Abstract
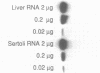
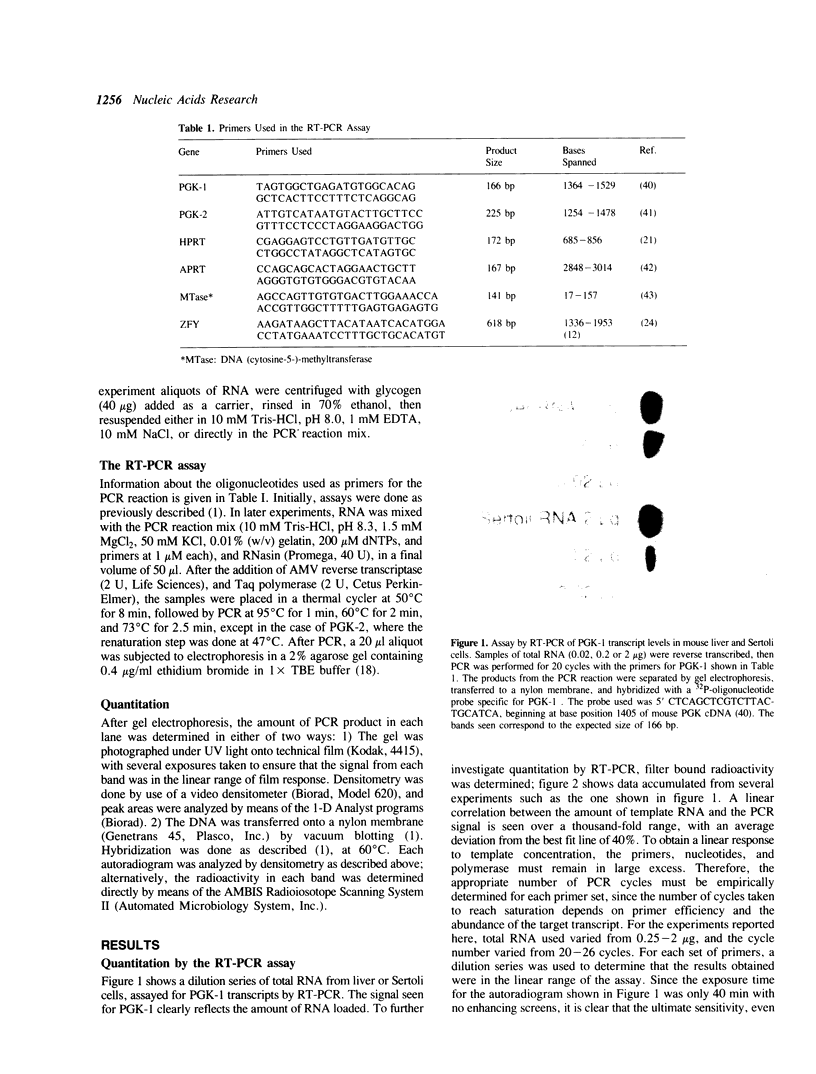
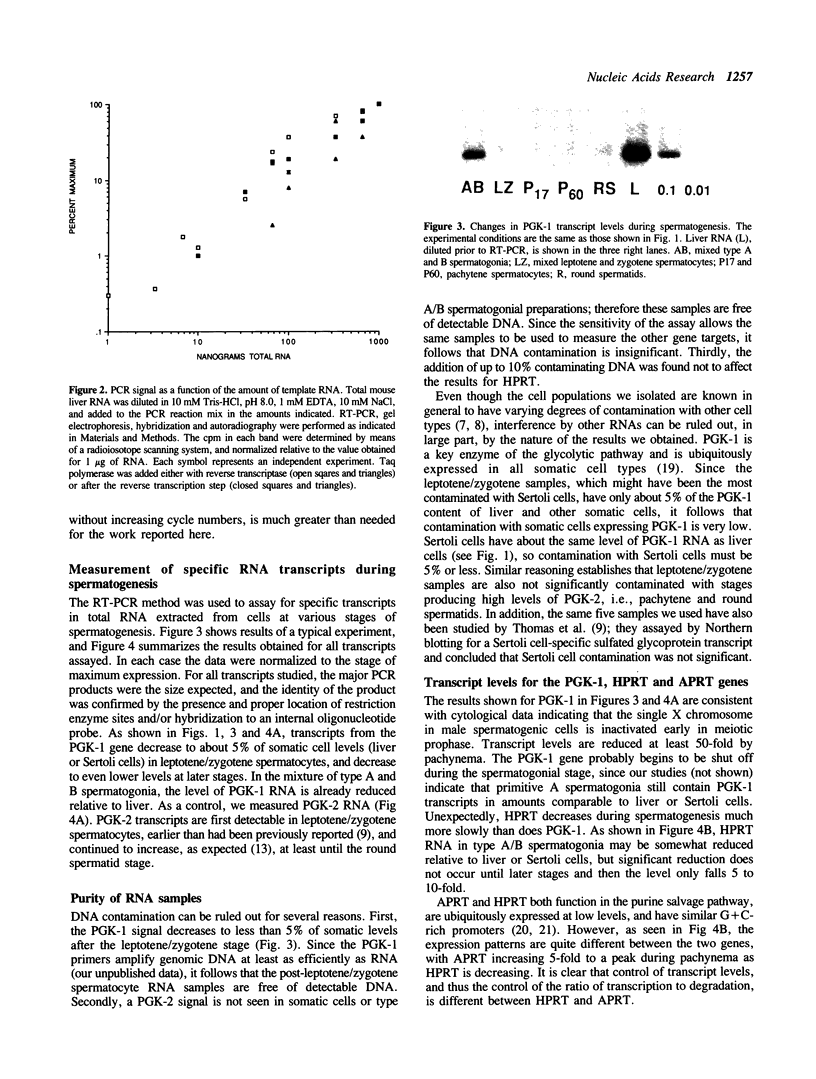
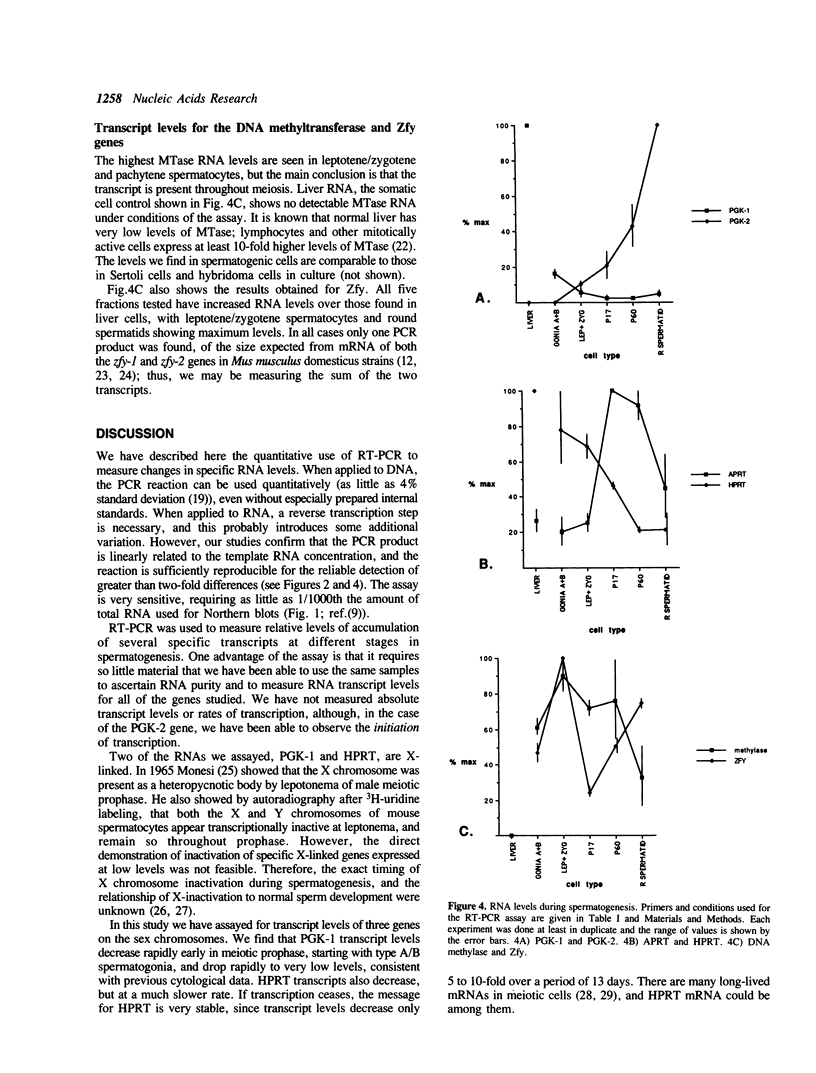
A reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay (RT-PCR) was used quantitatively to measure accumulated levels of RNA transcripts in total mouse RNAs derived from male germ cells at various spermatogenic stages. RNA levels for two X-linked enzymes, phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK-1) and hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT), both decrease during spermatogenesis, although the transcript levels decrease much more rapidly for PGK-1. RNA for the Y-linked ZFY (zinc finger protein) is elevated in all spermatogenic cell fractions tested, being particularly high in leptotene/zygotene spermatocytes and round spermatids. RNA for adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) increases 5-fold to a peak during late pachynema. RNA for PGK-2, undetectable in spermatogonial cells, increases at least 50-fold by the round spermatid stage. DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase (MTase) transcript levels are over an order of magnitude higher throughout spermatogenesis than in non-dividing liver cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsop J., Watts R. W. Purine phosphoribosyltransferase (EC 2.4.2.7 and 2.4.2.8) and purine de novo synthesis activity in rat testicular tissue at different stages of development, and their correlation with the circulating levels of gonadotrophins and testosterone, and with structural changes. Differentiation. 1986;32(2):144–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker-André M., Hahlbrock K. Absolute mRNA quantification using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A novel approach by a PCR aided transcript titration assay (PATTY). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9437–9446. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Cavicchia J. C., Millette C. F., O'Brien D. A., Bhatnagar Y. M., Dym M. Spermatogenic cells of the prepuberal mouse. Isolation and morphological characterization. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):68–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R., Millette C. F., Bhatnagar Y. M., O'Brien D. A. Dissociation of the mouse testis and characterization of isolated spermatogenic cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):480–494. doi: 10.1177/25.7.893996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestor T., Laudano A., Mattaliano R., Ingram V. Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding DNA methyltransferase of mouse cells. The carboxyl-terminal domain of the mammalian enzymes is related to bacterial restriction methyltransferases. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):971–983. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer P. H., Adra C. N., Lau Y. F., McBurney M. W. The testis-specific phosphoglycerate kinase gene pgk-2 is a recruited retroposon. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3107–3112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. J., Huesca-Contreras M., Dosch H. M., Pan S. Rapid amplification of complementary DNA from small amounts of unfractionated RNA. Anal Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;177(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dush M. K., Briggs M. R., Royce M. E., Schaff D. A., Khan S. A., Tischfield J. A., Stambrook P. J. Identification of DNA sequences required for mouse APRT gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8509–8524. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dush M. K., Sikela J. M., Khan S. A., Tischfield J. A., Stambrook P. J. Nucleotide sequence and organization of the mouse adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene: presence of a coding region common to animal and bacterial phosphoribosyltransferases that has a variable intron/exon arrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2731–2735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Riggs A. D. Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold B., Fujimoto H., Kramer J. M., Erickson R. P., Hecht N. B. Haploid accumulation and translational control of phosphoglycerate kinase-2 messenger RNA during mouse spermatogenesis. Dev Biol. 1983 Aug;98(2):392–399. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbarth P., Vosberg H. P. Enzymatic amplification of myosin heavy-chain mRNA sequences in vitro. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):297–306. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper M., Hardy K., Handyside A., Hunter S., Monk M. HPRT-deficient (Lesch-Nyhan) mouse embryos derived from germline colonization by cultured cells. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):292–295. doi: 10.1038/326292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman P., Gubbay J., Collignon J., Lovell-Badge R. Zfy gene expression patterns are not compatible with a primary role in mouse sex determination. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):940–942. doi: 10.1038/342940a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M. R., Bradley A., Robertson E. J., Evans M. J. A potential animal model for Lesch-Nyhan syndrome through introduction of HPRT mutations into mice. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):295–298. doi: 10.1038/326295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Lindsley D. L. The role of X-chromosome inactivation during spermatogenesis (Drosophila-allocycly-chromosome evolution-male sterility-dosage compensation). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):182–186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardon G., Page D. C. The sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome encodes a protein with a highly acidic domain and 13 zinc fingers. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):765–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90680-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren A. Sex determination in mammals. Trends Genet. 1988 Jun;4(6):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W. HPRT gene organization and expression. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1987;4:34–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monesi V., Geremia R., D'Agostino A., Boitani C. Biochemistry of male germ cell differentiation in mammals: RNA synthesis in meiotic and postmeiotic cells. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1978;12:11–36. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60592-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monesi V. Synthetic activities during spermatogenesis in the mouse RNA and protein. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Aug;39(1):197–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Boubelik M., Lehnert S. Temporal and regional changes in DNA methylation in the embryonic, extraembryonic and germ cell lineages during mouse embryo development. Development. 1987 Mar;99(3):371–382. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.3.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M. Genomic imprinting. Memories of mother and father. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):203–204. doi: 10.1038/328203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M. Genomic imprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):921–925. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M. Methylation and the X chromosome. Bioessays. 