Abstract
Time to flowering has an important impact on yield and has been a key trait in the domestication of crop plants and the spread of agriculture. In 1961, the cultivar Mari (mat-a.8) was the very first induced early barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) mutant to be released into commercial production. Mari extended the range of two-row spring barley cultivation as a result of its photoperiod insensitivity. Since its release, Mari or its derivatives have been used extensively across the world to facilitate short-season adaptation and further geographic range extension. By exploiting an extended historical collection of early-flowering mutants of barley, we identified Praematurum-a (Mat-a), the gene responsible for this key adaptive phenotype, as a homolog of the Arabidopsis thaliana circadian clock regulator Early Flowering 3 (Elf3). We characterized 87 induced mat-a mutant lines and identified >20 different mat-a alleles that had clear mutations leading to a defective putative ELF3 protein. Expression analysis of HvElf3 and Gigantea in mutant and wild-type plants demonstrated that mat-a mutations disturb the flowering pathway, leading to the early phenotype. Alleles of Mat-a therefore have important and demonstrated breeding value in barley but probably also in many other day-length-sensitive crop plants, where they may tune adaptation to different geographic regions and climatic conditions, a critical issue in times of global warming.
Keywords: earliness, food security, timing of flowering, molecular breeding, synteny
In all plant species, time to flowering is regulated by seasonal cues that include temperature and photoperiod, and it is tightly connected to the requirement for vernalization and the circadian clock (1–3). As early as the 1930s, Russian plant breeders identified the importance of early flowering as a breeding target (4), recognizing that, although earliness may limit high productivity in highly fertile areas because of inefficient use of the entire growing season, it allows marginal environments with a short growing season to enter into cultivation. These generally low-yielding areas constitute the majority of the land used for agriculture and therefore offer the greatest opportunity to substantially increase worldwide food production (5). Early cultivars are important for farmers, allowing them to manage the harvest by growing crops that mature at different times and establish an effective crop rotation.
Induced mutagenesis of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) was reported in 1928 (6), only a year after Muller reported that ionizing irradiation could increase the mutation frequency in Drosophila (7). This finding promoted barley as a model plant and one of the first crops in which mutations were induced for applied purposes (8). In the 1940s, it was established that time to flowering in barley could easily be modified by physical or chemical mutagenesis (8). Although late maturity occurred more frequently in mutant populations, screening for early (or praematurum) mutants was much easier (9) and potentially more beneficial. Between 1941 and 1988, >1,200 early-flowering barley mutants were isolated at the Swedish Seed Association (later Svalöf AB), Sweden. Allelism tests using 195 mutants distinguished nine complementation groups (Table 1). The praematurum-a (mat-a) mutant group was the largest and covered 85 different alleles. It was also found that mat-a mutants were allelic to a mutant with erect growth, erectoides-o.16 (ert-o.16) (10) and a series of early maturity 8 (eam8) mutants from Japan (11, 12). Like the mat-a lines, ert-o.16, eam8.q, eam8.r, eam8.s, eam8.u, and eam8.v were induced mutants, whereas eam8.k occurred naturally in the cultivars Kinai 5 and Kagoshima Gold, and eam8.w occurred naturally in Early Russian (Fig. 1) (13).
Table 1.
Early-maturity barley mutants and their distribution to nine assigned early-maturity (Mat) loci
| Locus Mat | -a | -b | -c | -d | -e | -f | -g | -h | -i | l.n.d.* |
| Frequency of alleles | 85 | 49 | 31 | 2 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 1,013 |
| Days of heading earlier than wild type | 9 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 |
Shown are the number of early-maturity barley mutants isolated at the Swedish Seed Association (later Svalöf AB), Sweden, 1941–1988 and their distribution to nine assigned early-maturity (Mat) loci.
*l.n.d., locus not determined.
Fig. 1.
Phenotyping of the heading date trait in barley based on appearance of the awns protruding from the flag leaf. (A) One-month-old barley plants carrying the wild-type Mat-a allele (Left) and the recessive mat-a allele (Right). Arrows indicate regions of the main stems around the flag leaf of these two genotypes, which are shown magnified in B and C. (B) The cultivar Bowman. (C) The Bowman backcross-derived line BW290 that carries the eam8.w allele on a 1.5-cM introgressed segment from Early Russian.
