Abstract
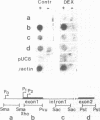
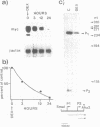
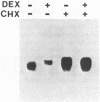
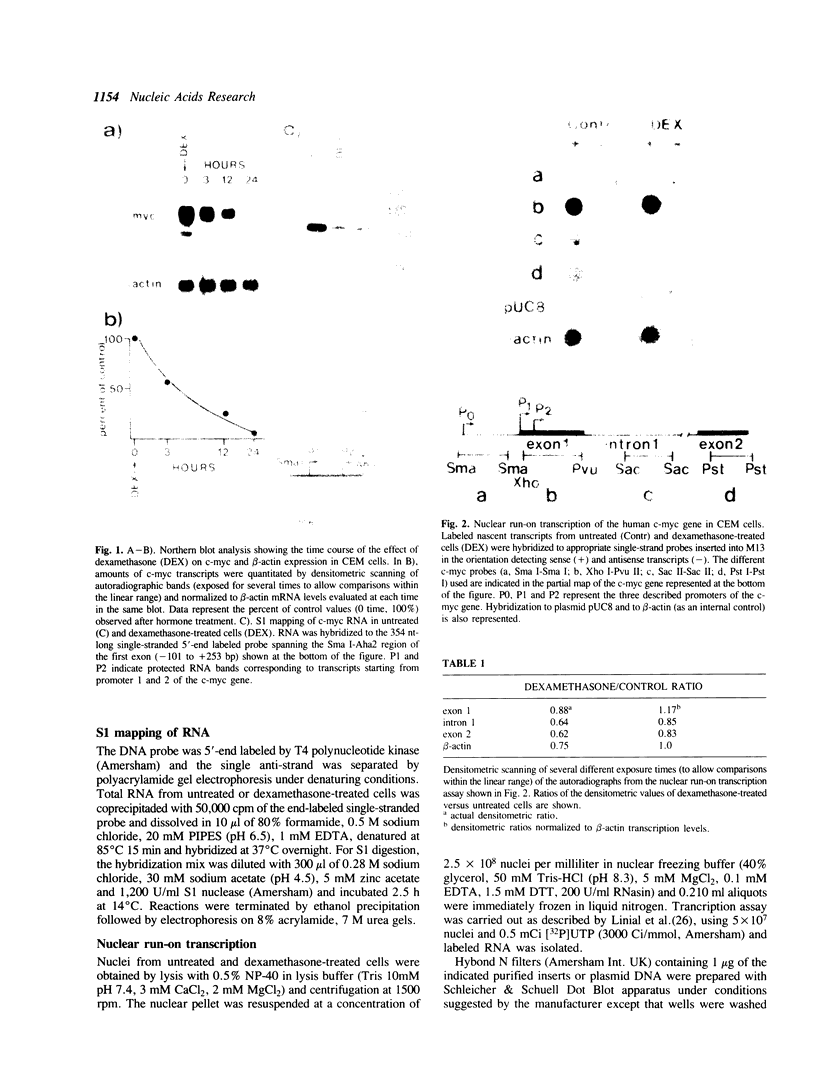
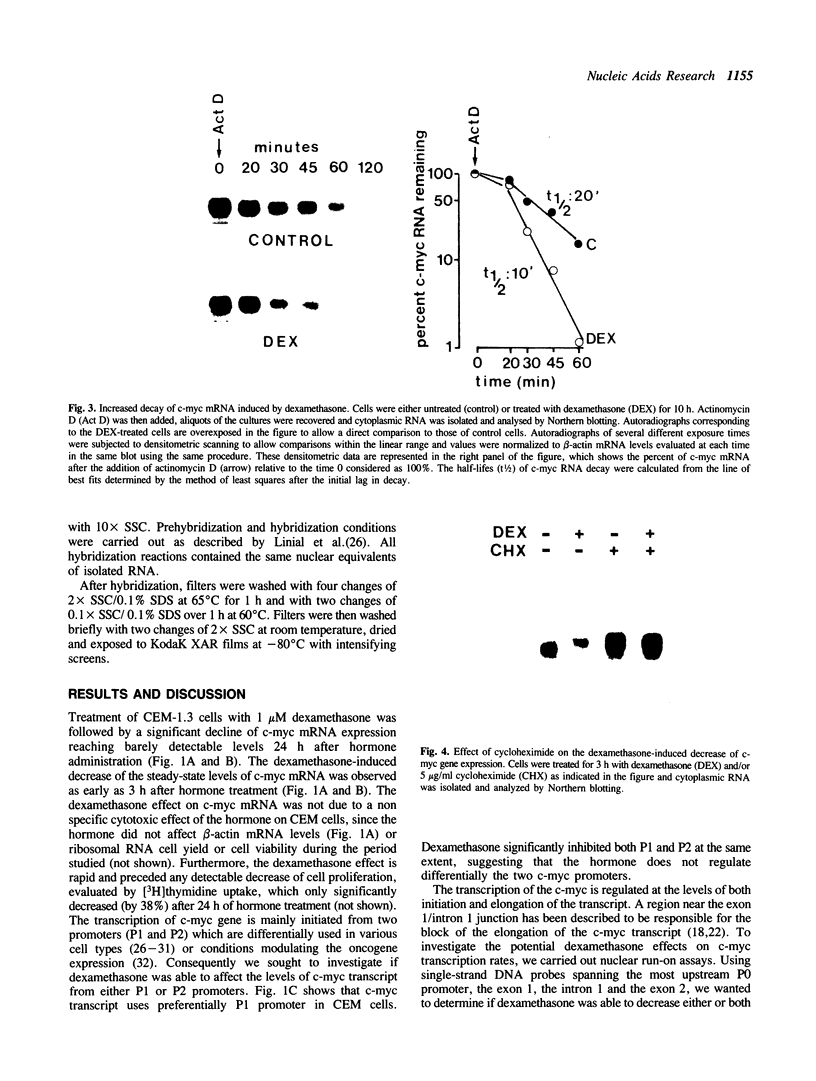
We have studied the regulation of the human c-myc proto-oncogene by glucocorticoid hormones in T lymphoblastic leukemic cells. A significant decrease (50%) of the steady state levels of c-myc mRNA was observed as early as 3 h after dexamethasone treatment of CEM-1.3 human lymphoma cells, reaching less than 5% values, with respect to untreated cells, 24 h after hormone administration. Nuclear run-on experiments showed no modifications of the transcriptional rate from the first exon. However, a slight decrease (15%) of the transcript elongation from the first exon/first intron boundary was observed in the dexamethasone-treated cells. Using actinomycin D to block gene transcription, we have observed a significant increase in the rate of c-myc RNA specific decay after dexamethasone treatment. Furthermore, cycloheximide was able to overcome completely the dexamethasone-induced down-regulation of the c-myc gene expression. Our data suggest that dexamethasone is able to inhibit human c-myc gene expression primarily at the post-transcriptional level, through the synthesis of hormone-induced regulatory protein(s) controlling c-myc transcript stability.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S., Waterman M. L., He X., Rosenfeld M. G. Steroid receptor-mediated inhibition of rat prolactin gene expression does not require the receptor DNA-binding domain. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):685–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90406-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerblom I. E., Slater E. P., Beato M., Baxter J. D., Mellon P. L. Negative regulation by glucocorticoids through interference with a cAMP responsive enhancer. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):350–353. doi: 10.1126/science.2838908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. Sequence requirements for premature termination of transcription in the human c-myc gene. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broome H. E., Reed J. C., Godillot E. P., Hoover R. G. Differential promoter utilization by the c-myc gene in mitogen- and interleukin-2-stimulated human lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2988–2993. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Gelmann E. P., Martinotti S., Franchini G., Papas T. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Cloning and characterization of different human sequences related to the onc gene (v-myc) of avian myelocytomatosis virus (MC29). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6497–6501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Levine R. A., Campisi J. c-myc regulation during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of F9 cells is posttranscriptional and associated with growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):518–524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Y., Poellinger L., Okret S., Hög J. O., von Bahr-Lindström H., Jörnvall H., Gustafsson J. A. Regulation of gene expression of class I alcohol dehydrogenase by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):767–771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman-Reks S. B., Vedeckis W. V. Glucocorticoid inhibition of c-myc, c-myb, and c-Ki-ras expression in a mouse lymphoma cell line. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2457–2462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsthoefel A. M., Thompson E. A. Glucocorticoid regulation of transcription of the c-myc cellular protooncogene in P1798 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Dec;1(12):899–907. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-12-899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. M., Norman M. R., Fowlkes B. J., Thompson E. B. Dexamethasone induces irreversible G1 arrest and death of a human lymphoid cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Feb;98(2):267–278. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040980203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Bishop J. M., Levens D. Regulatory elements that modulate expression of human c-myc. