Abstract
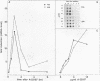
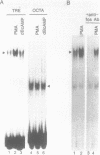
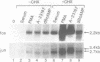
The nuclear oncoproteins fos and jun are associated as a heterodimer which binds to TPA (PMA or TPA: phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate)- responsive promoter elements (TRE), the recognition site for the transcription factor AP-1. The fos/jun heterodimer has a higher affinity to the TRE and stimulates transcription of responsive genes more than the jun homodimer. The association of these two oncoproteins may play a central role in signal transduction and regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. We further defined the regulation of fos and jun by studying their inducibility by second messengers in cells of hematopoietic origin. In THP-1 monocytic leukemia cells fos and jun mRNA levels are regulated in a coupled manner by second messengers activated after membrane phospholipid turnover. Addition of phospholipase C to cells, as well as stimulation of protein kinase C and release of intracellular Ca2+, caused a rapid induction of fos and jun mRNA levels, but the induction of jun mRNA showed a more persistant and less transient pattern than fos. In contrast to the phosphoinositol system, stimulation of the adenylate cyclase pathway in THP-1 cells induced only fos transcription whereas jun mRNA levels remained unchanged. A similar uncoupling of fos and jun inducibility was found after phorbol ester addition to the human erythroleukemia cell line HEL and the human promyelocytic cell line HL-60. The uncoupling of fos and jun levels might predispose cells to the formation of combinatorial transcription complexes of a different composition and activity than the fos/jun heterodimer. Indeed, nuclear extracts from THP-1 cells before or after activation of the phosphinositol or adenylate cyclase second messenger pathways revealed a correlation in fos and jun expression and specific binding of the heterocomplex to a TRE sequence.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J. H., Chait A., Deeb S. S. Regulation of the low density lipoprotein receptor and hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase genes by protein kinase C and a putative negative regulatory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1133–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J. H., Deeb S., Brunzell J. D., Peng R., Chait A. Transcriptional activation of the lipoprotein lipase and apolipoprotein E genes accompanies differentiation in some human macrophage-like cell lines. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2651–2655. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel D. P., Sheng M., Lau L. F., Greenberg M. E. Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):304–313. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Viral oncogenes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Neuberg M., Burckhardt J., Almendral J., Wallich R., Müller R. Involvement of common and cell type-specific pathways in c-fos gene control: stable induction of cAMP in macrophages. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. A., O'Hara M., Angel P., Chojkier M., Karin M. Prolonged activation of jun and collagenase genes by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):661–663. doi: 10.1038/337661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B. Dissociation of c-fos induction from macrophage differentiation in human myeloid leukemic cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):769–774. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Newell M. K., Justement L. B., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Chen Z. Z. Ia binding ligands and cAMP stimulate nuclear translocation of PKC in B lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):629–632. doi: 10.1038/327629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins are complexed with a 39,000-dalton cellular protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., McGuire M., Buckmire M., Lee W. M. Involvement of the 'leucine zipper' region in the oligomerization and transforming activity of human c-myc protein. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):664–666. doi: 10.1038/337664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Ro H. S., Rosen B. S., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleoprotein complexes that regulate gene expression in adipocyte differentiation: direct participation of c-fos. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Josephs S. F., Curran T. The Fos complex and Fos-related antigens recognize sequence elements that contain AP-1 binding sites. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1150–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.2964084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. G., Crothers D. M. CAP and RNA polymerase interactions with the lac promoter: binding stoichiometry and long range effects. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):141–158. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Georgopoulos K., Greenberg M. E., Leder P. c-Jun dimerizes with itself and with c-Fos, forming complexes of different DNA binding affinities. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori K., Angel P., Le Beau M. M., Karin M. Structure and chromosomal localization of the functional intronless human JUN protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9148–9152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S. I., Ryseck R. P., Mechta F., Bravo R., Yaniv M. Characterization of junD: a new member of the jun proto-oncogene family. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1433–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent C. Stimulation of phospholipid metabolism in embryonic muscle cells treated with phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):280–282. doi: 10.1038/312280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Henning-Chubb C., Huberman E., Verma I. M. c-fos expression is neither sufficient nor obligatory for differentiation of monomyelocytes to macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Zokas L., Schreiber R. D., Verma I. M. Rapid induction of the expression of proto-oncogene fos during human monocytic differentiation. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moye-Rowley W. S., Harshman K. D., Parker C. S. Yeast YAP1 encodes a novel form of the jun family of transcriptional activator proteins. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):283–292. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Müller D., Guilbert L. Differential expression of c-fos in hematopoietic cells: correlation with differentiation of monomyelocytic cells in vitro. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1887–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T., Nakamoto B., Yokochi T., Chait A., Kannagi R. Human erythroleukemia cell line (HEL) undergoes a drastic macrophage-like shift with TPA. Blood. 1983 Oct;62(4):832–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quantin B., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor stimulates transcription of the c-jun proto-oncogene in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):538–539. doi: 10.1038/334538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sambucetti L. C., Curran T., Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Common DNA binding site for Fos protein complexes and transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M., Verrier B., Kurz C., Müller R. Chromatin association and DNA binding properties of the c-fos proto-oncogene product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):277–292. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lanahan A., Perez-Albuerne E., Nathans D. jun-D: a third member of the jun gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1500–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Nathans D. Induction of protooncogene c-jun by serum growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8464–8467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambucetti L. C., Curran T. The Fos protein complex is associated with DNA in isolated nuclei and binds to DNA cellulose. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1417–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.3491427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Lamph W. W., Kamps M., Verma I. M. fos-associated cellular p39 is related to nuclear transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M. Direct interaction between fos and jun nuclear oncoproteins: role of the 'leucine zipper' domain. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):692–695. doi: 10.1038/336692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Sisson J. C., Verma I. M. Transcriptional autoregulation of the proto-oncogene fos. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):314–319. doi: 10.1038/334314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuermann M., Neuberg M., Hunter J. B., Jenuwein T., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Müller R. The leucine repeat motif in Fos protein mediates complex formation with Jun/AP-1 and is required for transformation. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoyama C., Frunzio R., Liau G., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Transcriptional activation encoded by the v-fos gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone R. M., Weber B. L., Spriggs D. R., Kufe D. W. Phospholipase C activates protein kinase C and induces monocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):739–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya S., Yamabe M., Yamaguchi Y., Kobayashi Y., Konno T., Tada K. Establishment and characterization of a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line (THP-1). Int J Cancer. 1980 Aug;26(2):171–176. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910260208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Sassone-Corsi P. Proto-oncogene fos: complex but versatile regulation. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):513–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Fos C-terminal mutations block down-regulation of c-fos transcription following serum stimulation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4193–4202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa T., Sibley D. R., Bouvier M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Cross-talk between cellular signalling pathways suggested by phorbol-ester-induced adenylate cyclase phosphorylation. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):67–70. doi: 10.1038/327067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Straaten F., Müller R., Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a human c-onc gene: deduced amino acid sequence of the human c-fos protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3183–3187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]