Mutant line mat-a.8, under the name Mari, was the very first early barley mutant released as a commercial cultivar (in 1961) (14). It was derived as a one-step X-ray mutant 10 y earlier. In field trials in Sweden and under long-day conditions in phytotron experiments, it flowered 8–10 d earlier than the mother cultivar Bonus (14). In moderate day length, heading was found to be as much as 3 wk earlier (14), and field studies in Japan showed that heading of mat-a.8 in a Bonus or a Tochigi Golden genetic background was at least 17 d earlier than for the parental cultivars (15). The remarkable earliness, combined with resistance to lodging, of Mari allowed two-row barley to break through a climate barrier, thereby extending barley cultivation into Northern Scandinavia and Iceland. However, due to its photoperiod insensitivity, Mari can also be grown near the Equator as a day-length-neutral plant. Its daughter cultivar Mona is high yielding even under tropical conditions at altitudes of ∼350 m in Colombia (16). Consequently, breeders servicing a wide geographic range have frequently used Mari or its derivatives in their programs (Table S1).
Environmental stability is now prioritized by global organizations that seek to maintain crop yields under increasingly variable climatic conditions, reduced inputs, and expansion into marginal lands. Consequently, the mat-a.8 mutant allele of Mari has once again emerged as a potentially valuable breeding trait. In this study, which was enabled by research conducted on flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana and by a collection of early-flowering barley mutants that were generated before the era of molecular biology, we identified and characterized the Mat-a gene and >20 mat-a mutant alleles at the DNA level.
Results
Fine Mapping of Mat-a and Identification of Early Flowering 3 as a Candidate Gene.
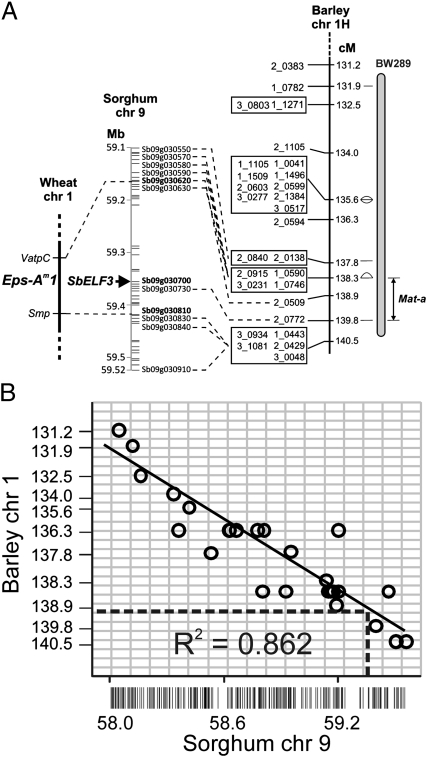
The natural early allele eam8.k of Mat-a has been mapped to the end of the long arm of barley chromosome 1H, 11.4 cM distal to the third outer glume 1 (trd1) locus, 20.9 cM distal to the Black lemma and pericarp 1 (Blp1) locus (12), and proximal to the RFLP marker ABG055 (GrainGenes; http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/GG2/). In wheat, a similar flowering phenotype, called Earliness per se (Eps), has been mapped as Eps-Am1 to a similar region between wheat chromosome 1A markers Smp and VatpC (Fig. 2A) (17). Sequence comparison of VatpC and ABG055 revealed 98% identity over a 66-bp region (e value = 1024). To assess gene content at the Mat-a locus, we exploited the conserved synteny that exists between physical and genetic maps of sequenced and unsequenced grasses. In Sorghum bicolor, VatpC and Smp are the genes Sb09g030620 and Sb09g030810, respectively (18). The two genes flank a 267-kb region containing only 25 gene models (Fig. 2A). A S. bicolor homolog (Sb09g030700) of A. thaliana Early Flowering 3 (Elf3; At2g25930), located 76 kb (12 gene models) proximal to Sb09g030810, was identified as a candidate for a Mat-a homolog. Mutant alleles of A. thaliana Elf3 cause photoperiod-insensitive early flowering (19), similar to the phenotypes caused by mutations at the barley Mat-a and wheat Eps-Am1 loci. Of the 24 remaining genes, there were no other obvious candidates.
