Abstract
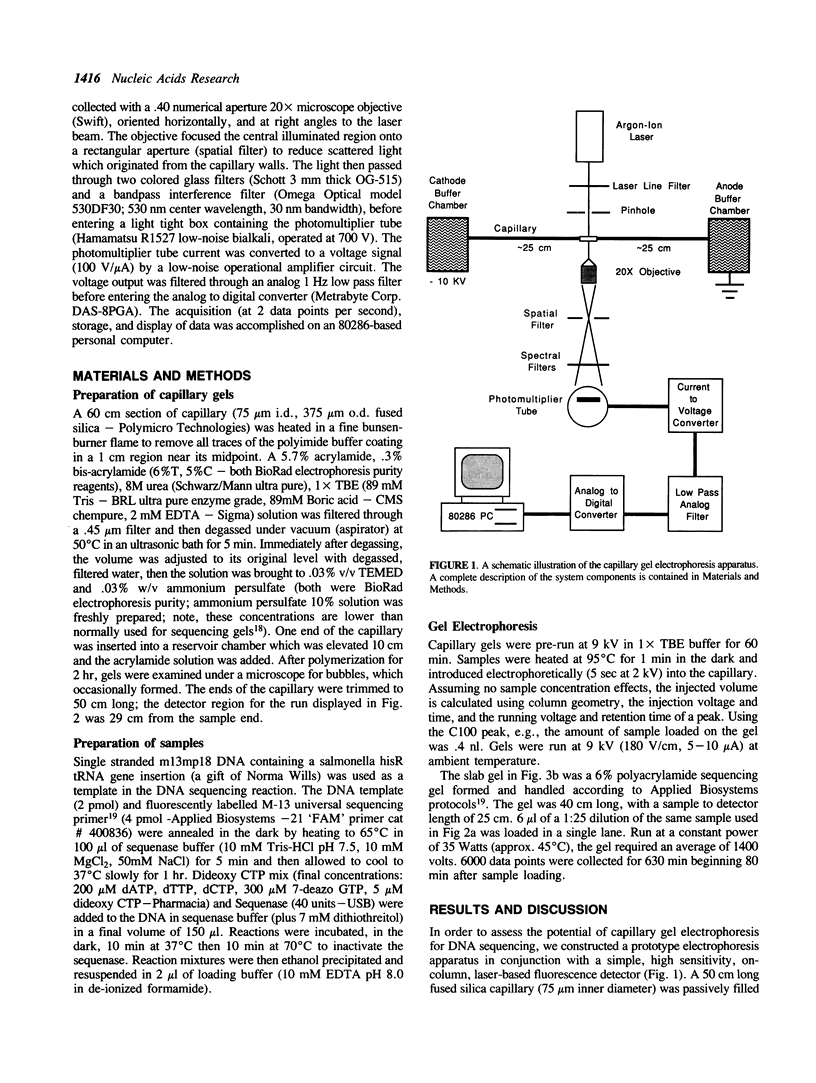
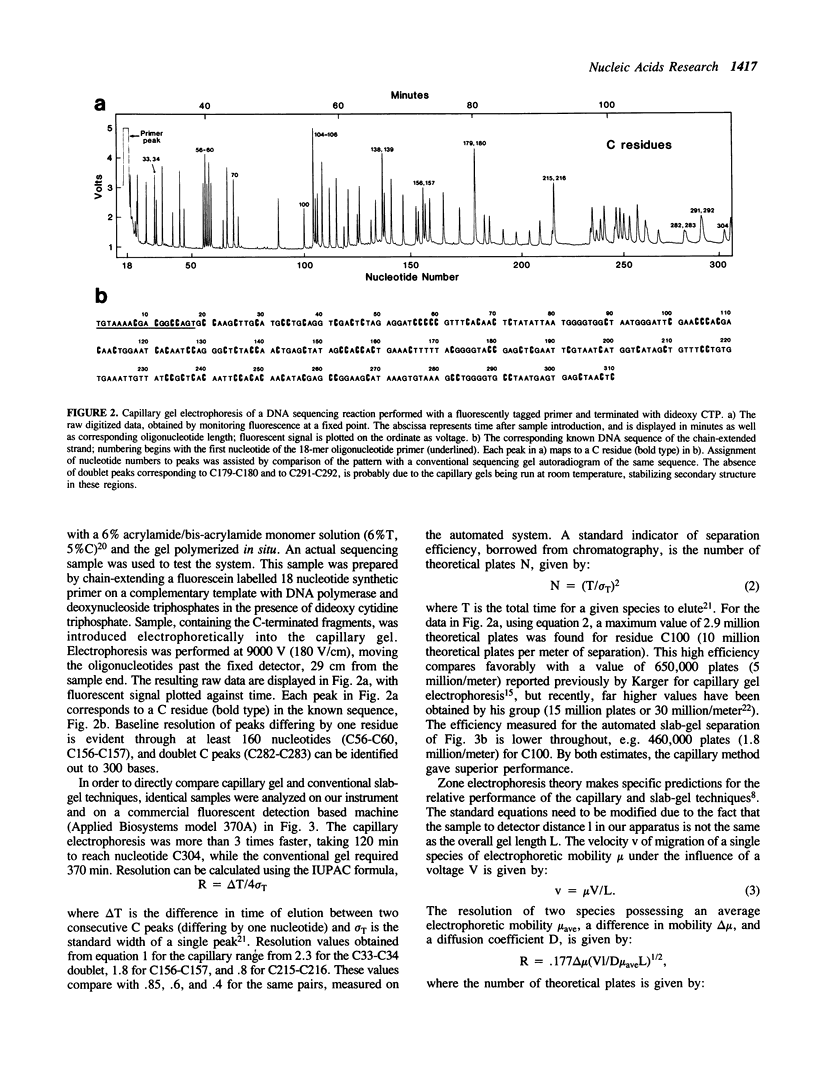
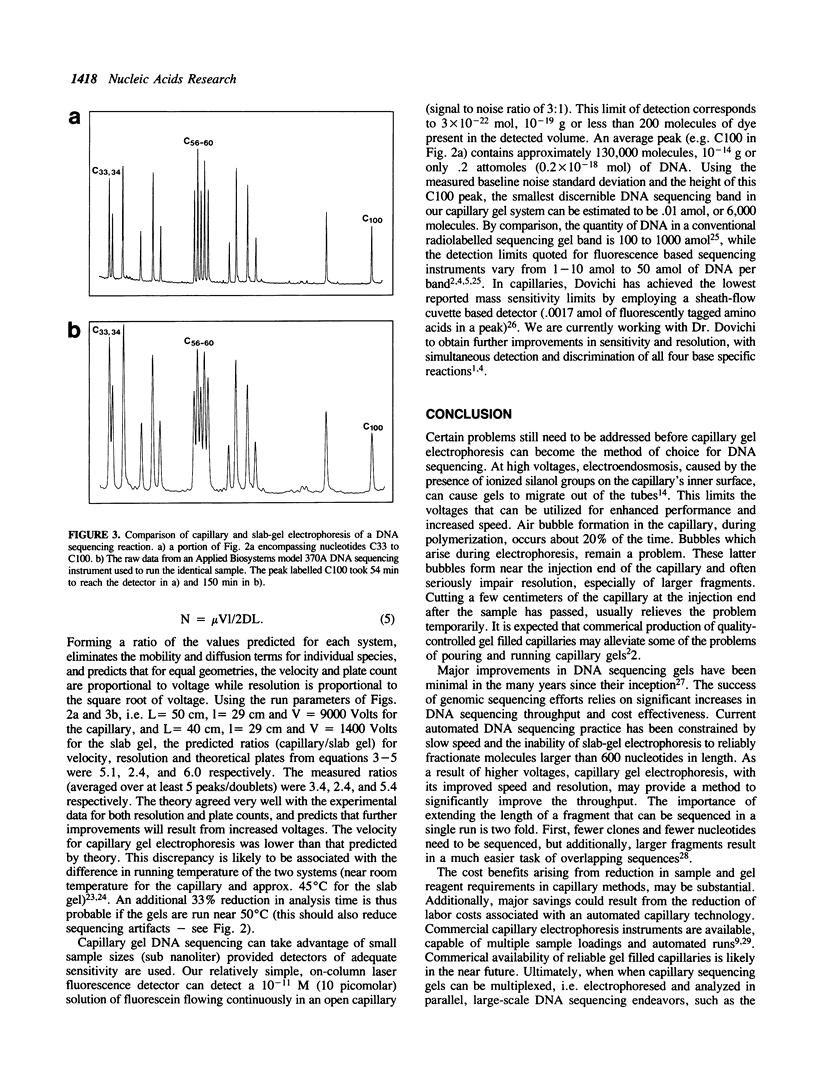
Capillary gel electrophoresis has been demonstrated for the separation and detection of DNA sequencing samples. Enzymatic dideoxy nucleotide chain termination was employed, using fluorescently tagged oligonucleotide primers and laser based on-column detection (limit of detection is 6,000 molecules per peak). Capillary gel separations were shown to be three times faster, with better resolution (2.4 x), and higher separation efficiency (5.4 x) than a conventional automated slab gel DNA sequencing instrument. Agreement of measured values for velocity, resolution and separation efficiency with theory, predicts further improvements will result from increased electric field strengths (higher voltages and shorter capillaries). Advantages of capillary gel electrophoresis for automatic DNA sequencing instruments and for genomic sequencing are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge W., Sproat B., Stegemann J., Schwager C., Zenke M. Automated DNA sequencing: ultrasensitive detection of fluorescent bands during electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4593–4602. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbaugh J. A., Middendorf L. R., Grone D. L., Ruth J. L. Continuous, on-line DNA sequencing using oligodeoxynucleotide primers with multiple fluorophores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5610–5614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. F., Dovichi N. J. Subattomole amino acid analysis by capillary zone electrophoresis and laser-induced fluorescence. