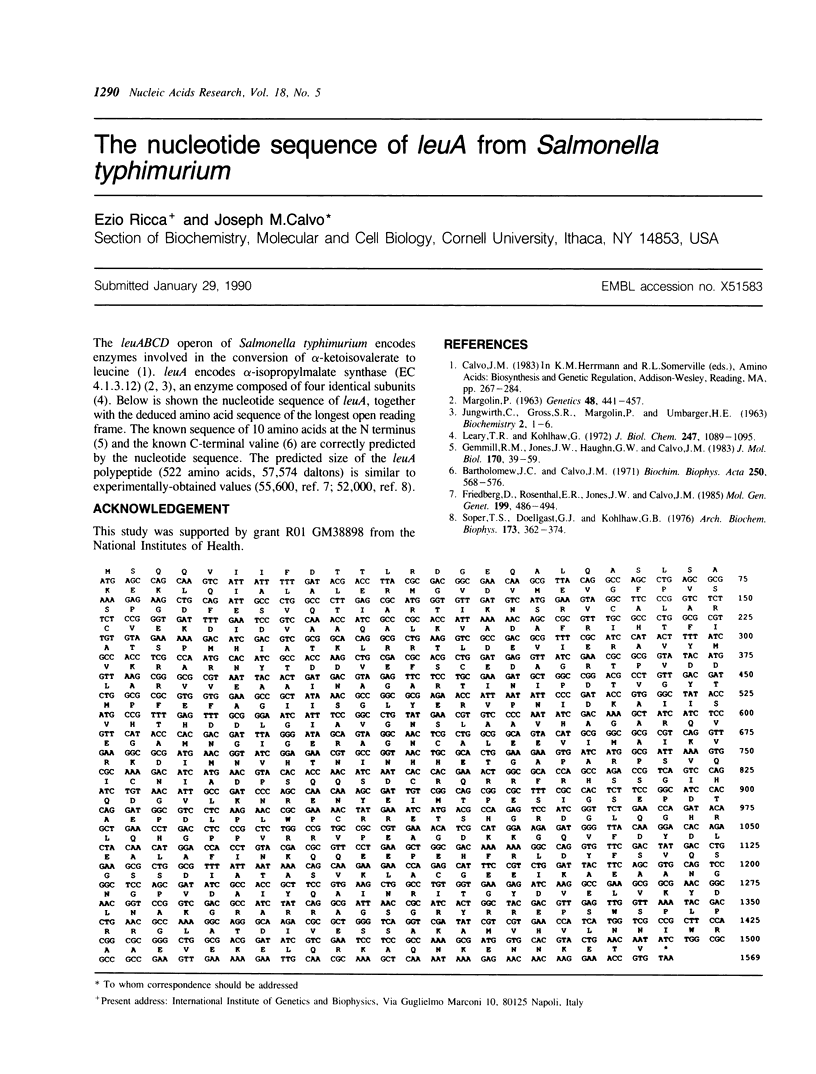
Full text
PDFPage 1290
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomew J. C., Calvo J. M. Alpha-isopropylmalate synthase from Salmonella typhimurium. Carboxypeptidase digestion studies of parent and feedback-insensitive enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 15;250(3):568–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg D., Rosenthal E. R., Jones J. W., Calvo J. M. Characterization of the 3' end of the leucine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(3):486–494. doi: 10.1007/BF00330763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmill R. M., Jones J. W., Haughn G. W., Calvo J. M. Transcription initiation sites of the leucine operons of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):39–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNGWIRTH C., GROSS S. R., MARGOLIN P., UMBARGER H. E. The biosynthesis of leucine. I. The accumulation of beta-carboxy-beta-hydroxyisocaproate by leucine auxotrophs of Salmonella typhimurium and Neurospora crassa. Biochemistry. 1963 Jan-Feb;2:1–6. doi: 10.1021/bi00901a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary T. R., Kohlhaw G. B. -isopropylmalate synthase from Salmonella typhimurium. Analysis of the guaternary structure and its relation to function. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1089–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIN P. Genetic fine structure of the leucine operon in Salmonella. Genetics. 1963 Mar;48:441–457. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.3.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soper T. S., Doellgast J., Kohlhaw G. B. Mechanism of feedback inhibition by leucine. Purification and properties of a feedback-resistant alpha-isopropylmalate synthase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Mar;173(1):362–374. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



