Abstract
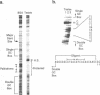
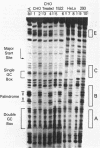
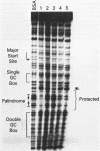
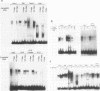
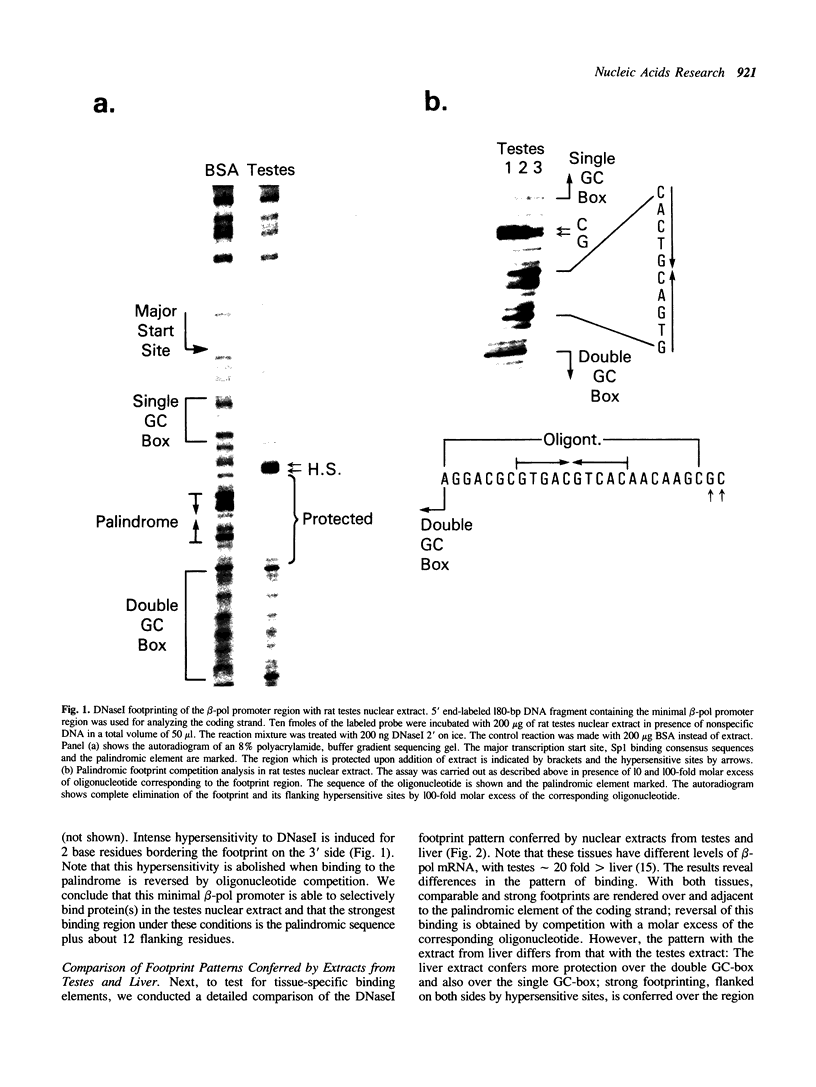
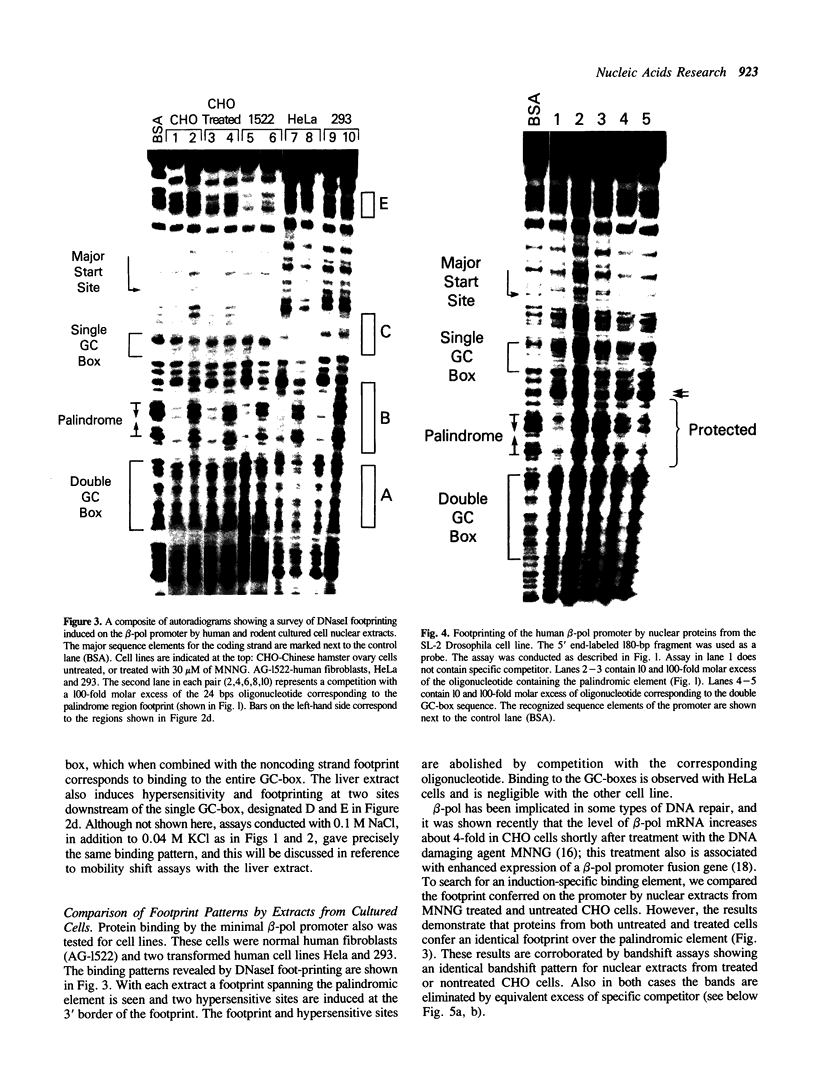
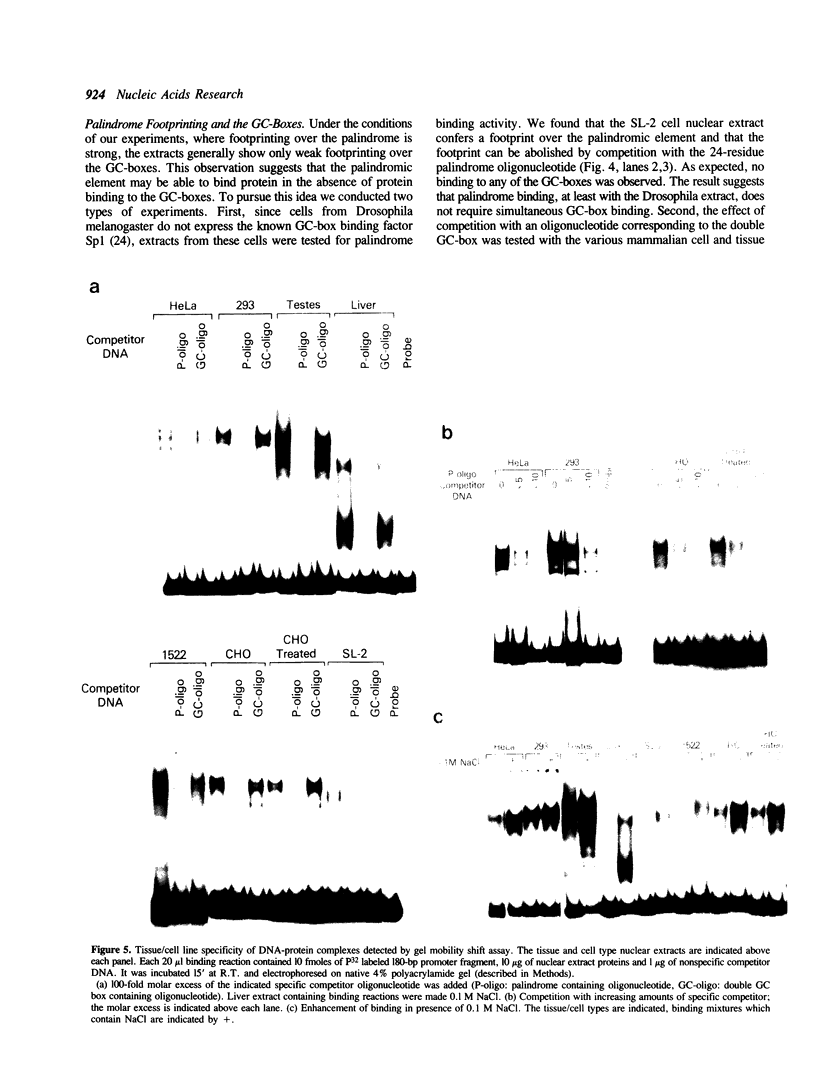
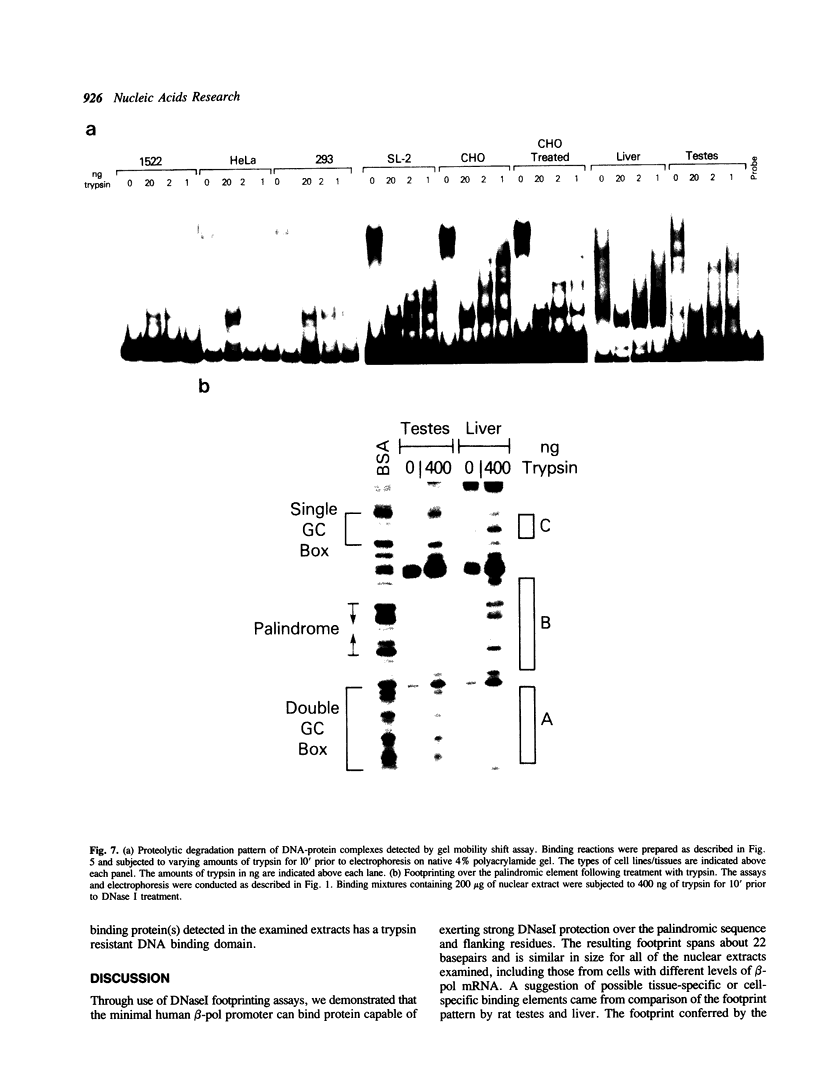
The core promoter for human DNA polymerase beta contains discrete binding sites for mammalian nuclear proteins, as revealed by DNasel footprinting and gel mobility shift assays. Two sites correspond to sequences identical with the Sp1 factor binding element, and a third site includes an eight residue palindromic sequence, TGACGTCA, known as the CRE element of several cAMP responsive promoters; the 5 to 10 residues flanking this palindrome on each side have no apparent sequence homology with known elements in other promoters. Nuclear extract from a variety of tissues and cells were examined; these included rat liver and testes and cultured cells of human and hamster origin. The DNasel footprint is strong over and around the palindromic element for each of the extracts and is equivalent in size (approximately 22 residues); footprinting over the Sp1 binding sites is seen also. Two potential tissue-specific binding sites, present in liver but not in testes, were found corresponding to residues -13 to -10 and +33 to +48, respectively. Protein binding to the palindromic element was confirmed