was confirmed. (A) Nematode colonization of each deletion mutant assessed by microscopy. P was <0.05 for differences from values for the negative control (eTn7) (#) or positive control (NF) (*). Strain eTn7 lacks nilB, while NF contains nilB but no FLAG tag. (C) NilB-FLAG proteins of various abundances and mobilities are produced in whole cells by all deletion mutants except that lacking aa 292 to 298. + indicates detectable NilB, and − indicates no detectable NilB protein. NF contains nilB but no FLAG tag. FLAG26 contains the FLAG tag before aa 26 of nilB. (D) Schematics of NilB structures and deletions. The bars represent the N-terminal periplasmic domain from aa 26 to 164. The length of the shaded area represents the size of the deletion. The color of the shading represents the effect of the deletion on nematode colonization; black indicates no effect relative to that of the wild type, gray indicates an effect intermediate between those of the wild type and the negative control (no NilB), and the cross-hatched shading indicates no significant difference from the effect of the negative control.
Table 3.
Fold change in two independent experiments between bacterial load and nematode colonization frequency of nilB-FLAG insertion mutants
| FLAG insertion | Expt 1 |
Expt 2 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative bacterial load (%)a | Relative frequency (%)b | Fold differencec | Relative bacterial load (%) | Relative frequency (%) | Fold difference | |
| aa 26 | 55.882 | 89.490 | 1.60 | 119.156 | 102.007 | 1.17 |
| aa 186 | 52.574 | 52.352 | 1.00 | 61.039 | 49.763 | 1.23 |
| aa 273 | 106.985 | 96.734 | 1.11 | 99.675 | 91.455 | 1.09 |
| aa 322 | 32.279 | 25.762 | 1.25 | 60.390 | 38.542 | 1.57 |
| aa 399 | 1.397 | 0.960 | 1.46 | 4.789 | 4.721 | 1.01 |
| eTn7 | 0.042 | 0.015 | 2.86 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 1.00 |
| None | 100.000 | 100.000 | 1.00 | 100.000 | 100.000 | 1.00 |
Bacterial load was assessed by sonication of 10,000 nematodes and dilution plating to determine bacterial counts. Data are presented as percentages of the value for cells expressing wild-type nilB with no FLAG insertion.
Nematode colonization frequency was assessed by epifluorescence microscopy of nematodes grown on GFP-expressing bacteria. Data are presented as percentages of the value for cells expressing wild-type nilB with no FLAG insertion.
Fold difference represents the ratio of relative colonization frequency to relative bacterial load. A ratio of 1 indicates that the colonization defect of the strain is explained by a reduced frequency of colonization (e.g., initiation). A ratio of greater than 1 indicates that a defect in outgrowth contributes to observed defects in bacterial load.
Colonization function of nilB deletion mutants.
NilB surface-exposed loops and portions of the predicted N-terminal periplasmic domain (Fig. 6D) were deleted to further assess the importance of these regions in nematode colonization. Since microscopic analysis gave greater sensitivity and smaller errors between replicates than sonication assays, and results were generally similar to those derived from sonication assays (Table 3), deletion constructs were introduced into a GFP-expressing X. nematophila background and colonization was assessed by epifluorescence microscopy. In each of these deletion mutants, nematode receptacles appeared to be empty or fully colonized, consistent with our previous observations. Deletions in SL4 (of aa 314 to 320), SL5 (aa 352 to 357), and SL6 (aa 389 to 410) had significant negative yet variable effects on nematode colonization (Fig. 6B), and deleting SL6 caused the most severe colonization deficiency (equivalent to a strain lacking nilB entirely). The finding that the SL3 (aa 266 to 279) deletion strain colonized greater than 50% of the nematodes in the population emphasizes that some extracellular domains play a more significant role in colonization than others.
Some regions of the predicted N-terminal globular domain (aa 26 to 156) are also important for nematode colonization (Fig. 6B). Strains carrying deletions of aa 92 to 108 or aa 109 to 156 (the latter encompassing the predicted TPR domain) reduce colonization to levels equivalent to that of a strain lacking nilB, whereas deletions of aa 76 to 91, 26 to 108, and 26 to 156 have a milder, yet significant, colonization defect. In contrast, deleting aa 26 to 42 and aa 26 to 59 does not reduce colonization levels, and deleting aa 43 to 59 has only a mildly deleterious effect on nematode colonization frequency.
