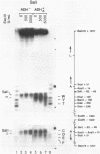
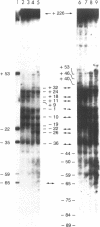
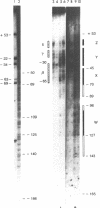
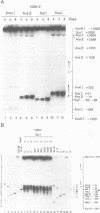
Abstract
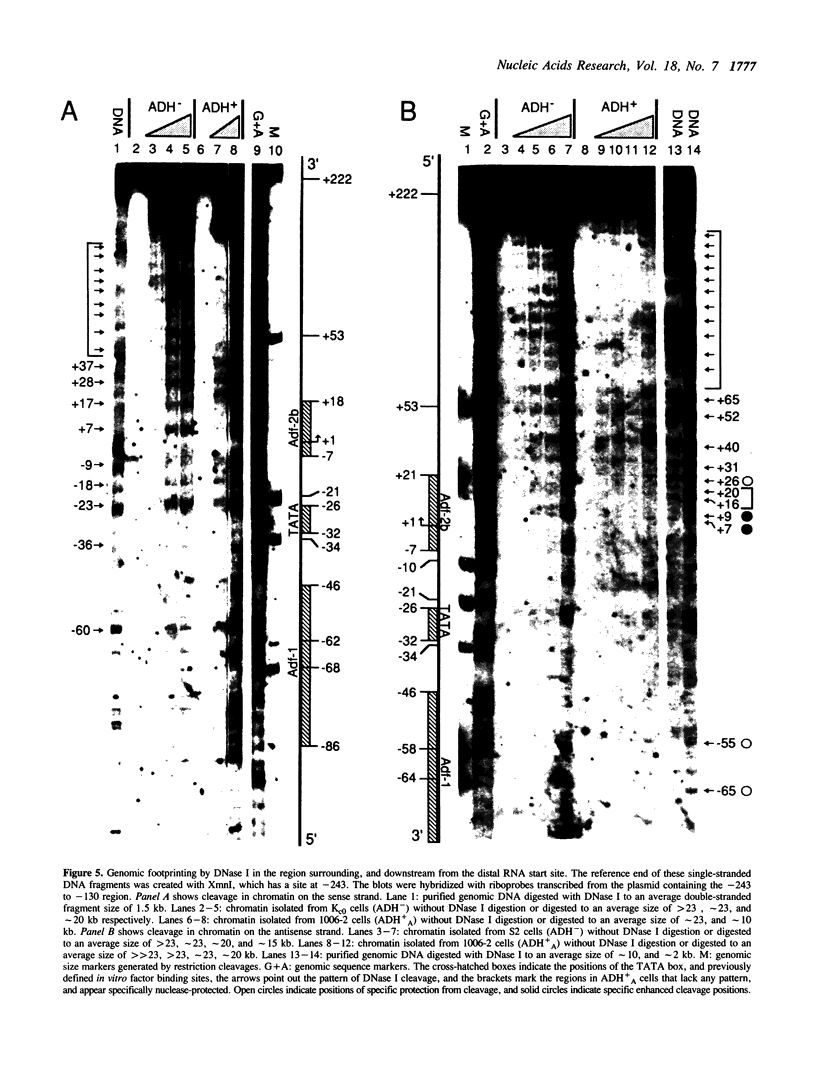
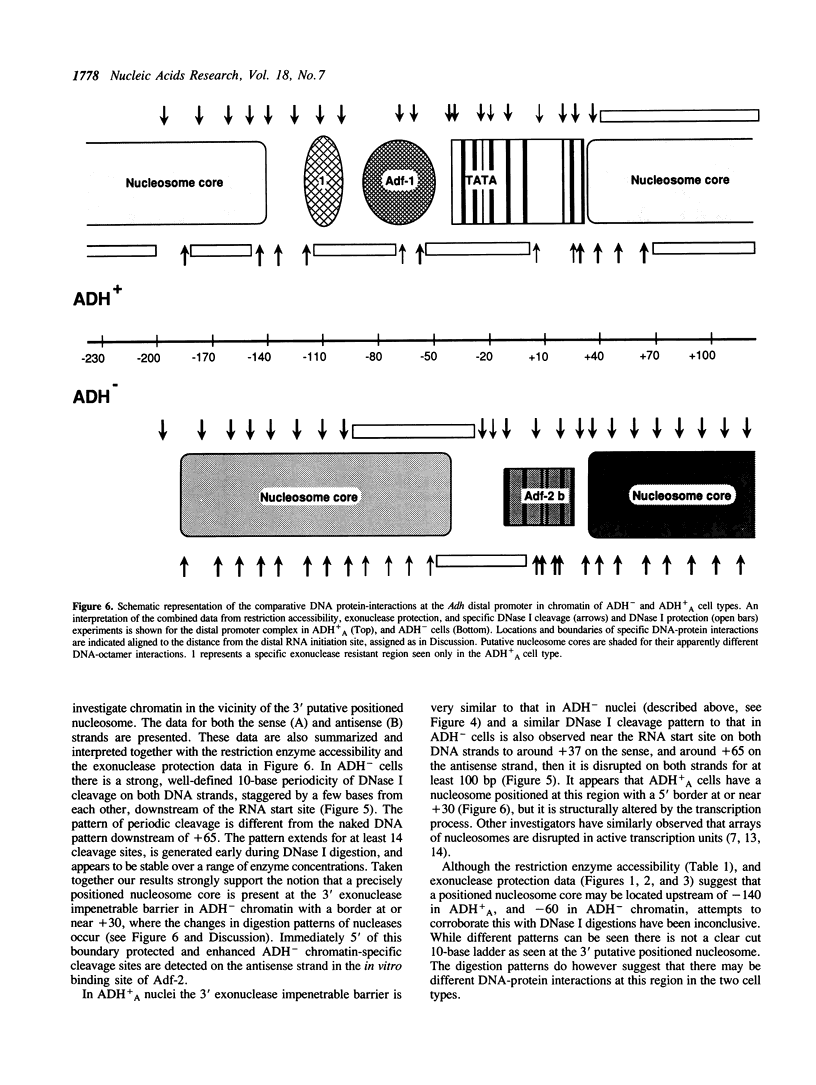
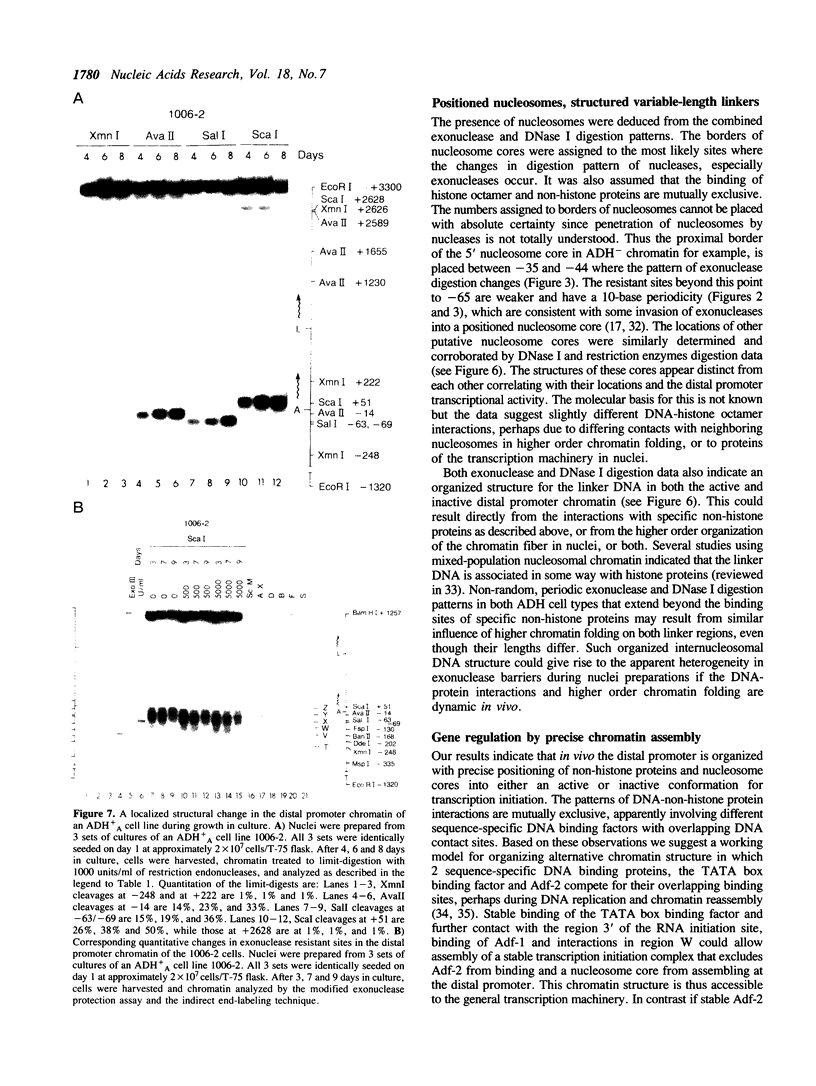
Chromatin at the Drosophila Adh distal promoter displays an ordered but different conformation in different cell types as detected by a modified exonuclease protection assay and accessibility to endonucleases. In cells not transcribing Adh (ADH-) sequences between -40 to +30 of the distal RNA initiation site exist as a DNA linker between positioned nucleosomes, and appear to interact with a specific DNA-binding protein. In contrast, a longer linker DNA, from -140 to +30, is bound in a multi-protein transcription initiation complex in cells that specifically transcribe the distal (adult) ADH RNA (ADH+A). These DNA-protein interactions can account for a localized open chromatin structure at the distal promoter in ADH+A cells. The observed mutually exclusive patterns of DNA-protein interactions in the linkers of different ADH cell types between -40 to +30 suggest a model for organizing alternative chromatin structure associated with gene regulation. Two DNA binding proteins, one being a TATA box binding factor, compete for overlapping sites to allow either assembly of a transcription initiation complex and transcription, or positioning of nucleosomes for stable repression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almer A., Hörz W. Nuclease hypersensitive regions with adjacent positioned nucleosomes mark the gene boundaries of the PHO5/PHO3 locus in yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2681–2687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almer A., Rudolph H., Hinnen A., Hörz W. Removal of positioned nucleosomes from the yeast PHO5 promoter upon PHO5 induction releases additional upstream activating DNA elements. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2689–2696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Ayer S., McKeon J., Ewel A., Huang J. Roles of cis-acting elements and chromatin structure in Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7903–7920. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Dray J. F. Cloned Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase genes are correctly expressed after transfection into Drosophila cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1701–1705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors and the control of Drosophila development. Trends Genet. 1989 Nov;5(11):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L. Developmental switch in chromatin structure associated with alternate promoter usage in the Drosophila melanogaster alcohol dehydrogenase gene. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3097–3101. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V., Gralla J., Martinson H. G. DNA sequence directs placement of histone cores on restriction fragments during nucleosome formation. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1068–1074. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin V., Maniatis T. Role of transcriptional interference in the Drosophila melanogaster Adh promoter switch. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):279–282. doi: 10.1038/337279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between RNA polymerase II, factors, and template leading to accurate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2509–2516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Dietz T. J., Elgin S. C. TATA box-dependent protein-DNA interactions are detected on heat shock and histone gene promoters in nuclear extracts derived from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3204–3214. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., Tjian R. Temporal pattern of alcohol dehydrogenase gene transcription reproduced by Drosophila stage-specific embryonic extracts. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):410–415. doi: 10.1038/331410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Cloning exons of mapping of transcription: characterization of the Drosophila melanogaster alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4735–4752. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M. E., Rooney T. F., Austin R. H. Evidence for kinks in DNA folding in the nucleosome. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):554–557. doi: 10.1038/328554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Lutter L. C. The helical periodicity of DNA on the nucleosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4267–4283. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman M. Nucleotide polymorphism at the alcohol dehydrogenase locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):412–417. doi: 10.1038/304412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladiges W. C., Raff R. F., Brown S., Deeg H. J., Storb R. The canine major histocompatibility complex. Supertypic specificities defined by the primed lymphocyte test (PLT). Immunogenetics. 1984;19(4):359–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00345410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. DNA-DNA gyrase complex: the wrapping of the DNA duplex outside the enzyme. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):979–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockett T. J., Ashburner M. Temporal and spatial utilization of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene promoters during the development of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):430–437. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Precise location of DNase I cutting sites in the nucleosome core determined by high resolution gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):41–56. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchionni M., Gilbert W. The triosephosphate isomerase gene from maize: introns antedate the plant-animal divergence. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90867-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse R. H., Simpson R. T. DNA in the nucleosome. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):285–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prunell A., Kornberg R. D. Variable center to center distance of nucleosomes in chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 25;154(3):515–523. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay N. Deletion analysis of a DNA sequence that positions itself precisely on the nucleosome core. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90389-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. Sequence-specific positioning of nucleosomes over the steroid-inducible MMTV promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2321–2328. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D., Weintraub H. Nucleosomal DNA is digested to repeats of 10 bases by exonuclease III. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simcox A. A., Sobeih M. M., Shearn A. Establishment and characterization of continuous cell lines derived from temperature-sensitive mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Jan;11(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01534735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Melchior W., Jr, Felsenfeld G. DNAase I, DNAase II and staphylococcal nuclease cut at different, yet symmetrically located, sites in the nucleosome core. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):611–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Reeder R. H. The nucleotide sequence of the initiation and termination sites for ribosomal RNA transcription in X. laevis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):485–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Protein/DNA architecture of the DNase I hypersensitive region of the Drosophila hsp26 promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2191–2201. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly and propagation of repressed and depressed chromosomal states. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Abmayr S. M., Cromlish W. A., Roeder R. G. Transcriptional regulation by the immediate early protein of pseudorabies virus during in vitro nucleosome assembly. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]