Abstract
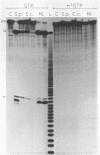
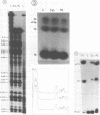
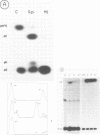
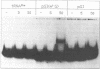
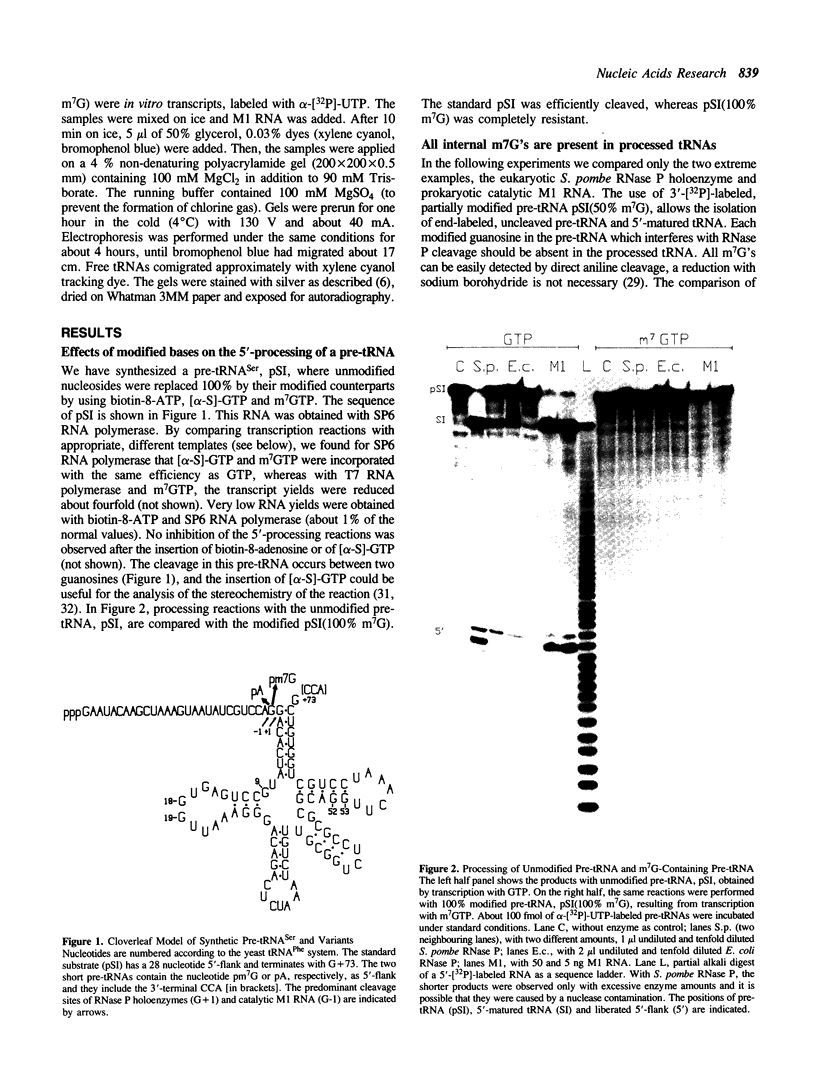
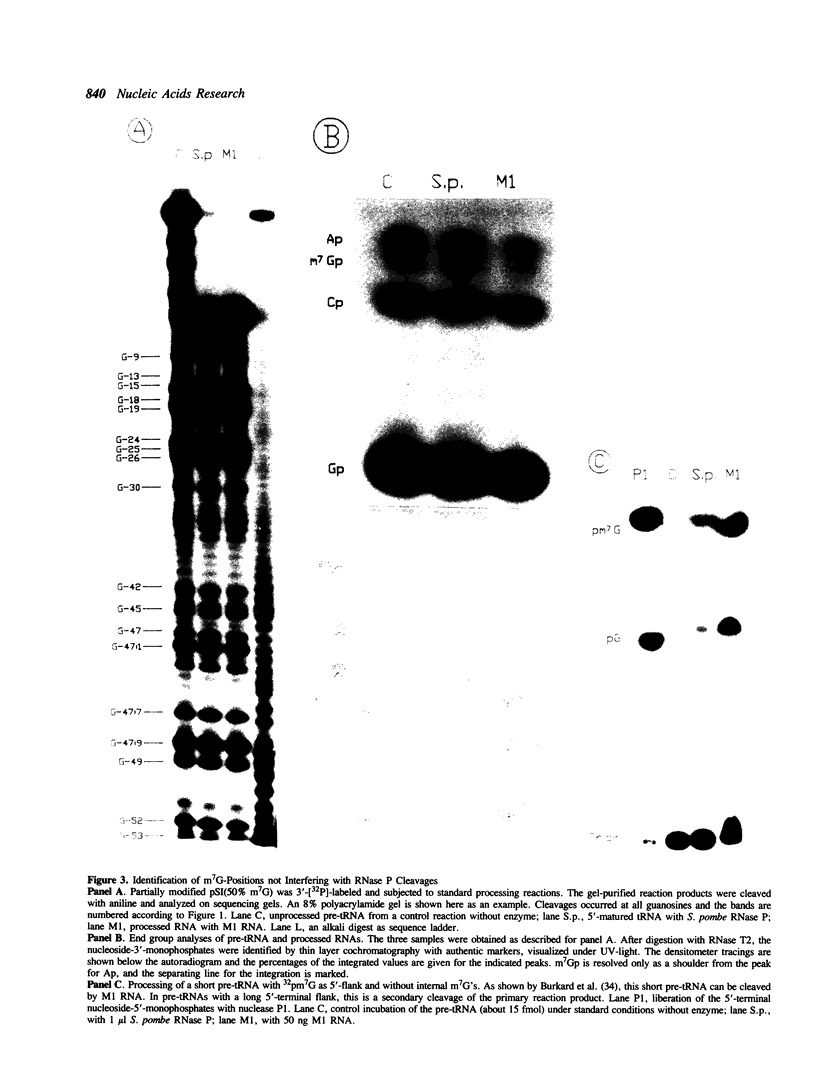
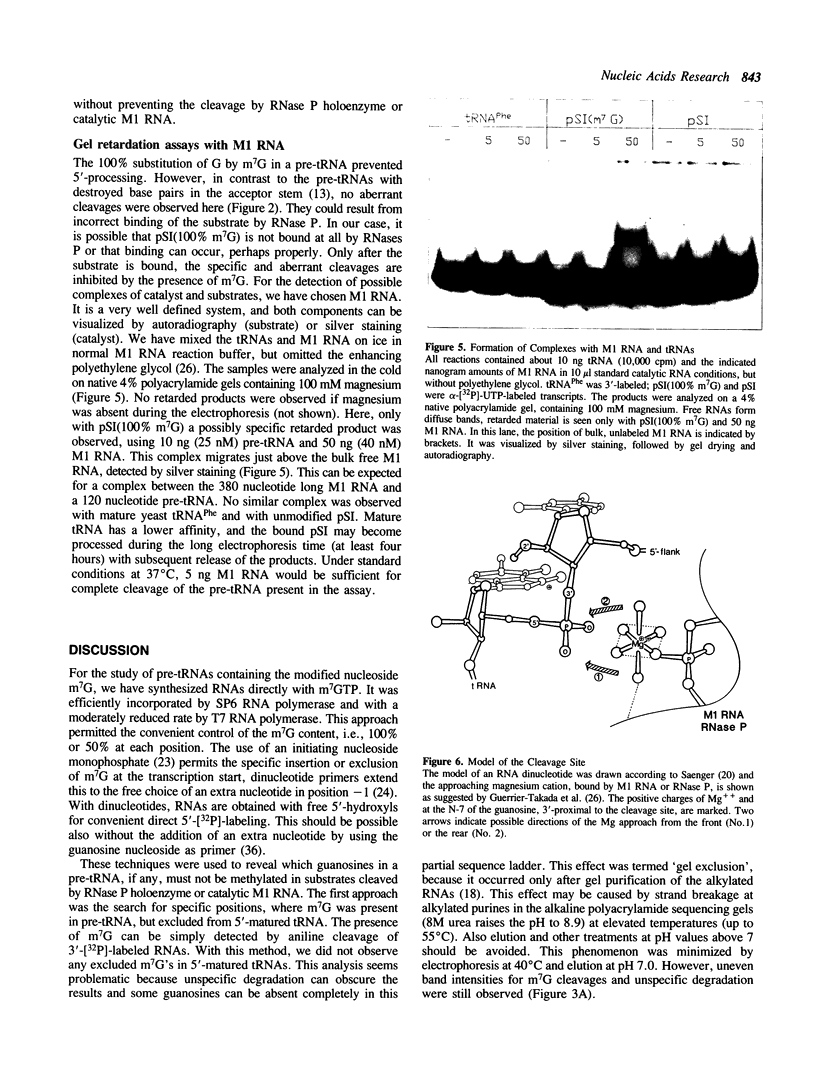
Several modified nucleosides were introduced during in vitro RNA synthesis into a pre-tRNA(Ser). The pre-tRNAs were used as substrates for RNase P enzymes. No effects were observed with biotin-8-ATP or [alpha-S]-GPT, whereas with m7GTP, the cleavage reaction was completely inhibited. Analysis of pre-tRNAs which contained m7G at various positions has revealed a single base at the 5'-end of the acceptor stem where this modification absolutely prevents cleavage by catalytic M1 RNA, eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNase P holoenzymes. These results suggest that a critical contact must be made between pre-tRNA substrate and enzyme/ribozyme or that the approach of the potential cleaving agent (a positive magnesium ion) is made impossible by the positive charge at N-7 of the guanosine. In addition, we have shown that a pre-tRNA containing only m7G's can still form a complex with M1 RNA in a gel retardation assay.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson J. RNA processing and the intervening sequence problem. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:1035–1069. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.005131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod V. D., Kramer F. R. Transcription from bacteriophage T7 and SP6 RNA polymerase promoters in the presence of 3'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate chain terminators. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5716–5723. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartkiewicz M., Gold H., Altman S. Identification and characterization of an RNA molecule that copurifies with RNase P activity from HeLa cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):488–499. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkard U., Willis I., Söll D. Processing of histidine transfer RNA precursors. Abnormal cleavage site for RNase P. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2447–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrara G., Calandra P., Fruscoloni P., Doria M., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Site selection by Xenopus laevis RNAase P. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90400-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P. Processing of tRNA in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;17(1):45–71. doi: 10.3109/10409238409110269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dock-Bregeon A. C., Westhof E., Giegé R., Moras D. Solution structure of a tRNA with a large variable region: yeast tRNASer. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):707–722. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90578-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Baudin F., Mougel M., Romby P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Probing the structure of RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9109–9128. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Gegenheimer P., Abelson J. Nucleolytic processing of a tRNAArg-tRNAAsp dimeric precursor by a homologous component from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1271–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. Enzymatic oligoribonucleotide synthesis with T4 RNA ligase. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2069–2076. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K. J., Marsh T. L., Pace N. R. Ion dependence of the Bacillus subtilis RNase P reaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5415–5419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Pace N. R. RNase P of Bacillus subtilis has a RNA component. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7507–7509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green C. J., Vold B. S., Morch M. D., Joshi R. L., Haenni A. L. Ionic conditions for the cleavage of the tRNA-like structure of turnip yellow mosaic virus by the catalytic RNA of RNase P. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11617–11620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Haydock K., Allen L., Altman S. Metal ion requirements and other aspects of the reaction catalyzed by M1 RNA, the RNA subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1509–1515. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., McClain W. H., Altman S. Cleavage of tRNA precursors by the RNA subunit of E. coli ribonuclease P (M1 RNA) is influenced by 3'-proximal CCA in the substrates. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90543-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., van Belkum A., Pleij C. W., Altman S. Novel reactions of RNAase P with a tRNA-like structure in turnip yellow mosaic virus RNA. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90388-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole R., Altman S. Properties of purified ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1902–1906. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp G., Cherayil B., Frendewey D., Nishikawa S., Söll D. Two RNA species co-purify with RNase P from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1697–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp G. RNA synthesis: strategies for the use of bacteriophage RNA polymerases. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):75–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp G. Unusual promoter-independent transcription reactions with bacteriophage RNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3023–3036. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankat-Buttgereit B., Gross H. J., Krupp G. Detection of modified nucleosides by rapid RNA sequencing methods. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7649–7649. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Engelke D. R. Partial characterization of an RNA component that copurifies with Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNase P. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2536–2543. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leontis N., DaLio A., Strobel M., Engelke D. Effects of tRNA-intron structure on cleavage of precursor tRNAs by RNase P from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2537–2552. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. T., Coleman J. E. T7 RNA polymerase does not interact with the 5'-phosphate of the initiating nucleotide. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2760–2762. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain W. H., Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. Model substrates for an RNA enzyme. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):527–530. doi: 10.1126/science.2443980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSwiggen J. A., Cech T. R. Stereochemistry of RNA cleavage by the Tetrahymena ribozyme and evidence that the chemical step is not rate-limiting. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):679–683. doi: 10.1126/science.2470150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols M., Söll D., Willis I. Yeast RNase P: catalytic activity and substrate binding are separate functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1379–1383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal J., Doudna J. A., Szostak J. W. Stereochemical course of catalysis by the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.2470151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson J. R., Uhlenbeck O. C. Biochemical and physical characterization of an unmodified yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA transcribed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1033–1037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spacciapoli P., Doviken L., Mulero J. J., Thurlow D. L. Recognition of tRNA by the enzyme ATP/CTP:tRNA nucleotidyltransferase. Interference by nucleotides modified with diethyl pyrocarbonate or hydrazine. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3799–3805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark B. C., Kole R., Bowman E. J., Altman S. Ribonuclease P: an enzyme with an essential RNA component. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3717–3721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann R., Gross H. J., Krupp G. Protocol for rapid chemical RNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7209–7209. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]