Fig. 2.
Mapping and synteny at the Mat-a locus. (A) Inference of HvElf3 as a candidate gene for Mat-a using genetic mapping data from wheat and barley and the Sorghum physical map. The wheat map shows a fragment of the Eps-Am1 locus. The Sorghum physical map shows only those gene model names that have barley homologs mapped on the telomeric region of barley chromosome 1H (shown as connecting lines to barley consensus map loci). Markers colocating on the barley consensus map (21) are boxed. The mapping of the backcross-derived near-isogenic line BW289, carrying the Mat-a allele eam8.k, is indicated. (B) Barley-Sorghum synteny model-based prediction of the genetic position of the HvElf3 gene. Positions of barley genetic markers were regressed against physical map positions of homologous sequences in Sorghum. The scatter plot shows only those homologous pairs that map in the syntenic regions. R2 is the coefficient of determination for the linear regression function. Physical distances (in kb) in Sorghum are shown on the x axis. Genetic map distances (21) on barley chromosome 1H are given on the y axis.
The likelihood of the barley ortholog of A. thaliana Elf3 being a candidate gene for Mat-a was further strengthened by the location of an Elf3-like gene in a segment of Brachypodium distachyon chromosome Bd02 (Bradi2g14290), which shows conserved synteny with the end of the long arm of barley chromosome 1H (20). In rice (Oryza sativa), Elf3-like genes are found on chromosomes Os01 (LOC_Os01g38530) and Os06 (LOC_Os06g05060), and not on chromosome Os05, which is the chromosome that shows the best conservation of synteny with the barley chromosome 1H (20). Using a barley–Sorghum synteny model (Fig. 2B), we predicted the position of the barley homolog of Elf3 (HvElf3) to be between 138.9 and 139.8 cM on the barley consensus map (21). This genetic interval is in accordance with the recently reported mapping of the backcross-derived line BW289, carrying the Mat-a allele eam8.k, to the 130.4- to 140.5-cM region of barley chromosome 1H (Fig. 2A) (22).
Linkage of mat-a Phenotype and DNA Variation of the HvElf3 Gene.
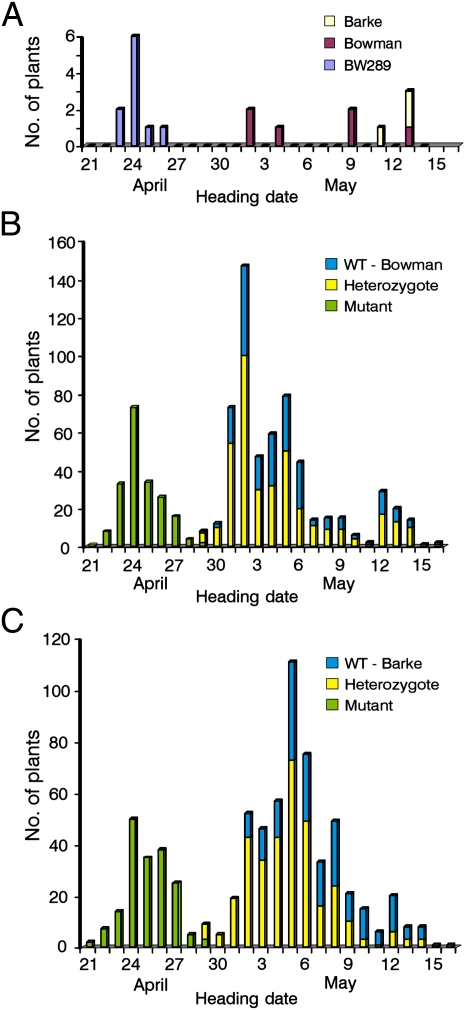
Genetic linkage of the mat-a phenotype and HvElf3 was further supported by our finding of exact cosegregation of the earliness phenotype with a mutant allele of HvElf3 in a population of F2 recombinant lines. The near-isogenic line BW289, carrying the eam8.k mutation, was crossed with the cultivars Bowman and Barke. For each cross, 803 and 718 F2 seeds were planted, and the day of heading was determined for each plant (Fig. S1A). All BW289 mutant plants headed at least 6 d earlier than the Bowman control plants and 17 d earlier than the Barke control plants (Fig. 3A). The eam8.k mutation is very distinctive (Fig. 4), allowing the design of primers for specific amplification of the mutant allele or the wild-type allele in the same PCR (Fig. S1 B and C). In both crosses, an early-heading group of recombinant lines was homozygous for the eam8.k mutation (Fig. 3 B and C), thus strengthening the hypothesis that Mat-a is HvElf3. The segregation in the cross to Bowman was 199, 394, and 210 for homozygous mutants, heterozygous plants, and wild-type plants, respectively (for 1:2:1 ratio, χ2 test = 0.58, P = 0.75) (Fig. 3B). The mean heading dates of the mutant, heterozygous, and wild-type populations were April 25, May 4, and May 5, respectively. The mean heading date of the mutant population was