Although NilB protein levels and mobilities on SDS-PAGE gels vary for the different deletion mutants, the migration differences correlate with the expected size change due to deletion of residues (Fig. 6C). NilB is detectable for every deletion mutant except that with a deletion of aa 292 to 298, consistent with the prediction that these amino acids form a TM domain. As seen with the FLAG insertion mutants, colonization levels do not correlate with NilB protein levels. For example, NilB is relatively abundant in the colonization-defective ΔSL6 strain (deletion of aa 389 to 410), in the colonization-defective strain with a deletion of aa 76 to 91, and in the colonization-proficient strain with a deletion of aa 26 to 42 but not in the colonization-proficient strain with a deletion of aa 26 to 59. Therefore, low protein levels likely do not fully explain the colonization defects of deletion mutants.
DISCUSSION
We have shown that NilB is a surface-exposed protein that is poorly expressed under laboratory growth conditions. When nilB expression is derepressed by deletion of nilR, NilB protein levels are highest under nutrient-limiting conditions (e.g., in defined medium and/or stationary phase) (Fig. 2), indicating that NilB expression responds to nutrient conditions independently of NilR. Because of this, we predict that, during nematode colonization, NilB expression is triggered by multiple signals, both NilR dependent and NilR independent. Since under laboratory growth conditions NilR-dependent repression occurred regardless of growth phase or medium, we suggest that the signal necessary for NilR derepression is absent under these conditions and may be specific to the nematode host. Analysis of the colonization phenotypes of nilB mutant alleles revealed that NilB functions at the stage of entry into the nematode receptacle, rather than during later stages of growth and persistence, indicating that the signals necessary for NilB expression likely are present at the very early stages of colonization.
Our analysis of nilB mutants supports the model that NilB adopts a 14-TM beta-barrel structure, based on the premise that insertions within, or deletions of, TM domains prevent proper localization and lead to protein degradation, while insertions or deletions in other regions (e.g., those that are surface exposed) are generally tolerated (23, 49). Insertions or deletions that prevented detection of NilB protein were in TM strands (aa 292 to 298, 379, and 421) predicted by the 14-TM model. In contrast, NilB protein was detectable in mutants with insertions or deletions in regions predicted to be TM in an 18-TM model but periplasmic in a 14-TM model (aa 68, 92 to 108, 102, 109 to 156, and 121). We also show that NilB is membrane localized and has surface-exposed regions, based on its sensitivity to proteinase K digestion in whole cells (Fig. 3). The appearance of truncated, large-molecular-weight FLAG-reactive proteins after proteinase K digestion is consistent with cleavage of the C-terminal but not the N-terminal (antibody-reactive) domain (Fig. 3), supporting the bioinformatically predicted location of the N terminus in the periplasm. Taken together, these data support a protein structure prediction model where NilB has 7 SLs (SL1 to -7) and an ∼140-aa N-terminal periplasmic domain. Below we discuss how these results provide insight into possible mechanisms of NilB function in colonization.
We identified several connections between NilB function and nutrient availability/transport through our studies on NilB expression, genomic context, and predicted topology. As discussed above, NilB expression is elevated by nutrient limitation during laboratory growth. Further, pathogens such as Mannheimia haemolytica and Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, which derive iron from host-specific transferrin, lactoferrin, or hemoglobin molecules (51), encode NilB homologs near iron binding (YP_002173032) or host transferrin utilization (ZP_04464085) genes, respectively. This genomic context suggests that NilB homologs, and perhaps NilB, may also function in nutrient acquisition. Finally, our data suggest that NilB is a 14-TM beta-barrel protein with a large periplasmic N-terminal domain. In many beta-barrel proteins, large periplasmic domains function as plugs that help control beta-barrel pore permeability. For example, such topology is typical of small-molecule transporters (47, 53, 57) that depend on the inner membrane protein TonB to provide the energy for nutrient transport (e.g., iron, vitamin B12) (31). TonB-dependent transporters include transferrin receptors (31), such as those encoded near nilB homologs. At first glance, NilB seems unlikely to be a TonB-dependent protein since it lacks a canonical TonB box, since most TonB-dependent transporters are 22-TM domain proteins, and since an X. nematophila tonB mutant does not have a colonization defect (38). However, TonB box identities are varied among TonB-dependent transporters (34), and the X. nematophila genome encodes two additional TonB-like genes (13), one of which is oriented in tandem with the NilB-like protein XNC1_0074 (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). Taken together, the links between NilB and TonB detailed above are consistent with a role for NilB in nutrient transport. However, our data do not exclude the possibility of an adhesin function for NilB, and adhesion and nutrient acquisition models are not mutually exclusive.