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):659–671. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Okazaki T., Itani T., Ogata M., Sato Y., Ariga H. An initiation site of DNA replication with transcriptional enhancer activity present upstream of the c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3135–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. A., McCormack J. E., Buckler A., Sonenshein G. E. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of c-myc gene expression in WEHI 231 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4112–4116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroder M., Vacca A., Screpanti I., Petrangeli E., Frati L., Gulino A. Enhancement of c-erbA proto-oncogene expression by glucocorticoid hormones in S49.1 lymphoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 2;1009(2):188–190. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. E., Gronemeyer H., Turcotte B., Bocquel M. T., Tasset D., Chambon P. Steroid hormone receptors compete for factors that mediate their enhancer function. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):433–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90918-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Leder P. Nuclear localization and DNA binding properties of a protein expressed by human c-myc oncogene. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):718–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6463648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sambucetti L. C., Curran T., Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Common DNA binding site for Fos protein complexes and transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reicin A., Yang J. Q., Marcu K. B., Fleissner E., Koehne C. F., O'Donnell P. V. Deregulation of the c-myc oncogene in virus-induced thymic lymphomas of AKR/J mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4088–4092. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hayday A. C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of the c-myc gene by translocation: a model for translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos G. F., Scott G. K., Lee W. M., Liu E., Benz C. Estrogen-induced post-transcriptional modulation of c-myc proto-oncogene expression in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9565–9568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Kaltschmidt C., Renkawitz R. Many transcription factors interact synergistically with steroid receptors. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.3201230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Watt R., Marcu K. B. Translocation, breakage and truncated transcripts of c-myc oncogene in murine plasmacytomas. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):401–406. doi: 10.1038/303401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Bellvé A. R., Leder P. Transcription and promoter usage of the myc gene in normal somatic and spermatogenic cells. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):707–710. doi: 10.1126/science.6494906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartwout S. G., Kinniburgh A. J. c-myc RNA degradation in growing and differentiating cells: possible alternate pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):288–295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilding G., Lippman M. E., Gelmann E. P. Effects of steroid hormones and peptide growth factors on protooncogene c-fos expression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):802–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. Q., Bauer S. R., Mushinski J. F., Marcu K. B. Chromosome translocations clustered 5' of the murine c-myc gene qualitatively affect promoter usage: implications for the site of normal c-myc regulation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1441–1447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh Y. S., Thompson E. B. Glucocorticoid effect on oncogene/growth gene expression in human T lymphoblastic leukemic cell line CCRF-CEM. Specific c-myc mRNA suppression by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10904–10910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]