Abstract
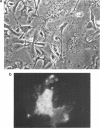
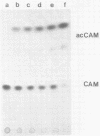
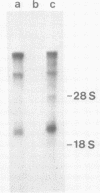
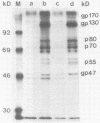
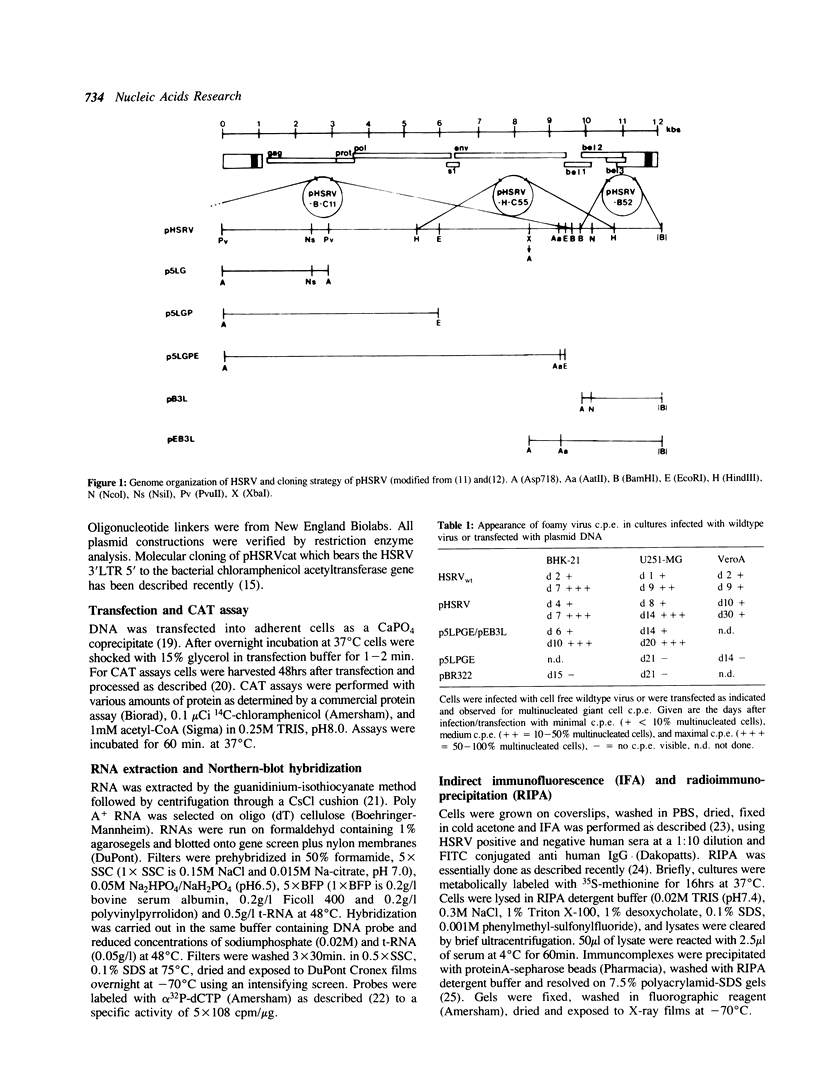
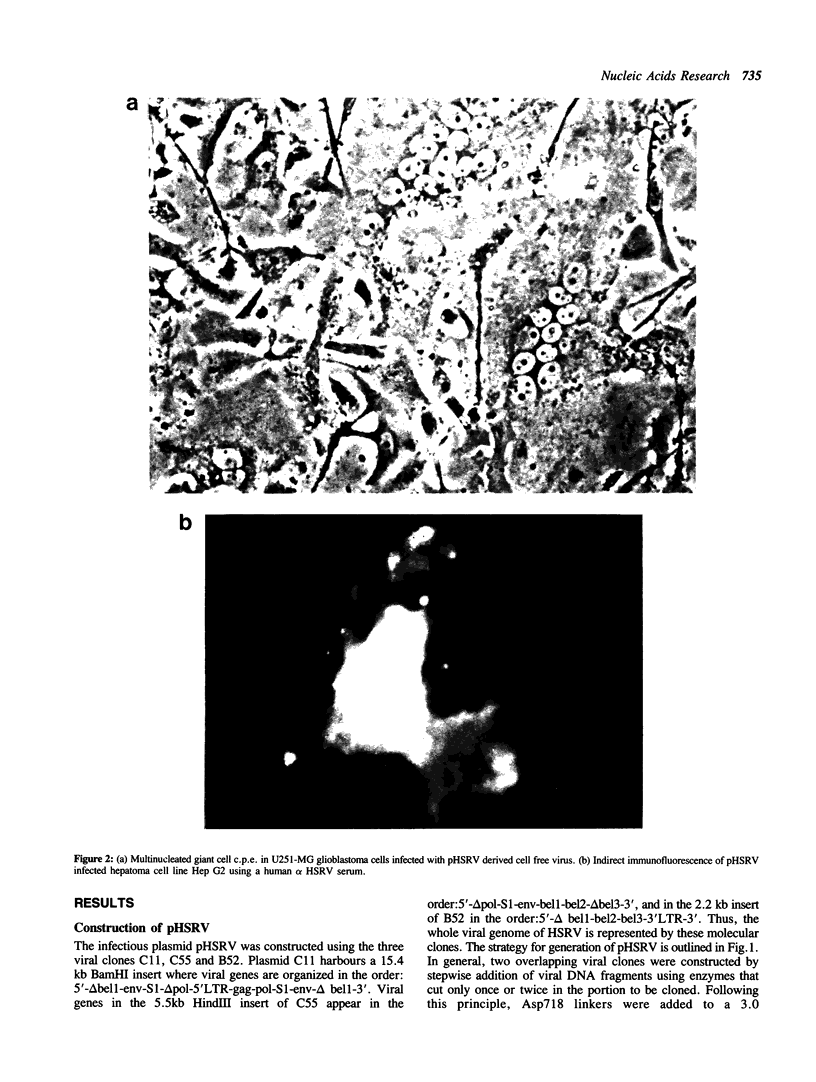
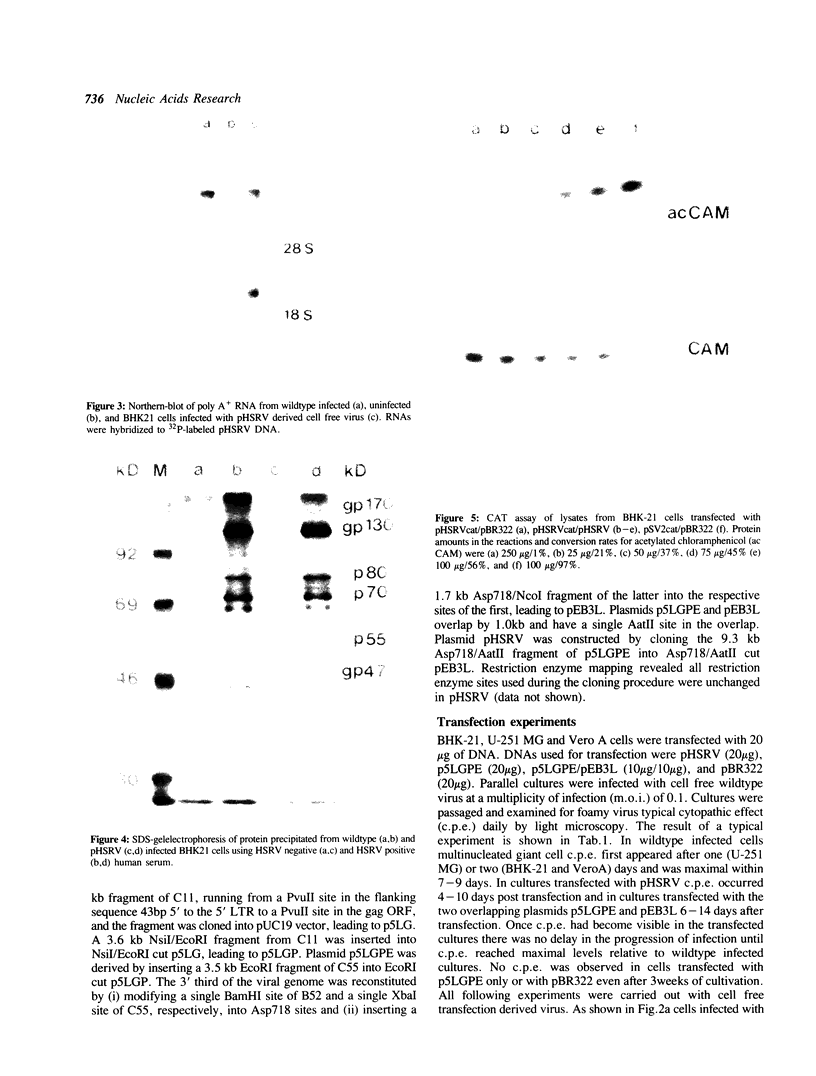
An infectious molecular clone (pHSRV) of the human Spumaretrovirus (HSRV) was constructed using viral DNA and cDNA clones. The infectivity of pHSRV was proven by transfection of cell cultures and subsequent infection of susceptible cultures with cell free transfection derived virus. pHSRV derived virus produced foamy virus typical cytopathic effects in susceptible cultures. Infected cells could be stained specifically with foamy virus antisera by means of indirect immunofluorescence. Radioimmunoprecipitation revealed the presence of characteristic HSRV structural proteins in pHSRV infected cultures. By cotransfection of pHSRV and an indicator plasmid it was found that pHSRV is able to transactivate the viral LTR. Viral transcripts were found to be approximately 200 bases longer in pHSRV infected cultures compared to wildtype infected cultures. This difference is most likely due to an insertion of DNA of non-viral origin in the U3 region of the 3'LTR of the infectious clone.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achong B. G., Mansell P. W., Epstein M. A., Clifford P. An unusual virus in cultures from a human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Feb;46(2):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron K. R., Birchall S. M., Moses M. A. Isolation of foamy virus from patient with dialysis encephalopathy. Lancet. 1978 Oct 7;2(8093):796–796. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92691-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., Darai G. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the env gene and its flanking regions of the human spumaretrovirus reveals two novel genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2077–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh P. C., Matsuura F., Mizumoto C. Seroepidemiology of human syncytial virus: antibody prevalence in the Pacific. Intervirology. 1980;13(2):87–90. doi: 10.1159/000149112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Bannert H., Darai G., Flügel R. M. Analysis of the primary structure of the long terminal repeat and the gag and pol genes of the human spumaretrovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1590-1597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Flügel R. M. Genomic organization of the human spumaretrovirus and its relatedness to AIDS and other retroviruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Dec;4(6):467–473. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Flügel R. M. The 3'-orf protein of human immunodeficiency virus 2 shows sequence homology with the bel3 gene of the human spumaretrovirus. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):286–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller H. K., Ball G., Epstein M. A., Achong B. G., Lenoir G., Levin A. The prevalence of naturally occurring antibodies to human syncytial virus in East African populations. J Gen Virol. 1980 Apr;47(2):399–406. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann-Haefelin D., Rethwilm A., Bauer G., Gudat F., zur Hausen H. Characterization of a foamy virus isolated from Cercopithecus aethiops lymphoblastoid cells. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1983;172(2):75–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02124508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Darai G., Rösen A., Maurer B., Flügel R. M. Molecular cloning of the genome of human spumaretrovirus. Gene. 1987;59(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hikikoshi A., Taniguchi T., Yoshida M. Expression of the pX gene of HTLV-I: general splicing mechanism in the HTLV family. Science. 1985 Jun 28;228(4707):1532–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2990031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stancek D., Stanceková-Gressnerová M., Janotka M., Hnilica P., Oravec D. Isolation and some serological and epidemiological data on the viruses recovered from patients with subacute thyroiditis de Quervain. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975;161(2):133–144. doi: 10.1007/BF02121755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A. Foamy retroviruses. A virus in search of a disease. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):497–498. doi: 10.1038/333497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner J., Gelderblom H. Isolation of foamy virus from patients with de Quervain thyroiditis. Lancet. 1979 Aug 4;2(8136):258–259. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Samuels J., Clarke J. K. A foamy virus of possible human origin isolated in BHK-21 cells. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;42(3):228–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01265647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]