Abstract
Vertebrate cells contain a site-specific endoribonuclease (RNase MRP) that cleaves mitochondrial RNA transcribed from the origin of leading-strand mitochondrial DNA replication. This report presents the characterization of the human enzyme and its essential RNA component. Human RNase MRP is a ribonucleoprotein with a nucleus-encoded RNA of 265 nucleotides. As expected, the single-copy RNA coding region is homologous (84%) to the corresponding mouse gene; surprisingly, at least 700 nucleotides of the immediate 5'-flanking region are conserved. The 265-nucleotide MRP RNA and an MRP RNA cleavage product representing the 3'-terminal 108 nucleotides exist in nuclear and mitochondrial RNA isolates; the larger MRP RNA is present in greatest abundance in the nucleus. The putative processing site within the 265-nucleotide MRP RNA is offset from that of mouse MRP RNA, but in each case cleavage is precise and occurs at the sequence ANCCCGC. Oligonucleotide-mediated inhibition experiments reveal that both the 5' and 3' portions of the MRP RNA are involved in cleavage by RNase MRP; this implies that full length MRP RNA complexed with proteins is an active species in vertebrate cells.
Full text
PDF

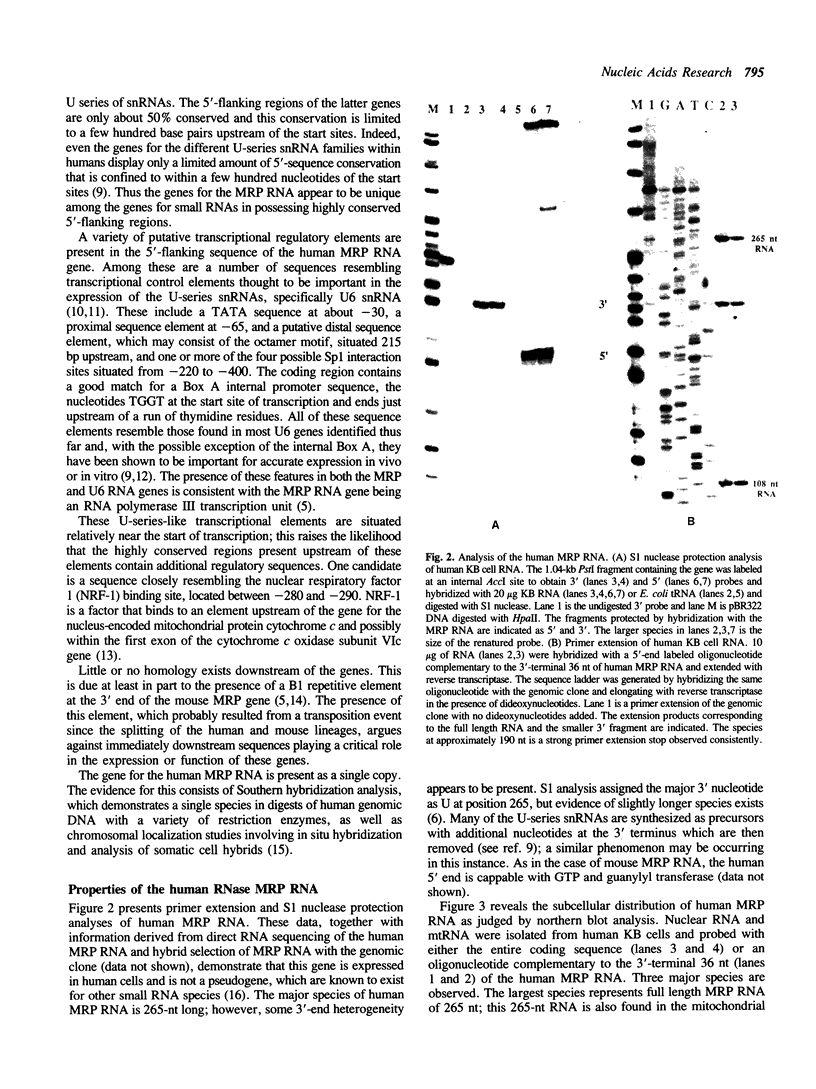
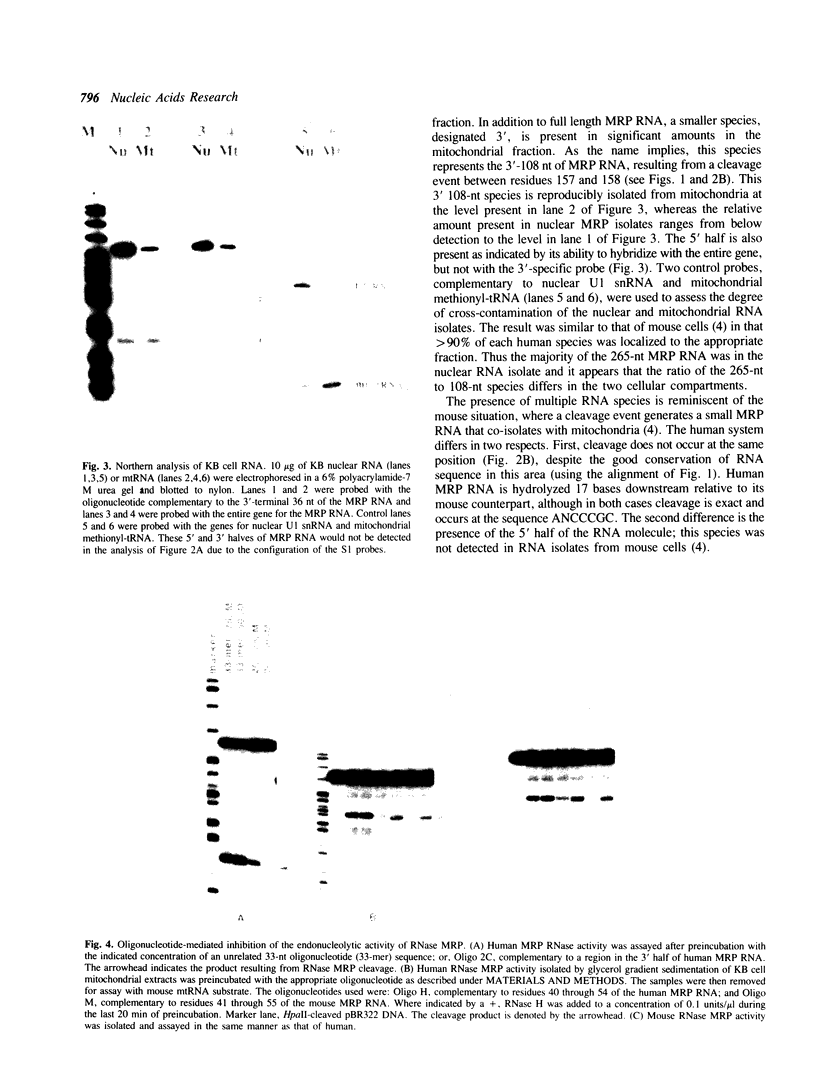
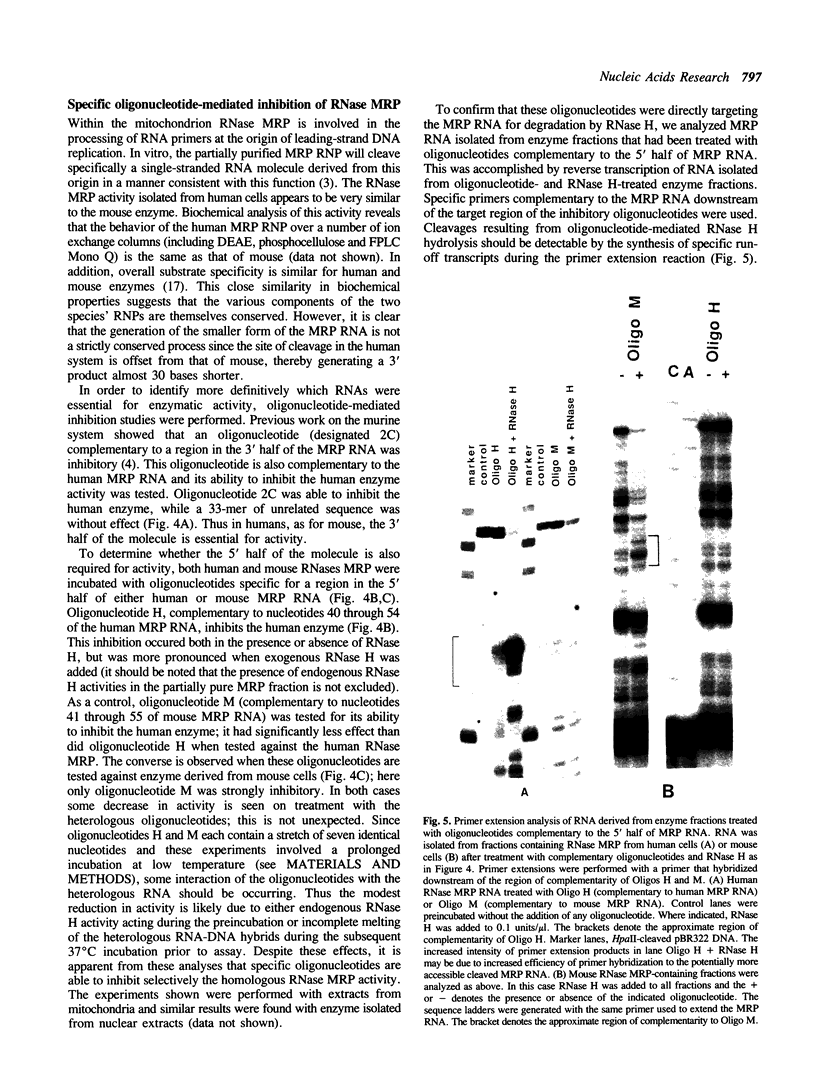


