Abstract
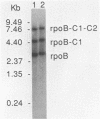
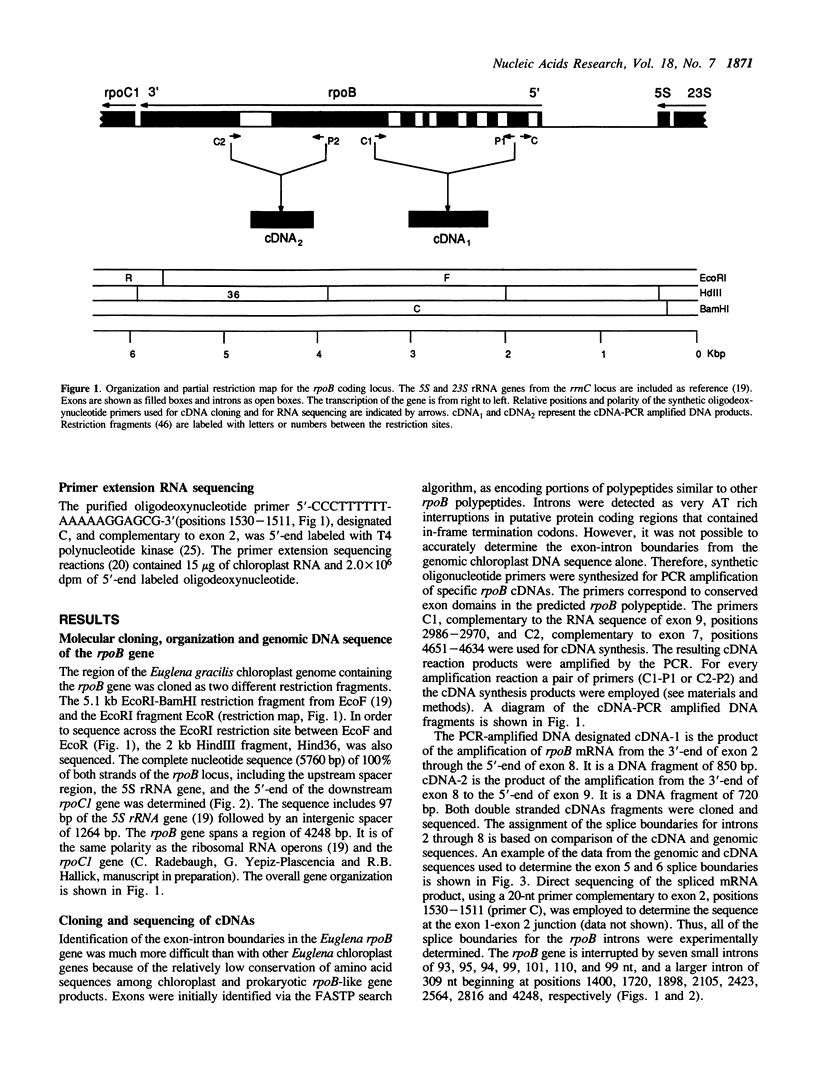
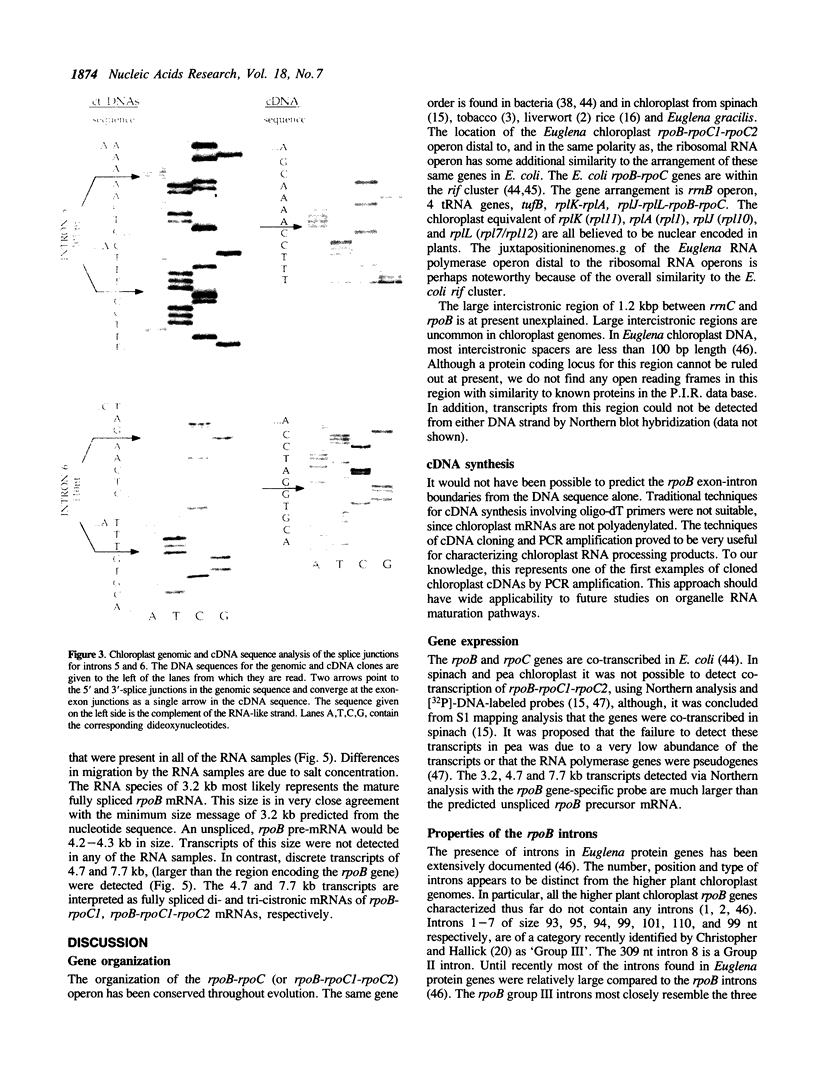
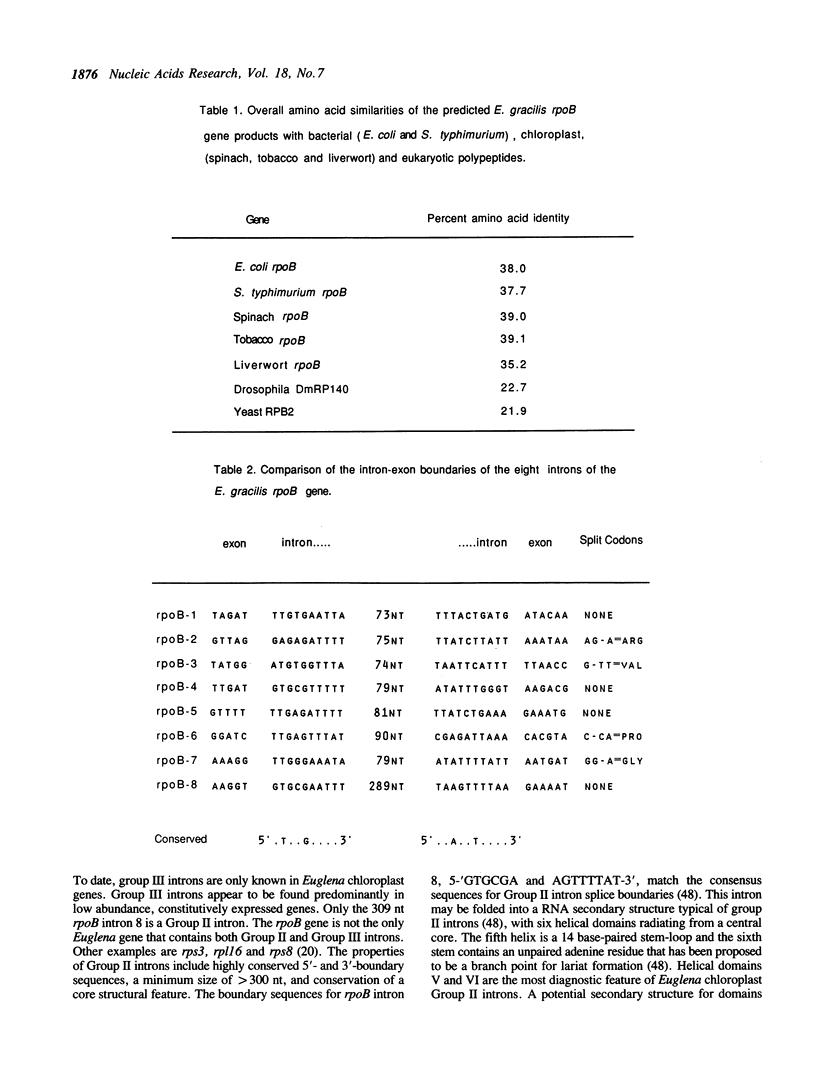
The rpoB gene coding for a beta-like subunit of the chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase has been located on the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis distal to the rrnC ribosomal RNA operon. We have determined 5760 base-pairs of DNA sequence, including 97 bp of the 5S rRNA gene, an intergenic spacer of 1264 bp, the rpoB gene of 4249 bp, 84 bp spacer and 67 bp of the rpoC1 gene. The rpoB gene is of the same polarity as the rRNA operons. The organization of the rpoB and rpoC genes resembles the E. coli rpoB-rpoC and higher plant chloroplast rpoB-rpoC1-rpoC2 operons. The Euglena rpoB gene (1082 codons) encodes a polypeptide with a predicted molecular weight of 124,288. The rpoB gene is interrupted by seven Group III introns of 93, 95, 94, 99, 101, 110 and 99 bp respectively and a Group II intron of 309 bp. All other known rpoB genes lack introns. All the exon-exon junctions were experimentally determined by cDNA cloning and sequencing or direct primer extension RNA sequencing. Transcripts from the rpoB locus were characterized by Northern hybridization. Fully-spliced, monocistronic rpoB mRNA, as well as rpoB-rpoC1 and rpoB1-rpoC1-rpoC2 mRNAs were identified.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Cushman J. C., Price C. A., Hallick R. B. Organization of ribosomal protein genes rpl23, rpl2, rps19, rpl22 and rps3 on the Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome. Curr Genet. 1988 Sep;14(3):275–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00376748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L., Cadena D. L., Ahearn J. M., Jr, Dahmus M. E. A unique structure at the carboxyl terminus of the largest subunit of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7934–7938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani M., Benatti L., Lorenzetti R., Martini D., Minganti C., Sassano M., Sidoli A., Soria M. A DNA sequence from Saponaria officinalis is similar to various RNA polymerase genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):3103–3103. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.3103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenburg D., Dworniczak B., Faust D. M., Bautz E. K. RNA polymerase II of Drosophila. Relation of its 140,000 Mr subunit to the beta subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90496-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grachev M. A., Lukhtanov E. A., Mustaev A. A., Zaychikov E. F., Abdukayumov M. N., Rabinov I. V., Richter V. I., Skoblov Y. S., Chistyakov P. G. Studies of the functional topography of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. A method for localization of the sites of affinity labelling. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):577–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf L., Roux E., Stutz E., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of a Euglena gracilis chloroplast gene coding for the 16S rRNA: homologies to E. coli and Zea mays chloroplast 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6369–6381. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Greenberg B. M., Zurawski G., Prescott D. M., Hallick R. B. Biosynthesis of chloroplast transfer RNA in a spinach chloroplast transcription system. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):815–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick R. B., Chelm B. K., Gray P. W., Orozco E. M., Jr Use of aurintricarboxylic acid as an inhibitor of nucleases during nucleic acid isolation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3055–3064. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka J., Shimada H., Whittier R., Ishibashi T., Sakamoto M., Mori M., Kondo C., Honji Y., Sun C. R., Meng B. Y. The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02464880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G. S., Holton T. A., Whitfield P. R., Bottomley W. Spinach chloroplast rpoBC genes encode three subunits of the chloroplast RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):639–654. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karabin G. D., Narita J. O., Dodd J. R., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal RNA transcription units. Nucleotide sequence polymorphism in 5 S rRNA genes and 5 S rRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14790–14796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerbs S., Bräutigam E., Parthier B. Polypeptides of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of spinach chloroplasts: characterization by antibody-linked polymerase assay and determination of sites of synthesis. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1661–1666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03834.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little M. C., Hallick R. B. Chloroplast rpoA, rpoB, and rpoC genes specify at least three components of a chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase active in tRNA and mRNA transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14302–14307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Knuchel-Aegerter C., Stutz E. Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA: the untranslated leader of tufA-ORF206 gene contains an intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7809–7822. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Conrad B. Improved programs for DNA and protein sequence analysis on the IBM personal computer and other standard computer systems. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):443–454. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita J. O., Rushlow K. E., Hallick R. B. Characterization of a Euglena gracilis chloroplast RNA polymerase specific for ribosomal RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11194–11199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Morgan E. A. Genetics of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:297–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohme M., Tanaka M., Chunwongse J., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. A tobacco chloroplast DNA sequence possibly coding for a polypeptide similar to E. coli RNA polymerase beta-subunit. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 5;200(1):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80516-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Monastyrskaya G. S., Gubanov V. V., Guryev S. O., Chertov OYu, Modyanov N. N., Grinkevich V. A., Makarova I. A., Marchenko T. V., Polovnikova I. N. The primary structure of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Nucleotide sequence of the rpoB gene and amino-acid sequence of the beta-subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun 1;116(3):621–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozeki H., Ohyama K., Inokuchi H., Fukuzawa H., Kohchi T., Sano T., Nakahigashi K., Umesono K. Genetic system of chloroplasts. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:791–804. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purton S., Gray J. C. The plastid rpoA gene encoding a protein homologous to the bacterial RNA polymerase alpha subunit is expressed in pea chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):77–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00330945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow K. E., Orozco E. M., Jr, Lipper C., Hallick R. B. Selective in vitro transcription of Euglena chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes by a transcriptionally active chromosome. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3786–3792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sijben-Müller G., Hallick R. B., Alt J., Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Spinach plastid genes coding for initiation factor IF-1, ribosomal protein S11 and RNA polymerase alpha-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1029–1044. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steege D. A., Graves M. C., Spremulli L. L. Euglena gracilis chloroplast small subunit rRNA. Sequence and base pairing potential of the 3' terminus, cleavage by colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10430–10439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D., Nonet M., Young R. A. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases have homologous core subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1192–1196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Nomura M. Organization of genes for transcription and translation in the rif region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):584–594. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.584-594.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]