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):562–564. doi: 10.1126/science.3140381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S., Karger B. L. High-performance sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel capillary electrophoresis of peptides and proteins. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jun 26;397:409–417. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)85026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S., Najarian D. R., Paulus A., Guttman A., Smith J. A., Karger B. L. Rapid separation and purification of oligonucleotides by high-performance capillary gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9660–9663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S., Najarian D., Smith J. A., Karger B. L. Rapid separation of DNA restriction fragments using capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr. 1988 Dec 23;458:323–333. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)90576-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton S. W., Brownlee R. G. Capillary electrophoresis. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):432–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing A. G., Wallingford R. A., Olefirowicz T. M. Capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem. 1989 Feb 15;61(4):292A–303A. doi: 10.1021/ac00179a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. J., Huang X., Pentoney S. L., Jr, Zare R. N. Capillary electrophoresis. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):224–228. doi: 10.1126/science.242.4876.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S. "Molecular sieve" chromatography on polyacrylamide gels, prepared according to a simplified method. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karger B. L. High-performance capillary electrophoresis. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):641–642. doi: 10.1038/339641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Waterman M. S. Genomic mapping by fingerprinting random clones: a mathematical analysis. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober J. M., Trainor G. L., Dam R. J., Hobbs F. W., Robertson C. W., Zagursky R. J., Cocuzza A. J., Jensen M. A., Baumeister K. A system for rapid DNA sequencing with fluorescent chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):336–341. doi: 10.1126/science.2443975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Beck J., Cahill P., Ciarkowski M., Page G., Glynn S., Hungerman E., Levi E., Ikeda R., McKenney K. A system for on-line detection and resolution of radiolabeled DNA molecules and its application to automated DNA sequence analysis. Biotechniques. 1989 Sep;7(8):866–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S., Dovichi N. J. High-sensitivity fluorescence detector fluorescein isothiocyanate derivatives of amino acids separated by capillary zone electrophoresis. J Chromatogr. 1989 Oct 20;480:141–155. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)84284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