by an electrophoretic mobility shift assay with the core promoter as probe. Binding specificity of the 22 residue palindromic element, as revealed by oligonucleotide competition, is different from that of AP-1 binding element. Controlled proteolysis with trypsin was used to study structural properties of proteins forming the mobility shift bands. Following digestion with trypsin, most of the palindrome binding activity of each extract corresponded to a sharp, faster migrating band, potentially representing a DNA binding domain of the palindrome binding protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Blakeley M. S., Newby R. F., Ghazal P., Hennighausen L., Bourgeois S. Forskolin inducibility and tissue-specific expression of the fibronectin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Hoeffler J. P., Jameson J. L., Lin J. C., Habener J. F. Structural determinants for transcriptional activation by cAMP-responsive DNA elements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18466–18472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Zmudzka B., Hollander M. C., Wilson S. H. Induction of beta-polymerase mRNA by DNA-damaging agents in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):851–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Allegretto E. A., Karin M., Green M. R. A family of immunologically related transcription factors that includes multiple forms of ATF and AP-1. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1216–1226. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose F., Hotta Y., Yamaguchi M., Matsukage A. Difference in the expression level of DNA polymerase beta among mouse tissues: high expression in the pachytene spermatocyte. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Mar;181(1):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Complexities of gene regulation by cAMP. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):65–67. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Sudo T., Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. B., Karawya E., Kinsella T. J., Wilson S. H. Measurement of DNA polymerase beta in skin fibroblast cell lines from patients with ataxia telangiectasia. Mutat Res. 1985 Nov;146(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. How do different transcription factors binding the same DNA sequence sort out their jobs? Trends Genet. 1989 Feb;5(2):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. Cell lines derived from late embryonic stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1972 Apr;27(2):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4221–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Kumar P., Cobianchi F., Skowronski J., Wilson S. H. Sequence of human DNA polymerase beta mRNA obtained through cDNA cloning. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90916-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B. Enhancers and transcription factors in the control of gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 10;951(1):17–35. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widen S. G., Kedar P., Wilson S. H. Human beta-polymerase gene. Structure of the 5'-flanking region and active promoter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16992–16998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S., Abbotts J., Widen S. Progress toward molecular biology of DNA polymerase beta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 28;949(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hayashi Y., Matsukage A. Mouse DNA polymerase beta gene promoter: fine mapping and involvement of Sp1-like mouse transcription factor in its function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8773–8787. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zmudzka B. Z., Fornace A., Collins J., Wilson S. H. Characterization of DNA polymerase beta mRNA: cell-cycle and growth response in cultured human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9587–9596. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zmudzka B. Z., SenGupta D., Matsukage A., Cobianchi F., Kumar P., Wilson S. H. Structure of rat DNA polymerase beta revealed by partial amino acid sequencing and cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5106–5110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]