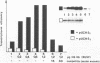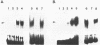Abstract
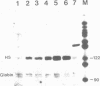
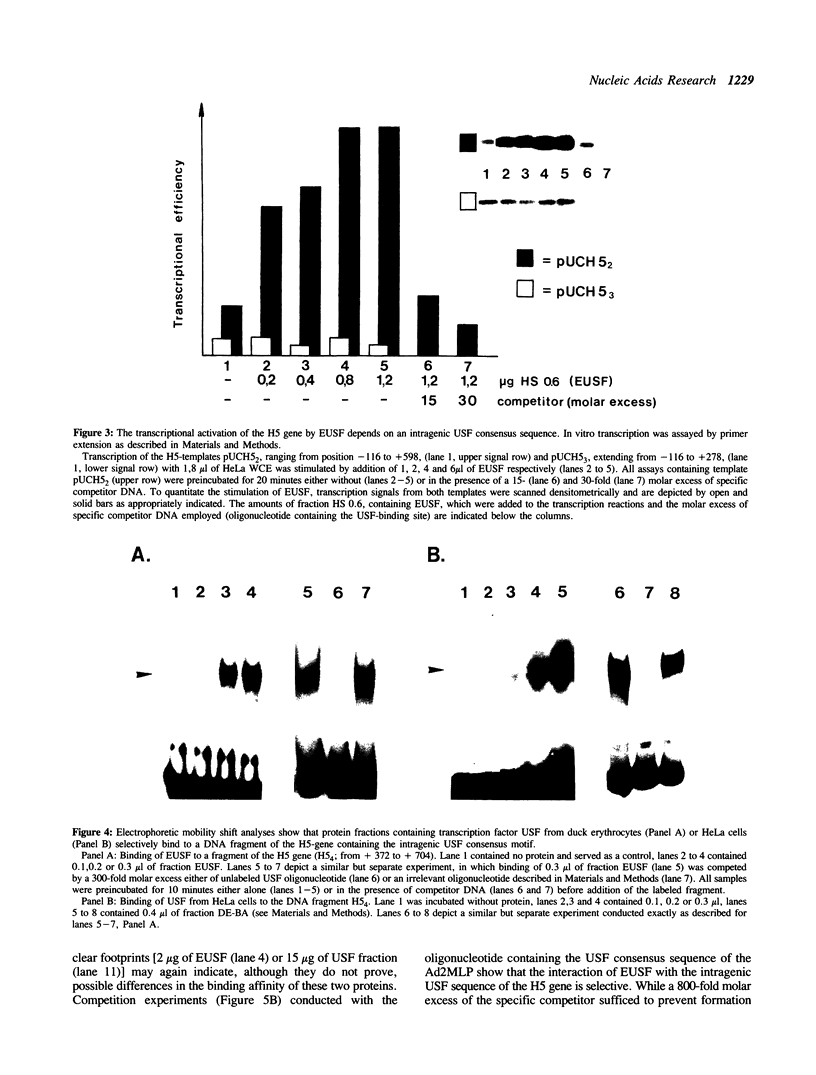
The duck histone H5 gene contains a 12 base pair (bp) sequence motif within the coding region, which shows homology in 10 out of 12 bp with the consensus sequence of the USF binding site in the Ad2ML-promoter. The functional equivalent of transcription factor USF, partially purified from whole cell extracts of duck erythrocytes (EUSF), was shown to interact with this intragenic sequence. Electrophoretic mobility shift analyses revealed the selective formation of a complex between this protein fraction and the duck H5 gene. Footprint assays with DNase I delineated specific binding to the intragenic sequence outlined above. Moreover this protein fraction, containing EUSF, transactivates the expression of the duck H5 gene in vitro and elimination of the USF-consensus sequence leads to a loss of stimulation but retains the basic transcription of the gene. These results suggest an as yet unknown functional role of EUSF in the expression of the H5 gene of the duck.
