Abstract
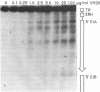
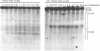
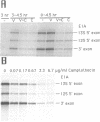
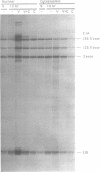
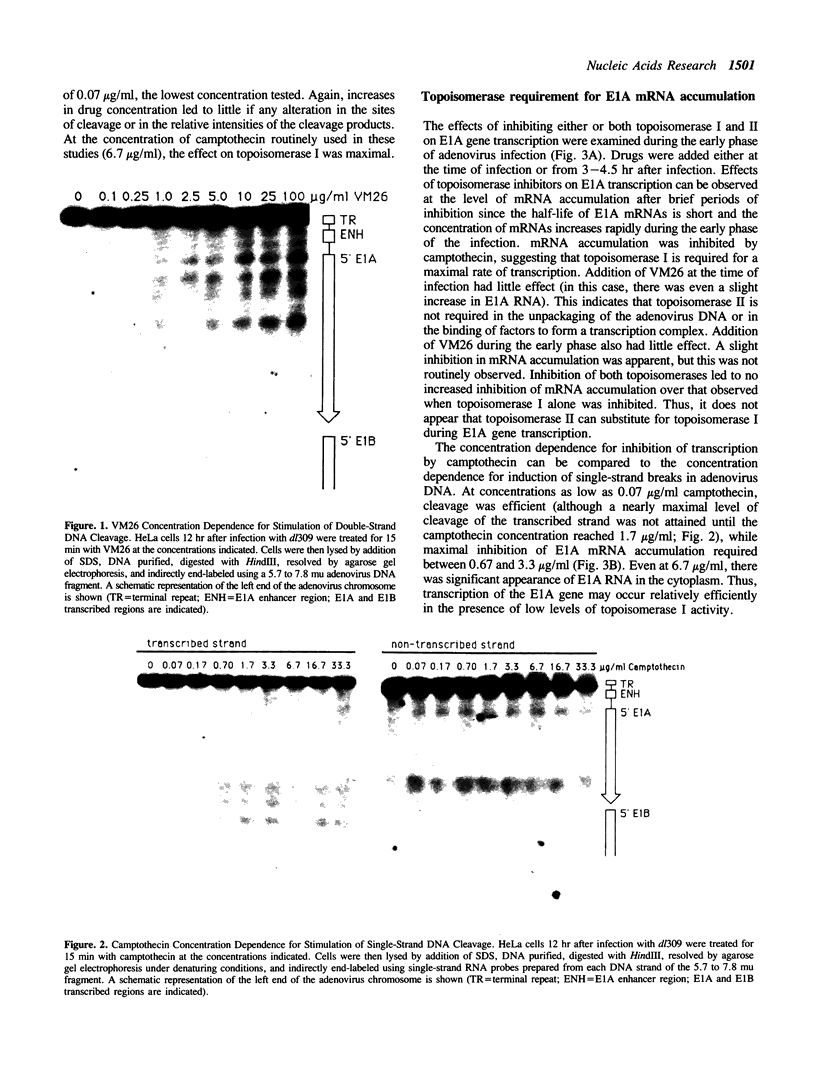
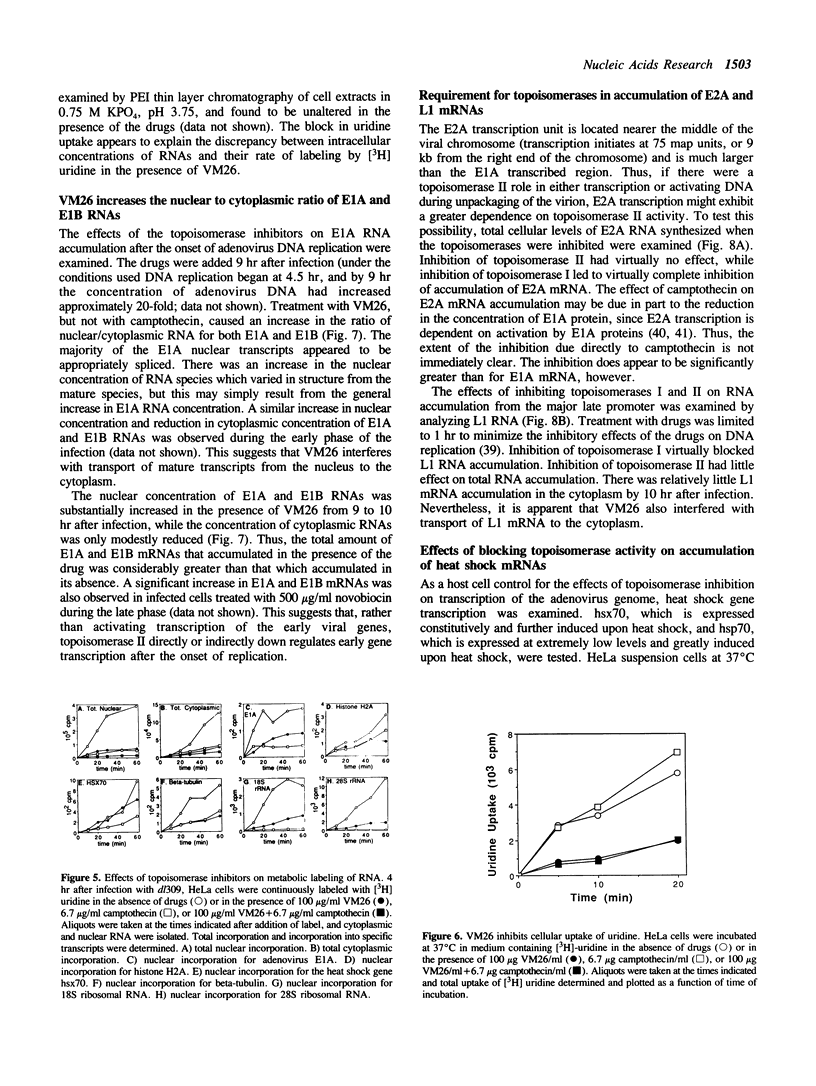
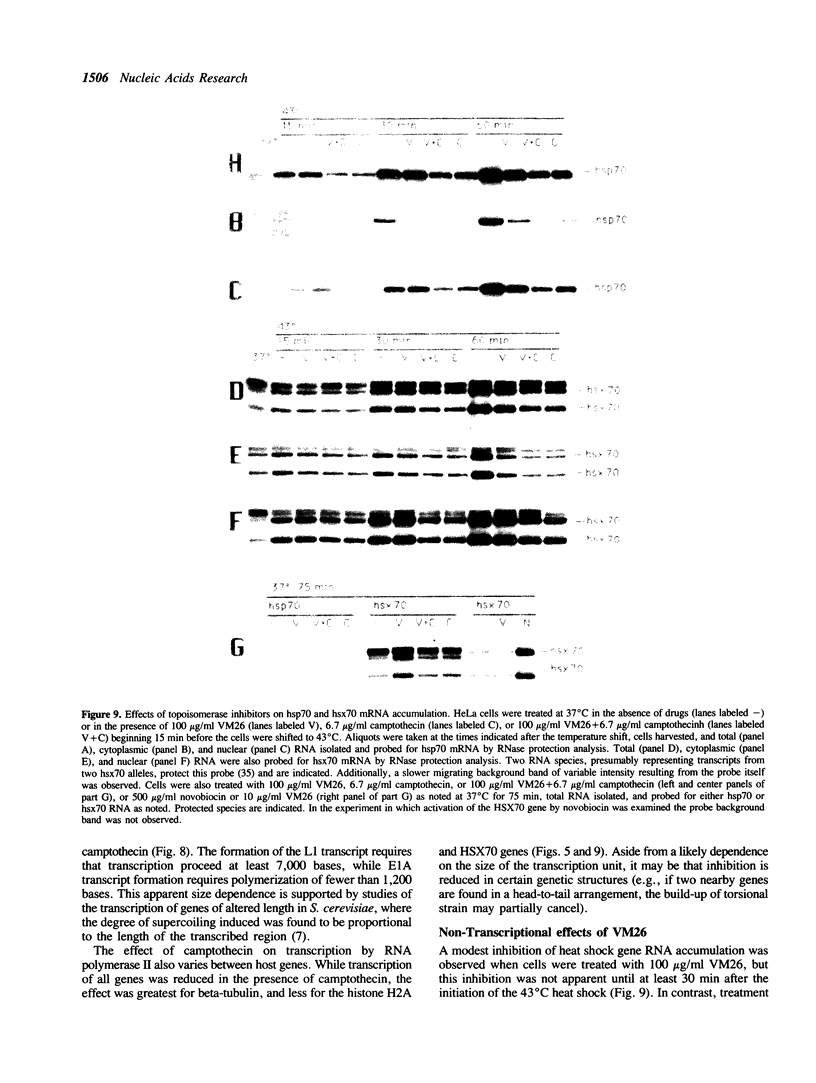
The requirements for topoisomerases in transcription of adenovirus and HeLa cell genes were analyzed using drugs that specifically inhibit either topoisomerases I or II. Cleavage of viral DNA by topoisomerases in the presence of either camptothecin or VM26 was used to determine drug concentrations that led to maximal inhibition of ligation in the cleavage and ligation step of topoisomerase I or II respectively. Inhibition of topoisomerase II with VM26 did not cause a direct reduction in transcription of adenoviral genes or HeLa cell heat shock genes. VM26 did, however, interfere with other cellular processes. It reduced nucleoside uptake into HeLa cells from the medium, and it altered the normal nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio of specific RNAs. Treatment of cells with camptothecin to inhibit topoisomerase I reduced but did not abolish transcription of viral and HeLa cell genes. Transcription mediated by both RNA polymerases I and II was reduced. Topoisomerase II did not appear to substitute for topoisomerase I in transcription since treatment of cells with VM26 and camptothecin did not reduce transcript accumulation relative to cells treated with camptothecin alone.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman P., Glover C. V., Osheroff N. Phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II by casein kinase II: modulation of eukaryotic topoisomerase II activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3164–3168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., DiNardo S., Voelkel-Meiman K., Sternglanz R. Need for DNA topoisomerase activity as a swivel for DNA replication for transcription of ribosomal RNA. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):414–416. doi: 10.1038/326414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Sternglanz R. Transcription-dependent DNA supercoiling in yeast DNA topoisomerase mutants. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee P. K., Vayda M. E., Flint S. J. Adenoviral protein VII packages intracellular viral DNA throughout the early phase of infection. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1633–1644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. L., Yang L., Rowe T. C., Halligan B. D., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Nonintercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13560–13566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Bresnahan D., Thompson S., Sealy L., Chalkley R. Novobiocin precipitates histones at concentrations normally used to inhibit eukaryotic type II topoisomerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3671–3686. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egyházi E., Durban E. Microinjection of anti-topoisomerase I immunoglobulin G into nuclei of Chironomus tentans salivary gland cells leads to blockage of transcription elongation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4308–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman R., Brutlag D. L. Expression of the Drosophila type II topoisomerase is developmentally regulated. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):560–565. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmann G., Pflugfelder G., Steiner E. K., Javaherian K., Howard G. C., Wang J. C., Elgin S. C. Drosophila DNA topoisomerase I is associated with transcriptionally active regions of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6958–6962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Elgin S. C. Localization of specific topoisomerase I interactions within the transcribed region of active heat shock genes by using the inhibitor camptothecin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):141–148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Lis J. T. Protein-DNA cross-linking reveals dramatic variation in RNA polymerase II density on different histone repeats of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3341–3344. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Pflugfelder G., Wang J. C., Lis J. T. Topoisomerase I interacts with transcribed regions in Drosophila cells. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlaczky G., Praznovszky T., Sófi J., Udvardy A. Intracellular forms of Drosophila topoisomerase II detected with monoclonal antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10013–10023. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S., Udvardy A., Schedl P. Novobiocin blocks the Drosophila heat shock response. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):13–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90277-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Earnshaw W. C. Topoisomerase II: A specific marker for cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2569–2581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Hittelman W. N., Earnshaw W. C. Differential expression of DNA topoisomerases I and II during the eukaryotic cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1086–1090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Hertzberg R., Hecht S., Liu L. F. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14873–14878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. Proliferation-dependent regulation of DNA topoisomerase II in cultured human cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):3230–3235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaxel C., Kohn K. W., Pommier Y. Topoisomerase I interaction with SV40 DNA in the presence and absence of camptothecin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11157–11170. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen E., Mollerup S., Thomsen B., Bonven B. J., Bolund L., Westergaard O. Sequence-dependent effect of camptothecin on human topoisomerase I DNA cleavage. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90462-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long B. H., Musial S. T., Brattain M. G. DNA breakage in human lung carcinoma cells and nuclei that are naturally sensitive or resistant to etoposide and teniposide. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):3809–3816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minocha A., Long B. H. Inhibition of the DNA catenation activity of type II topoisomerase by VP16-213 and VM26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90454-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins R., Miskimins W. K., Bernstein H., Shimizu N. Epidermal growth factor-induced topoisomerase(s). Intracellular translocation and relation to DNA synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jun;146(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M., Schaack J., Baim S. B., Morimoto R. I., Shenk T. Induced heat shock mRNAs escape the nucleocytoplasmic transport block in adenovirus-infected HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4505–4512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Cho K. R., Hsiang Y. H., Liu L. F., Coffey D. S. Growth-related elevations of DNA topoisomerase II levels found in Dunning R3327 rat prostatic adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 15;47(12):3246–3250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne B. I., Guarente L. Transcription by RNA polymerase II induces changes of DNA topology in yeast. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):766–772. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Shelton E. R., Brutlag D. L. DNA topoisomerase II from Drosophila melanogaster. Relaxation of supercoiled DNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9536–9543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Shelton E. R., Brutlag D. L. DNA topoisomerase II from Drosophila melanogaster. Relaxation of supercoiled DNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9536–9543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Couto E., Kroll D. J. Camptothecin inhibits hsp 70 heat-shock transcription and induces DNA strand breaks in hsp 70 genes in Drosophila. NCI Monogr. 1987;(4):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. In vivo localization of DNA topoisomerase II cleavage sites on Drosophila heat shock chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):985–992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra R. A., Huberman J. A. Both DNA topoisomerases I and II relax 2 micron plasmid DNA in living yeast cells. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90538-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Schedl P., Shenk T. Topoisomerase I and II cleavage of adenovirus DNA in vivo: both topoisomerase activities appear to be required for adenovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):78–85. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.78-85.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Trölltsch D., Friese U., Bachmann M., Müller W. E. Mature mRNA is selectively released from the nuclear matrix by an ATP/dATP-dependent mechanism sensitive to topoisomerase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8917–8925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan D. M., Latham M. D., Ross W. E. Proliferation-dependent topoisomerase II content as a determinant of antineoplastic drug action in human, mouse, and Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):3973–3979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao Y. P., Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. Transcription-driven supercoiling of DNA: direct biochemical evidence from in vitro studies. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90989-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P., Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Topoisomerase II cleavage in chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 20;191(2):231–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90260-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Morino K., Uzawa S., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. Cloning and sequencing of Schizosaccharomyces pombe DNA topoisomerase I gene, and effect of gene disruption. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9727–9739. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. L., Hsu M. T. Involvement of topoisomerases in replication, transcription, and packaging of the linear adenovirus genome. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):691–699. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.691-699.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi M., Nomura M. Deficiency in both type I and type II DNA topoisomerase activities differentially affect rRNA and ribosomal protein synthesis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Curr Genet. 1988 Apr;13(4):305–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00424424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Rowe T. C., Liu L. F. Identification of DNA topoisomerase II as an intracellular target of antitumor epipodophyllotoxins in simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5872–5876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Rowe T. C., Nelson E. M., Liu L. F. In vivo mapping of DNA topoisomerase II-specific cleavage sites on SV40 chromatin. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. Involvement of DNA topoisomerase I in transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1060–1064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]