significantly different from that of the heterozygous and wild-type populations (t test, P < 0.001). In the cross to Barke, the segregation was 185, 339, and 194 for homozygous mutants, heterozygous plants, and wild-type plants, respectively (for 1:2:1 ratio, χ2 test = 2.5, P = 0.29) (Fig. 3C). The mean heading dates were April 25, May 5, and May 7, respectively. All three mean heading dates were significantly different from each other (P < 0.001). This result suggests that eam8.k exhibits partial dominance or epistatic interactions, which can be seen in a mapping population with a late-flowering cultivar like Barke.
Fig. 3.
Correlation between phenotype and genotype in control plants (A) and two F2 mapping populations (B and C). (A) The day of heading for BW289 carrying the eam8.k mutation in comparison with the barley cultivars Bowman and Barke. (B and C) F2 mapping population from the cross BW289 × Bowman (B) and BW289 × Barke (C).
Fig. 4.
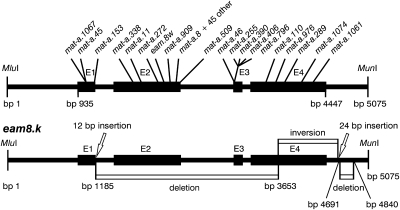
Structure of the barley Mat-a gene and the positions of the detected mutations. A 5,075-bp MluI–MunI DNA fragment from BAC clone HVVMRXALLhA0624F14 (34) was used as template for resequencing 87 mutant alleles. E1–E4 designate exons. The complex eam8.k allele with two deletions, one inversion, and two small insertions is shown separately in Lower.
Sequence Analysis of mat-a Mutants.
The principal proof of identity of HvElf3 as Mat-a came from comparative sequence analysis of HvElf3 in 87 putatively independent mat-a mutant alleles and corresponding parental cultivars (Fig. 4, Fig. S2, and Table S2). The mat-a.8 mutation associated with Mari is a 4-bp deletion, which causes a translational frame shift leading to a premature stop codon (Table S2). Truncated proteins were also the result of most other identified mutations due to deletions (48 cases in total), nonsense mutations (9 cases), or splice-site mutations (6 cases). Surprisingly, the Mari mutation was found in >40 mutant lines. At the moment, we cannot explain this finding, although we are aware that certain DNA structures can provide hotspots for mutations (23, 24). The original field books show that they were isolated, after various treatments, as independent lines between 1951 and 1983 (Table S2).
Nonsynonymous point mutations were only found in mat-a.45 and mat-a.1067, leading to the amino acid substitutions N44I and R43H. Both N44 and R43 are fully conserved residues, located in the most conserved region of the ELF3 polypeptide (Fig. S3). The functional significance of conserved regions in ELF3 is yet to be determined. The eam8.k mutation was complex; an insertion of AGCTGCATGGCG at position 1,189 is followed by a deletion of 2,466 bp at position 1,189–3,656, directly followed by an inversion of bps 3,657–4,697, immediately followed by an insertion of CCGTCTCCTCCGCCTCCGCACCGTT and a deletion of 147 bp at position 4,698–4,845 (Fig. 4). In mutants ert-o.16 and mat-a.12, no part of HvElf3 could be amplified by PCR, whereas only the most 5′ and 3′ parts could be amplified in mat-a.407. These results suggest that the three mutations involve larger rearrangements, possibly deletions. Initially, no mutations were detected in 19 lines. Repeated phenotyping and genotyping showed that the majority of them (13 lines) were erroneous because they did not show an early-flowering phenotype (Table S2). The remaining six lines represented heterogeneous stocks consisting of mutant and wild-type alleles.