Our work has revealed several critical regions of NilB necessary for its function in nematode colonization, including SL6 and the N-terminal TPR-like domain. Deletion of SL6 reduced nematode colonization to levels observed when nilB was absent, but this reduction in nematode colonization is not a result of NilB instability since NilB is detected in Western blots of both whole-cell lysates (Fig. 5B and 6C) and membrane preparations (data not shown). SL6 (28 residues) is the longest SL in NilB (9 residues longer than the next longest, SL1), and in a full-length alignment of all NilB homologs, NilB has more residues at SL6 than any other NilB homolog (data not shown). The longer length of SL6 in NilB than in NilB homologs may indicate the importance of SL6 residues in the specificity of NilB in S. carpocapsae association. Various functions could be envisioned for this region, including directly binding to host surfaces or molecules. For example, in beta-barrel transporters, surface loops act by trapping and directing transport of specific molecules through the pore and/or occluding foreign molecules during transport as part of a molecular airlock system (see, e.g., references 20 and 45).
Deletion of the TPR-like domain (Δ109–156) caused a colonization defect that could be ameliorated by concomitant deletion of aa 26 to 108 (in Fig. 6B, compare infective juvenile colonization of the Δ109–156 mutant [∼0.008% of nematodes] versus that of the Δ26–156 mutant [0.8%]). Such a result could be explained if the NilB periplasmic domain acts as a plug whose “open” and “closed” states, or some other pore modification, are regulated within the TPR region. Deletion of the domain necessary to transition to the “open” state would effectively block the pore and prevent transport, whereas deletion of the entire plug might result in a constitutively leaky pore that could function, albeit less efficiently than wild-type NilB, in colonization. Alternatively, the TPR-like domain may interact with other regions of the protein (e.g., a pore) to impact the structure and function of surface-exposed loops that may be necessary for adhesion, while deletion of additional residues of the N-terminal domain may allow NilB to adopt a more wild-type structure. Regardless, our data suggest that the TPR-like domain is critical for NilB function, possibly due to its role in mediating protein-protein interactions. In this regard, it will be of interest to determine if NilB interacts with other proteins and if such interactions depend on the TPR-like domain. NilC, an outer membrane, periplasmically oriented lipoprotein (15), is an obvious candidate for a NilB-interacting protein since it is encoded on the same genetic locus as NilB (30), is repressed by NilR (16), and is a species specificity factor for S. carpocapsae nematodes (17).
Although, based on our data, we are unable to definitively conclude that NilB functions as a transporter or an adhesin, either model warrants some speculation regarding the identity of its substrate and whether this molecule is specific to S. carpocapsae. NilB is a specificity determinant, and S. carpocapsae nematodes are colonized only by Xenorhabdus species that express nilB (17). Since no defects in nilB mutant growth, secondary metabolism, or other aspects of physiology have been observed in nilR+ cells during laboratory culture (30), including testing with the full panel of Biolog metabolic phenotype arrays (PM1 to PM10; Biolog) (data not shown), NilB may be involved in the metabolism of a nutrient or molecule that is absent under laboratory conditions. Alternatively, NilR repression of NilB under these conditions may preclude identification of NilB-dependent phenotypes. Therefore, further investigations of NilB-dependent laboratory growth phenotypes in a nilR mutant background are warranted. However, intriguing hypotheses are that NilB is necessary to transport a host-specific nutrient or adhere to a host-specific molecule and that NilR derepression occurs only in the presence of this molecule to prevent inappropriate expression of NilB (e.g., in the insect host, where it may be immunogenic).
