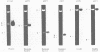Abstract
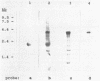
We have identified the promoter region of the large ribosomal DNA repeat unit of Crithidia fasciculata by northern blotting and nuclear run-on analyses. These data show that transcription starts approximately 1 kb upstream of the 18S rRNA gene. S1 protection experiments and sequence analysis of this area resulted in a precise localization of the start site. We have been unable to identify conserved sequence element(s) by a direct comparison of the crithidial RNA polymerase I promoter region and similar promoter regions of other eukaryotes; not even to the promoter region of the more closely related kinetoplastid species, Trypanosoma brucei. The absence of homology within the primary sequence of the promoter region, which is also found in other eukaryotes, might explain the observed species specificity of in vivo and in vitro rDNA transcription, since this resides in the interaction of initiation factor(s) and the core promoter domain.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. M., Platt T. Pol I transcription: which comes first, the end or the beginning? Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):839–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellofatto V., Cross G. A. Expression of a bacterial gene in a trypanosomatid protozoan. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1167–1169. doi: 10.1126/science.2499047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards A., Van der Ploeg L. H., Frasch A. C., Borst P., Boothroyd J. C., Coleman S., Cross G. A. Activation of trypanosome surface glycoprotein genes involves a duplication-transposition leading to an altered 3' end. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Stiege W. Structure and function of ribosomal RNA. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):1–17. doi: 10.1042/bj2290001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A., Kubo K., Clark C. G., Boothroyd J. C. Precise identification of cleavage sites involved in the unusual processing of trypanosome ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90514-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. C., White T. C., Laird P. W., Borst P. Stable introduction of exogenous DNA into Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2457–2461. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02525.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grondal E. J., Evers R., Kosubek K., Cornelissen A. W. Characterization of the RNA polymerases of Trypanosoma brucei: trypanosomal mRNAs are composed of transcripts derived from both RNA polymerase II and III. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3383–3389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Nucleotide sequence requirements for specific initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6908–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooter J. M., van der Spek H. J., Wagter R., d'Oliveira C. E., van der Hoeven F., Johnson P. J., Borst P. The anatomy and transcription of a telomeric expression site for variant-specific surface antigens in T. brucei. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90153-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Smale S. T., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. Regulation of human ribosomal RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3558–3562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal R. K. The organization and transcription of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:115–160. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. Transcription of cloned Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA microinjected into Xenopus oocytes, and the identification of an RNA polymerase I promoter. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Korn L. J. A comprehensive sequence analysis program for the IBM personal computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):581–599. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder R. H., Labhart P., McStay B. Processing and termination of RNA polymerase I transcripts. Bioessays. 1987 Mar;6(3):108–112. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Collings J. C., Gray M. W. Structure and evolution of the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene of Crithidia fasciculata. Curr Genet. 1986;10(5):405–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00418414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner J. A., Ohrlein A., Grummt I. In vitro mutagenesis and transcriptional analysis of a mouse ribosomal promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2137–2141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerville J. RNA polymerase I promoters and transcription factors. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):189–190. doi: 10.1038/310189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. F., Collings J. C., Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. Multiple spacer sequences in the nuclear large subunit ribosomal RNA gene of Crithidia fasciculata. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1063–1071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinkels B. W., Evers R., Borst P. The topogenic signal of the glycosomal (microbody) phosphoglycerate kinase of Crithidia fasciculata resides in a carboxy-terminal extension. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1159–1165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. C., Rudenko G., Borst P. Three small RNAs within the 10 kb trypanosome rRNA transcription unit are analogous to domain VII of other eukaryotic 28S rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9471–9489. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]