Abstract
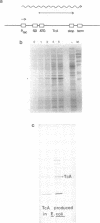
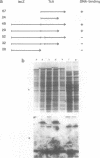
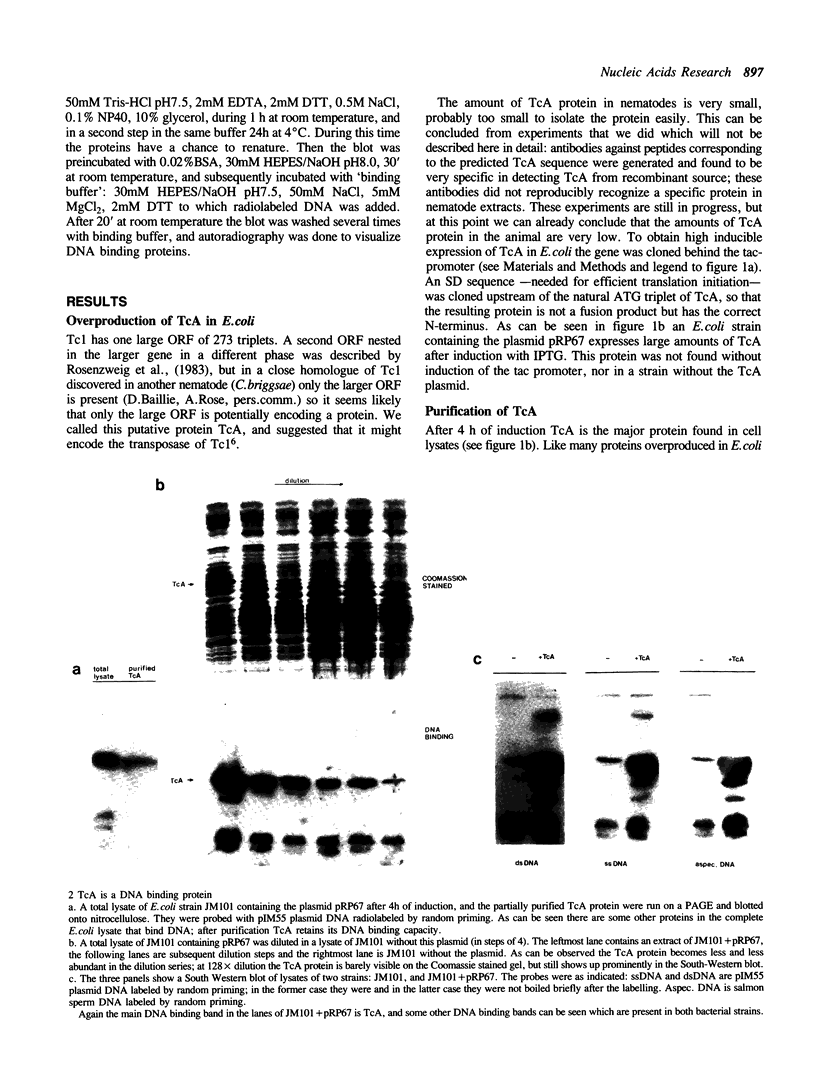
Tc1 is a transposon present in several copies in the genome of all natural isolates of the nematode C.elegans; it is actively transposing in many strains. In those strains Tc1 insertion is the main cause of spontaneous mutations. The transposon contains one large ORF that we call TcA; we assume that the TcA protein is the transposase of Tc1. We expressed TcA in E.coli, purified the protein and showed that it has a strong affinity for DNA (both single stranded and double stranded). A fusion protein of beta-galactosidase and TcA also exhibits DNA binding; deletion derivatives of this fusion protein were tested for DNA binding. A deletion of 39 amino acids at the N-terminal region of TcA abolishes the DNA binding, whereas a deletion of 108 C-terminal amino acids does not affect DNA binding. This shows that the DNA binding domain of TcA is near the N-terminal region. The DNA binding capacity of TcA supports the assumption that TcA is a transposase of Tc1.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bingham P. M., Chou T. B., Mims I., Zachar Z. On/off regulation of gene expression at the level of splicing. Trends Genet. 1988 May;4(5):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Saari B., Anderson P. Activation of a transposable element in the germ line but not the soma of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):726–728. doi: 10.1038/328726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide D., Anderson P. Transposition of Tc1 in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1756–1760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Yesner L., Ruan K. S., Katzenberg D. Evidence for a transposon in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A., Lütticke S., Saedler H. TnpA product encoded by the transposable element En-1 of Zea mays is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4045–4053. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. J., Baillie D. L., Rose A. M. Sequence identity between an inverted repeat family of transposable elements in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5991–5998. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Plasterk R. H. Related transposons in C.elegans and D.melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6234–6234. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P., Rutherford G., Banks J. A., Fedoroff N. Essential large transcripts of the maize Spm transposable element are generated by alternative splicing. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):755–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Spontaneous unstable unc-22 IV mutations in C. elegans var. Bergerac. Genetics. 1984 Dec;108(4):859–877. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori I., Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Analysis of a mutator activity necessary for germline transposition and excision of Tc1 transposable elements in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1988 Oct;120(2):397–407. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H. Differences between Tc1 elements from the C. elegans strain Bergerac. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10050–10050. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Kanaar R., van de Putte P. A genetic switch in vitro: DNA inversion by Gin protein of phage Mu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2689–2692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Barnes G., Laski F. A., Rine J., Rubin G. M. Evidence for Drosophila P element transposase activity in mammalian cells and yeast. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 20;200(2):411–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig B., Liao L. W., Hirsh D. Sequence of the C. elegans transposable element Tc1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4201–4209. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Tanese N., Goff S. P. Gene product of Moloney murine leukemia virus required for proviral integration is a DNA-binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]