Full text
PDF



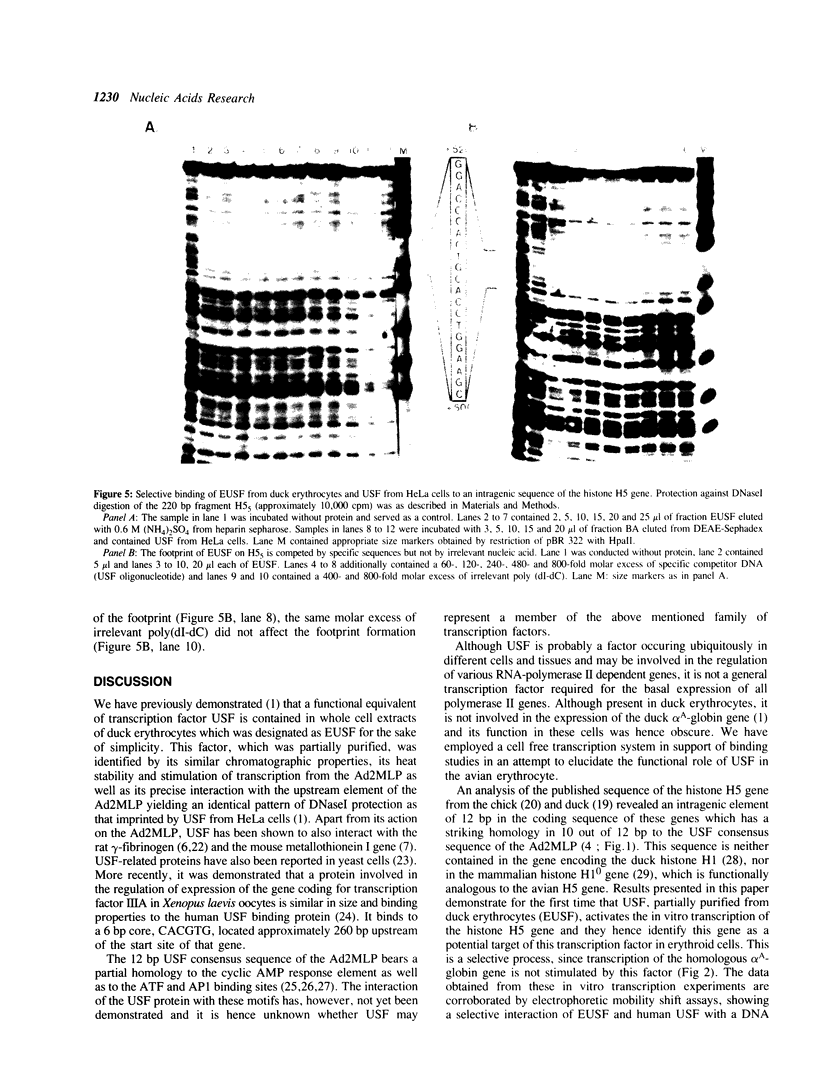

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K. L., Yamazaki A., Cashion P. J., Khorana H. G. Chemical synthesis of polynucleotides. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1972 Jun;11(6):451–459. doi: 10.1002/anie.197204511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso A., Breuer B., Bouterfa H., Doenecke D. Early increase in histone H1(0) mRNA during differentiation of F9 cells to parietal endoderm. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3003–3008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D., Townes T. M. Two 3' sequences direct adult erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7056–7060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Isolation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere DNA-binding protein, its human homolog, and its possible role as a transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):403–409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. The major late transcription factor binds to and activates the mouse metallothionein I promoter. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):973–980. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Morgan J. G., Crabtree G. R., Sharp P. A. The adenovirus major late transcription factor activates the rat gamma-fibrinogen promoter. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):684–688. doi: 10.1126/science.3672119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. A 3' enhancer is required for temporal and tissue-specific transcriptional activation of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):731–734. doi: 10.1038/323731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A., Krieg P., Wells J. R. Analysis of histone H5 and globin mRNAs in chick-embryo development. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 5;131(3):551–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Martin P. L., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Eukaryotic gene transcription with purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:582–598. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D., Tönjes R. Conserved dyad symmetry structures at the 3' end of H5 histone genes. Analysis of the duck H5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Translational and transcriptional control elements in the untranslated leader of the heat-shock gene hsp22. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knezetic J. A., Felsenfeld G. Identification and characterization of a chicken alpha-globin enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):893–901. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription: whole-cell extract. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:568–582. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Grodzicker T., Tjian R. Downstream sequences affect transcription initiation from the adenovirus major late promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2684–2694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Specific interaction between a transcription factor and the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3563–3570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. D., Marks A. R., Buckley D. I., Kapler G., Payvar F., Goodman H. M. The first intron of the human growth hormone gene contains a binding site for glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):699–702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. G., Courtois G., Fourel G., Chodosh L. A., Campbell L., Evans E., Crabtree G. R. Sp1, a CAAT-binding factor, and the adenovirus major late promoter transcription factor interact with functional regions of the gamma-fibrinogen promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2628–2637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Fine analysis of the active H5 gene chromatin of chicken erythroid cells at different stages of differentiation. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Affolter M., Renaud J. Genomic organization of the genes coding for the six main histones of the chicken: complete sequence of the H5 gene. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):843–859. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotto K. W., Kaulen H., Roeder R. G. Positive and negative regulation of the gene for transcription factor IIIA in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):651–662. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X. P., Lee R., Weinmann R. Protein factor(s) binding independently to two different regions of the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3729–3744. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Stamler S. J., Engel J. D. Erythroid-specific transcription of the chicken histone H5 gene is directed by a 3' enhancer. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):827–830. doi: 10.1038/328827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tönjes R., Doenecke D. A highly conserved sequence in H1 histone genes as an oligonucleotide hybridization probe: isolation and sequence of a duck H1 gene. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):361–370. doi: 10.1007/BF02603121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingart S., Sommer U., Gerhold H., Seifart K. H. Transcription of the alpha A-globin gene of the duck. Development of a homologous in vitro system and identification of trans-acting factors. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 15;183(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K., Elder R. T. A region internal to the coding sequences is essential for transcription of the yeast Ty-D15 element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3667–3678. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]