1986 May;4(5):204–208. doi: 10.1002/bies.950040505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Singer-Sam J., Lee C. Y., Riggs A. D. The nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone containing the entire coding region for mouse X-chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase. Gene. 1986;45(3):275–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa G. J., Zaia J. A., Spallone P. A., Stephens D. A., Kaplan B. E., Wallace R. B., Rossi J. J. Direct detection of HIV-1 RNA from AIDS and ARC patient samples. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):287–295. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine C. M., Chan K. M., Kozak C. A., Lau Y. F. Chromosome mapping and expression of a putative testis-determining gene in mouse. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):80–83. doi: 10.1126/science.2563174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Wang A., Mark D., Werb Z. Novel method for studying mRNA phenotypes in single or small numbers of cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Jan;39(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P. M., Reddy P. R. Regulation of DNA methyltransferase in the testis of rat. Biochem Int. 1988 Mar;16(3):543–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D. X inactivation, differentiation, and DNA methylation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(1):9–25. doi: 10.1159/000130315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford J. P., Clark H. J., Chapman V. M., Rossant J. Differences in DNA methylation during oogenesis and spermatogenesis and their persistence during early embryogenesis in the mouse. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1039–1046. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solter D. Differential imprinting and expression of maternal and paternal genomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:127–146. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. H., Wilkie T. M., Tomashefsky P., Bellvé A. R., Simon M. I. Differential gene expression during mouse spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod. 1989 Oct;41(4):729–739. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod41.4.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandeberg J. L. Developmental aspects of X chromosome inactivation in eutherian and metatherian mammals. J Exp Zool. 1983 Nov;228(2):271–286. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402280211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker K. E., Riggs A. D., Smith S. S. Purification of human DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(4):337–349. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]