Thus, throughout this work, our DNA sequence analysis of mat-a lines has identified >20 different mutations in the barley Elf3 gene that each lead to a clear nonfunctional putative translation product. This finding firmly establishes mutations in Elf3 as causal for the mat-a phenotype.
Expression Analysis of Gigantea in a mat-a Genetic Background.
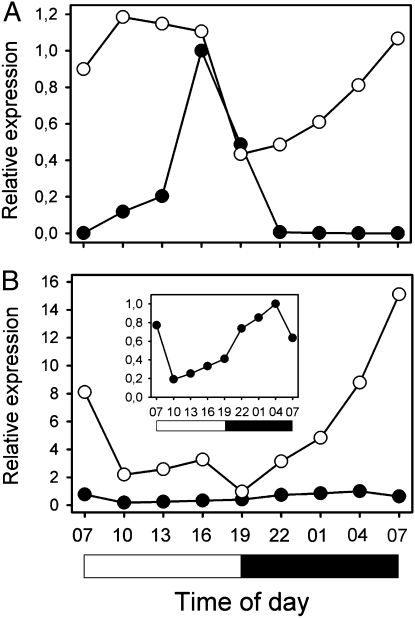
The major components of the regulatory flowering pathways are conserved among distantly related plants. Among the major floral inducers in A. thaliana are CONSTANS, GIGANTEA (AtGI), and FLOWERING LOCUS T (1). In view of the present study, AtGI is of special interest because studies with yeast two-hybrid systems have demonstrated the physical interaction between AtGI, AtELF3, and an E3 ubiquitin–ligase, AtCOP1, leading to turnover of AtGI (19). We analyzed whether the expression of barley Gigantea is affected in a mat-a genetic background, which could help us to understand the early-flowering phenotype in these plants. The expression level of barley Gigantea was studied by real-time quantitative PCR using RNA samples from leaves of the near-isogenic mat-a mutant line BW289 (eamk.8) and Bowman. The plants were grown in 12/12-h light/dark cycles and were harvested every 3 h over a 24-h period at the third true-leaf stage. In Bowman, Gigantea had a pronounced expression during the latter half of the light period, whereas no expression was detected during the dark period (Fig. 5A). This expression profile was very similar to those found earlier in barley and A. thaliana grown under 8/16- and 16/8-h light/dark cycles (19, 25). The level of Gigantea transcript in BW289 was similar to the peak value of Bowman at several time points and did not fluctuate to a similar extent. Gigantea expression was also pronounced during the dark period (Fig. 5A). Pronounced expression of flowering inducing genes like Gigantea might explain the early flowering of mat-a mutants.
Fig. 5.
Expression profiles of Gigantea (A) and Elf3 (B) in the near-isogenic mat-a mutant line BW289 (open circles) and Bowman (filled circles). Plants were harvested at 3-h intervals at the three-leaf stage. The open and filled bars at the bottom indicate the light and dark periods, respectively. (B Inset) The Elf3 expression in Bowman in more detail.
HvElf3 in the Bowman wild type showed the lowest expression during the beginning of the light period and peaked at the end of the dark phase (Fig. 5B), similar to what has been found in A. thaliana (19). Interestingly, the peak expression value of HvElf3 was 15 times higher in BW289 compared with Bowman (Fig. 5B). The abundance of HvElf3 in the mutant is most likely due to lack of functional HvELF3 protein, because AtElf3 has been shown to be autoregulated by its own gene product (26, 27).