We previously suggested (13, 17) that species specificity in Xenorhabdus does not follow the paradigm of host range specificity in the well-studied leguminous plant-Rhizobium symbioses. In these symbioses, each rhizobium species produces a common signaling molecule, the nod factor, and specificity is determined by modifications of the core nod factor molecule (24). In contrast, the host range specificity determinant NilB is lacking from other Xenorhabdus species, suggesting that it is a novel, derived trait that determines specificity in this bacterium. However, this idea is challenged by the results presented here. Structural predictions of NilB-like proteins, including one in X. bovienii, reveal similar topologies despite relatively low amino acid sequence similarity (∼18 to 25%), raising the possibility that NilB-like proteins with structural (and perhaps functional) similarity are produced by other Xenorhabdus species, but they have insufficiently low coding sequence identity to be identified by PCR (30), Southern hybridization (17; J. Chaston and H. Goodrich-Blair, unpublished data), or genome sequencing (14). Therefore, NilB-like proteins may play similar roles among all Xenorhabdus species in mediating host interactions and specificity, with NilB representing a highly diverged, horizontally acquired (17) member of this family. Subtle differences in surface-exposed loops (e.g., SL6) may determine specificity, much like nod factor modifications. Future studies that determine the mechanism of action of NilB and species specificity factors in other Xenorhabdus spp. will help test if the paradigm of specificity determined by “variations on a common theme” pertains to Xenorhabdus-nematode interactions.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by grants awarded to H.G.-B. from the National Science Foundation (NSF) (IOS-0950873) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (GM059776). J.M.C. was supported by NIH National Research Service Award T32 (grant AI55397, Microbes in Health and Disease) and an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship. A.B. was supported by NIH grant F32 GM072342.
We are grateful to Tom Silhavy for helpful discussions and to anonymous reviewers, whose comments significantly improved the manuscript. We are also grateful to Aaron Andersen for technical support and Xinxin Yu and Yang Zhao in the CALS statistical consulting service (UW—Madison) for assistance with choosing and applying statistical models.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 27 January 2012
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://jb.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1. Abe Y, et al. 2000. Structural basis of presequence recognition by the mitochondrial protein import receptor Tom20. Cell 100: 551–560 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Altschul SF, et al. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25: 3389–3402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Andrade MA, Perez-Iratxeta C, Ponting CP. 2001. Protein repeats: structures, functions, and evolution. J. Struct. Biol. 134: 117–131 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bagos PG, Liakopoulos TD, Hamodrakas SJ. 2005. Evaluation of methods for predicting the topology of beta-barrel outer membrane proteins and a consensus prediction method. BMC Bioinformatics 6: 7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Bagos PG, Liakopoulos TD, Spyropoulos IC, Hamodrakas SJ. 2004. A hidden Markov model method, capable of predicting and discriminating beta-barrel outer membrane proteins. BMC Bioinformatics 5: 29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Bagos PG, Liakopoulos TD, Spyropoulos IC, Hamodrakas SJ. 2004. PRED-TMBB: a web server for predicting the topology of beta-barrel outer membrane proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 32: W400–W404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Bao Y, Lies DP, Fu H, Roberts GP. 1991. An improved Tn7-based system for the single-copy insertion of cloned genes into chromosomes of Gram-negative bacteria. Gene 109: 167–168 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. 2004. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 340: 783–795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Bigelow HR, Petrey DS, Liu J, Przybylski D, Rost B. 2004. Predicting transmembrane beta-barrels in proteomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 32: 2566–2577 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Bird AF, Akhurst RJ. 1983. The nature of the intestinal vesicle in nematodes of the family Steinernematidae. Int. J. Parasitol. 13: 599–606 [Google Scholar]
- 11. Blatch GL, Lassle M. 1999. The tetratricopeptide repeat: a structural motif mediating protein-protein interactions. Bioessays 21: 932–939 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Boemare NE, Akhurst RJ, Mourant RG. 1993. DNA relatedness between Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae), symbiotic bacteria of entomopathogenic nematodes, and a proposal to transfer Xenorhabdus luminescens to a new genus, Photorhabdus, gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 43: 249–255 [Google Scholar]
