Abstract
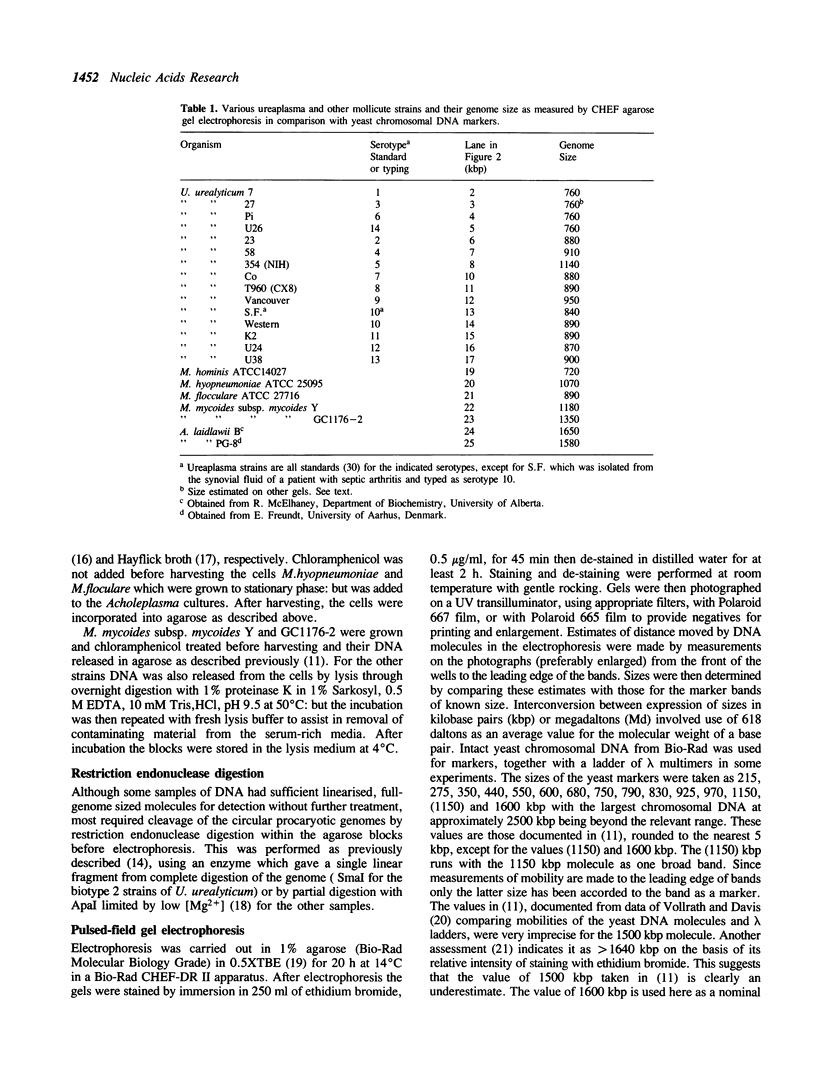
Contour clamped homogeneous field (CHEF) agarose gel electrophoresis (AGE), ramped to give linear separation of DNA molecules of 600-1600 kilobase pairs (kbp), was used to determine mobilities for full-sized genomic DNA of the serotype standard strains of the human genital mollicutes, Ureaplasma urealyticum relative to yeast chromosomal DNA markers. Indicated genome sizes (in kbp) were 760 for the four biotype 1 strains and 840-1140 for eleven biotype 2 strains. Other estimates were: 720 for Mycoplasma hominis, 1070 for Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, 890 for Mycoplasma flocculare, 1180 and 1350 for Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides Y and GC1176-2, respectively, and 1650 and 1580 for Acholeplasma laidlawii B and PG 8, respectively. These data supplement previous evidence from CHEF AGE that the genomes of the Mycoplasmataceae are diverse in size with some larger than previously estimated from DNA renaturation kinetics.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertsen H. M., Le Paslier D., Abderrahim H., Dausset J., Cann H., Cohen D. Improved control of partial DNA restriction enzyme digest in agarose using limiting concentrations of Mg++. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):808–808. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bak A. L., Black F. T., Christiansen C., Freundt E. A. Genome size of mycoplasmal DNA. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1209–1210. doi: 10.1038/2241209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bak A. L., Black F. T. DNA base composition of human T strain mycoplasmas. Nature. 1968 Sep 7;219(5158):1044–1045. doi: 10.1038/2191044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergemann A. D., Whitley J. C., Finch L. R. Homology of mycoplasma plasmid pADB201 and staphylococcal plasmid pE194. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):593–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.593-595.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Smith C. L., Mathew M. K. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of very large DNA molecules. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:287–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks B. G., Pyle L. E., Finch L. R. A physical map of the genome of Ureaplasma urealyticum 960T with ribosomal RNA loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6713–6719. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis N. F. Some recommendations concerning primary isolation of Mycoplasma suipneumoniae and Mycoplasma flocculare a survey. Nord Vet Med. 1975 Jun;27(6):337–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frutos R., Pages M., Bellis M., Roizes G., Bergoin M. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis determination of the genome size of obligate intracellular bacteria belonging to the genera Chlamydia, Rickettsiella, and Porochlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4511–4513. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4511-4513.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Weiss E. Lack of deoxyribonucleic acid homology between species of the genus Chlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1421–1423. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1421-1423.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J. Anomalous values of Mycoplasma genomes sizes determined by pulse-field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1268–1268. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew M. K., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. High-resolution separation and accurate size determination in pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA. 1. DNA size standards and the effect of agarose and temperature. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9204–9210. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Rogul M., Wittler R. G. Molecular genetic studies of relationships among mycoplasma, L-forms and bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouches C., Taylor-Robinson D., Stipkovits L., Bove J. M. Comparison of human and animal Ureaplasmas by one- and two-dimensional protein analysis on polyacrylamide slab gel. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Sep-Oct;132B(2):171–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimark H. Heterogeneity among the mycoplasma and relationships to bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):31–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Corcoran L. N., Cocks B. G., Bergemann A. D., Whitley J. C., Finch L. R. Pulsed-field electrophoresis indicates larger-than-expected sizes for mycoplasma genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6015–6025. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Finch L. R. A physical map of the genome of Mycoplasma mycoides subspecies mycoides Y with some functional loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6027–6039. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Finch L. R. Preparation and FIGE separation of infrequent restriction fragments from Mycoplasma mycoides DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2263–2268. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Barile M. F., Harasawa R., Amikam D., Glaser G. Characterization of the mycoplasma genome. Yale J Biol Med. 1983 Sep-Dec;56(5-6):357–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Molecular biology and genetics of mycoplasmas (Mollicutes). Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):419–455. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.419-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A. Bromothymol blue broth: improved medium for detection of Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain mycoplasma). J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):127–132. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.127-132.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Chen M. H. Effects of manganese on the growth and morphology of Ureaplasma urealyticum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):857–864. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.857-864.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. A., Stemke G. W. Modified metabolic inhibition test for serotyping strains of Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain Mycoplasma). J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jun;9(6):673–676. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.6.673-676.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. L., Morowitz H. J. Partial purification of native rRNA and tRNA cistrons from mycoplasma sp. (Kid). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1282–1289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley J. C., Finch L. R. Location of sites of transposon Tn916 insertion in the Mycoplasma mycoides genome. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6870–6872. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6870-6872.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



