Abstract
We have designed a computer program which rapidly scans nucleic acid sequences to select all possible pairs of oligonucleotides suitable for use as primers to direct efficient DNA amplification by the polymerase chain reaction. This program is based on a set of rules which define in generic terms both the sequence composition of the primers and the amplified region of DNA. These rules (1) enhance primer-to-target sequence hybridization avidity at critical 3'-end extension initiation sites, (2) facilitate attainment of full length extension during the 72 degrees C phase, by minimizing generation of incomplete or nonspecific product and (3) limit primer losses occurring from primer-self or primer-primer homologies. Three examples of primer sets chosen by the program that correctly amplified the target regions starting from RNA are shown. This program should facilitate the rapid selection of effective and specific primers from long gene sequences while providing a flexible choice of various primers to focus study on particular regions of interest.
Full text
PDF

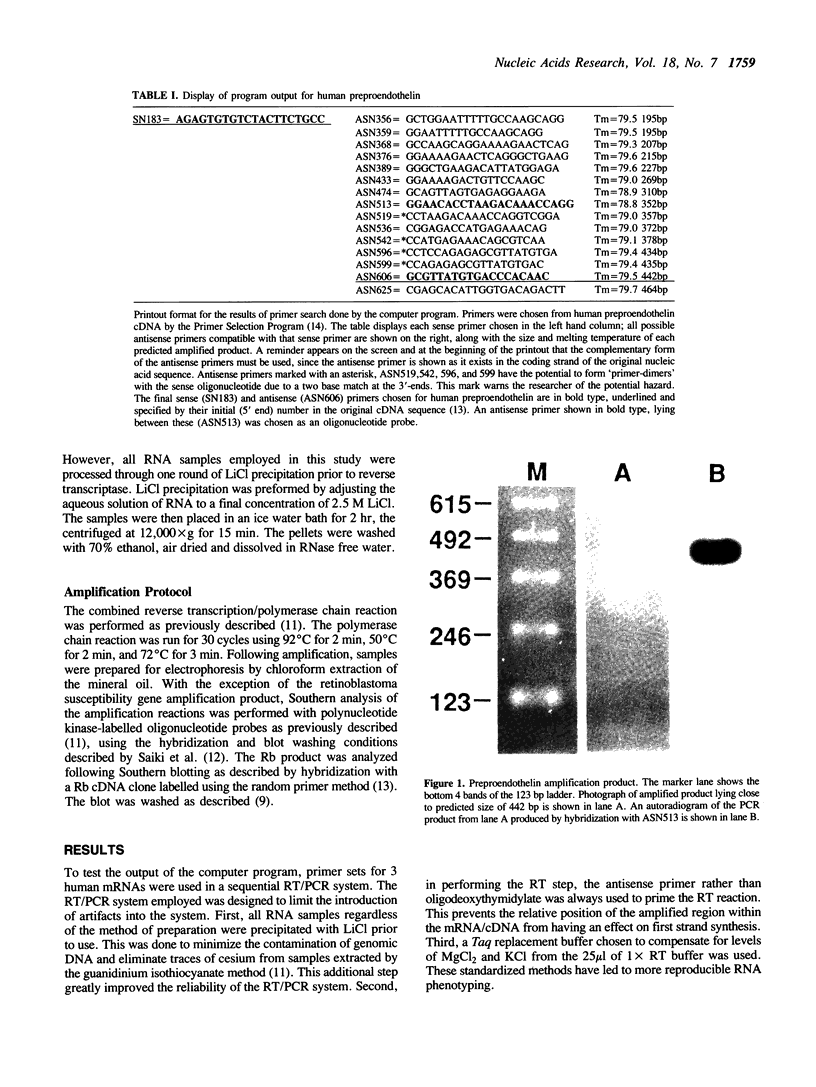


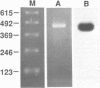
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck Y., Oren R., Amit B., Levanon A., Gorecki M., Hartman J. R. Human Mn superoxide dismutase cDNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9076–9076. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. J., Huesca-Contreras M., Dosch H. M., Pan S. Rapid amplification of complementary DNA from small amounts of unfractionated RNA. Anal Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;177(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Yanagisawa M., Ohkubo S., Kimura C., Kosaka T., Inoue A., Ishida N., Mitsui Y., Onda H., Fujino M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding the precursor of a human endothelium-derived vasoconstrictor peptide, endothelin: identity of human and porcine endothelin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 25;231(2):440–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80867-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen H., Mestan J., Mittnacht S., Dieffenbach C. W. Beta interferon subtype 1 induction by tumor necrosis factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3037–3042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R., Hong F., Young L. J., Shew J. Y., Lee E. Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: cloning, identification, and sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.3823889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., Laird C. D., McCarthy B. J. Nucleic acid reassociation in formamide. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3289–3295. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oste C. Polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):162–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Mark D., Banda M. J., Werb Z. Wound macrophages express TGF-alpha and other growth factors in vivo: analysis by mRNA phenotyping. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):708–712. doi: 10.1126/science.3041594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Wang A., Mark D., Werb Z. Novel method for studying mRNA phenotypes in single or small numbers of cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Jan;39(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. F. Optimization strategies for the polymerase chain reaction. Biotechniques. 1989 Jul-Aug;7(7):762–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]