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. A mammalian mitochondrial RNA processing activity contains nucleus-encoded RNA. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1178–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.2434997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. A novel endoribonuclease cleaves at a priming site of mouse mitochondrial DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):409–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Mouse RNAase MRP RNA is encoded by a nuclear gene and contains a decamer sequence complementary to a conserved region of mitochondrial RNA substrate. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90991-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison R. A., Van Arsdell S. W., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M. Abundant pseudogenes for small nuclear RNAs are dispersed in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):810–814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Baudin F., Mougel M., Romby P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Probing the structure of RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9109–9128. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Scarpulla R. C. Interaction of nuclear factors with multiple sites in the somatic cytochrome c promoter. Characterization of upstream NRF-1, ATF, and intron Sp1 recognition sequences. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14361–14368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold H. A., Topper J. N., Clayton D. A., Craft J. The RNA processing enzyme RNase MRP is identical to the Th RNP and related to RNase P. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1377–1380. doi: 10.1126/science.2476849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. Sequential association of nucleolar 7-2 RNA with two different autoantigens. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1379–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Upstream elements required for efficient transcription of a human U6 RNA gene resemble those of U1 and U2 genes even though a different polymerase is used. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):196–204. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. A., Steitz J. A. Structural analysis of the human U3 ribonucleoprotein particle reveal a conserved sequence available for base pairing with pre-rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2899–2913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Tan E. M., Henning D., Nohga K., Busch H. Detection of a nucleolar 7-2 ribonucleoprotein and a cytoplasmic 8-2 ribonucleoprotein with autoantibodies from patients with scleroderma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1383–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. W., Clayton D. A. DNA primase of human mitochondria is associated with structural RNA that is essential for enzymatic activity. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90556-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]