- 13. Chaston J, Goodrich-Blair H. 2010. Common trends in mutualism revealed by model associations between invertebrates and bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 34: 41–58 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Chaston JM, et al. 2011. The entomopathogenic bacterial endosymbionts Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus: convergent lifestyles from divergent genomes. PLoS One 6: e27909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Cowles CE, Goodrich-Blair H. 2004. Characterization of a lipoprotein, NilC, required by Xenorhabdus nematophila for mutualism with its nematode host. Mol. Microbiol. 54: 464–477 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Cowles CE, Goodrich-Blair H. 2006. nilR is necessary for co-ordinate repression of Xenorhabdus nematophila mutualism genes. Mol. Microbiol. 62: 760–771 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Cowles CE, Goodrich-Blair H. 2008. The Xenorhabdus nematophila nilABC genes confer the ability of Xenorhabdus spp. to colonize Steinernema carpocapsae nematodes. J. Bacteriol. 190: 4121–4128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Cowles KN, Cowles CE, Richards GR, Martens EC, Goodrich-Blair H. 2007. The global regulator Lrp contributes to mutualism, pathogenesis and phenotypic variation in the bacterium Xenorhabdus nematophila. Cell. Microbiol. 9: 1311–1323 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. D'Andrea LD, Regan L. 2003. TPR proteins: the versatile helix. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28: 655–662 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Ferguson AD, et al. 2002. Structural basis of gating by the outer membrane transporter FecA. Science 295: 1715–1719 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Flores-Lara Y, Renneckar D, Forst S, Goodrich-Blair H, Stock P. 2007. Influence of nematode age and culture conditions on morphological and physiological parameters in the bacterial vesicle of Steinernema carpocapsae (Nematoda: Steinernematidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 95: 110–118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Forst S, Dowds B, Boemare N, Stackebrandt E. 1997. Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus spp.: bugs that kill bugs. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 51: 47–72 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Freudl R. 1989. Insertion of peptides into cell-surface-exposed areas of the Escherichia coli OmpA protein does not interfere with export and membrane assembly. Gene 82: 229–236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Garg N, Geetanjali 2007. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation in legume nodules: process and signaling. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 27: 59–68 [Google Scholar]
- 25. Goetsch M, Owen H, Goldman B, Forst S. 2006. Analysis of the PixA inclusion body protein of Xenorhabdus nematophila. J. Bacteriol. 188: 2706–2710 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Goodrich-Blair H, Clarke DJ. 2007. Mutualism and pathogenesis in Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus: two roads to the same destination. Mol. Microbiol. 64: 260–268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Hancock RE, Carey AM. 1979. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat-2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J. Bacteriol. 140: 902–910 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Hay ID, Rehman ZU, Rehm BH. 2010. Membrane topology of outer membrane protein AlgE, which is required for alginate production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76: 1806–1812 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Herbert Tran EE, Andersen AW, Goodrich-Blair H. 2009. CpxRA influences Xenorhabdus nematophila colonization initiation and outgrowth in Steinernema carpocapsae nematodes through regulation of the nil locus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75: 4007–4014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Heungens K, Cowles CE, Goodrich-Blair H. 2002. Identification of Xenorhabdus nematophila genes required for mutualistic colonization of Steinernema carpocapsae nematodes. Mol. Microbiol. 45: 1337–1353 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Jarosik GP, Maciver I, Hansen EJ. 1995. Utilization of transferrin-bound iron by Haemophilus influenzae requires an intact tonB gene. Infect. Immun. 63: 710–713 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Kaya HK, Gaugler R. 1993. Entomopathogenic nematodes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 38: 181–206 [Google Scholar]
- 33. Knowles TJ, Scott-Tucker A, Overduin M, Henderson IR. 2009. Membrane protein architects: the role of the BAM complex in outer membrane protein assembly. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7: 206–214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Krewulak KD, Vogel HJ. 2011. TonB or not TonB: is that the question? Biochem. Cell Biol. 89: 87–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Marchler-Bauer A, et al. 2007. CDD: a conserved domain database for interactive domain family analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 35: D237–D240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Martelli PL, Fariselli P, Krogh A, Casadio R. 2002. A sequence-profile-based HMM for predicting and discriminating beta barrel membrane proteins. Bioinformatics 18(Suppl 1): S46–S53 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Martens EC, Heungens K, Goodrich-Blair H. 2003. Early colonization events in the mutualistic association between Steinernema carpocapsae nematodes and Xenorhabdus nematophila bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 185: 3147–3154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Martens EC, Russell FM, Goodrich-Blair H. 2005. Analysis of Xenorhabdus nematophila metabolic mutants yields insight into stages of Steinernema carpocapsae nematode intestinal colonization. Mol. Microbiol. 51: 28–45 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Morgan JAW, Kuntzelmann V, Tavernor S, Ousley MA, Winstanley C. 1997. Survival of Xenorhabdus nematophilus and Photorhabdus luminescens in water and soil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 83: 665–670 [Google Scholar]
- 40. Nguyen KA, et al. 2009. Verification of a topology model of PorT as an integral outer-membrane protein in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Microbiology 155: 328–337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Orchard SS, Goodrich-Blair H. 2004. Identification and functional characterization of a Xenorhabdus nematophila oligopeptide permease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70: 5621–5627 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Poinar GO. 1966. The presence of Achromobacter nematophilus in the infective stage of a Neoaplectana sp. (Steinernematidae: Nematoda). Nematologica 12: 105–108 [Google Scholar]
- 43. Poinar GO., Jr 1979. Nematodes for biological control of insects. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL [Google Scholar]
- 44. Poinar GO, Jr, Thomas GM. 1967. The nature of Achromobacter nematophilus as an insect pathogen. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 9: 510–514 [Google Scholar]
- 45. Postle K, Kadner RJ. 2003. Touch and go: tying TonB to transport. Mol. Microbiol. 49: 869–882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Rath A, Glibowicka M, Nadeau VG, Chen G, Deber CM. 2009. Detergent binding explains anomalous SDS-PAGE migration of membrane proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106: 1760–1765 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Ratledge C, Dover LG. 2000. Iron metabolism in pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 54: 881–941 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. R Development Core Team 2006. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria [Google Scholar]
- 49. Rehm BH, Hancock RE. 1996. Membrane topology of the outer membrane protein OprH from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: PCR-mediated site-directed insertion and deletion mutagenesis. J. Bacteriol. 178: 3346–3349 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Richards GR, Goodrich-Blair H. 2009. Masters of conquest and pillage: Xenorhabdus nematophila global regulators control transitions from virulence to nutrient acquisition. Cell. Microbiol. 11: 1025–1033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Schryvers AB, Gonzalez GC. 1990. Receptors for transferrin in pathogenic bacteria are specific for the host's protein. Can. J. Microbiol. 36: 145–147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Stabb EV, Ruby EG. 2002. RP4-based plasmids for conjugation between Escherichia coli and members of the Vibrionaceae. Methods Enzymol. 358: 413–426 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Usher KC, Özkan E, Gardner KH, Deisenhofer J. 2001. The plug domain of FepA, a TonB-dependent transport protein from Escherichia coli, binds its siderophore in the absence of the transmembrane barrel domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98: 10676–10681 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Vivas EI, Goodrich-Blair H. 2001. Xenorhabdus nematophilus as a model for host-bacterium interactions: rpoS is necessary for mutualism with nematodes. J. Bacteriol. 183: 4687–4693 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Volgyi A, Fodor A, Szentirmai A, Forst S. 1998. Phase variation in Xenorhabdus nematophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 1188–1193 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. White GF. 1927. A method for obtaining infective nematode larvae from cultures. Science 66: 302–303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Wiener MC. 2005. TonB-dependent outer membrane transport: going for Baroque? Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 15: 394–400 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Wouts WM. 1980. Biology, life cycle, and redescription of Neoaplectana bibionis Bovien, 1937 Nematoda: Steinernematidae. J. Nematol. 12: 62–72 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.