Discussion
Global food production must increase substantially to meet the needs of the rapidly growing human population (28, 29). At the same time, warming of the global climate system threatens the productivity of existing agricultural land. However, it can also be predicted that other geographic areas will become more amenable to cultivation. The implications of these changes are that breeding of early cultivars will be essential to meet shorter growing seasons in many existing agricultural locations and that crop plants requiring adaptation to local light regimes and temperatures will be introduced into new geographic areas. The mutation characterizing the barley cultivar Mari drastically alters earliness, which is a useful trait when adapting cultivars to agricultural land with a short growing season. At the same time, the photoperiod insensitivity of Mari gives it the remarkable ability to give high yield close to the polar circle in Northern Scandinavia and also near the Equator—for example, under tropical conditions in Colombia (16). Over the years, many breeders in various geographic regions have used Mari as a parent to produce new cultivars (Table S1). Breeding populations containing Mari have been tested at several Mexican stations, on Cyprus, in Spain, Tunisia, Turkey, Jordan, Iraq, Iran, South Korea, and Peru. Apart from earliness, they maintained the ability to give high yield at all locations (9). The present identification of >20 different mat-a mutant alleles will significantly expedite the use of mat-a in plant breeding, especially because selection of earliness by phenotyping is labor-intensive and will be much more easily done directly using known mat-a mutations as genetic markers.
The molecular mechanism of the Mat-a gene product is yet to be determined, but it is likely to be identical in all plants. The early flowering and photoperiod insensitivity of mat-a mutants are also striking in A. thaliana elf3 mutants under both long-day (16-h light/8-h dark) and short-day (8-h light/16-h dark) conditions. A. thaliana elf3-8 plants bolted already when seven or eight rosette leaves had appeared. In contrast, the wild-type controls bolted after the appearance of 11.6 leaves under long-day conditions and 46.1 leaves under short-day conditions (19). A T-DNA insertion in one of the two Elf3-like genes of rice also resulted in photoperiod insensitivity but with a late phenotype, which should be seen in the light that rice is categorized as a short-day plant in contrast to barley and A. thaliana, which are long-day plants (30). Networks underlying early, photoperiod-insensitive flowering in A. thaliana elf3 mutants include flowering time proteins such as CONSTANS and GIGANTEA (2, 26, 31) and regulation by COP1 and miRNA172 (19, 32). COP1 is an E3 ubiquitin–ligase that mediates ubiquitination and targeted degradation of light-signal regulators (33). By allowing COP1 and GI interaction in a temporal COP1–ELF3–GI complex, ELF3 likely acts as a substrate adaptor for COP1 action on GI, which promotes ubiquitination and degradation of GI (19). Accordingly to this idea, AtElf3 overexpression causes late flowering and nonfunctional mutations in AtElf3 (19), and HvElf3 show an early phenotype.
The work reported here is an example of how studies on a basic concept of plant physiology in A. thaliana can facilitate applied research in a crop plant. However, it also demonstrates the great potential of legacy collections of plant mutants and the importance of keeping them cataloged and alive, because multiple independent mutant alleles, when available, are the most effective approach to validating a candidate gene. Natural and induced mutations are also valuable assets for plant breeding, a topic of special importance in countries in which genetically modified plants are not publicly accepted. The Mat-a locus is an important breeding target in barley, but probably also in many other day-length-sensitive crop plants. Thus, alleles of Mat-a can be used by public and private plant breeders where it may be important in addressing problems of global food production and adapting crop plants to different geographic regions and climatic conditions, critical issues in times of global warming, and food security.
Materials and Methods
Plant Materials and Growth Conditions.
Barley (H. vulgare L.) cultivars Bowman, Barke, Bonus, Foma, Kristina, and Maja; mutant lines Kinai 5 (carrying the eam8.k mutation), mat-a (84 different mutants), ert-o.16, BW289 (a Bowman near-isogenic line carrying the eam8.k mutation), and BW290 (a Bowman near-isogenic line carrying the eam8.w mutation); and F2 mapping populations derived from crosses BW289 × Barke, and BW289 × Bowman were grown in a greenhouse at 18 °C under a cycle of 16-h light/8-h dark. Light intensity was set to a photon flux of 120 μmol⋅m−2⋅s−1. The F2 mapping populations were planted on March 20, 2009. Phenotyping concerning date of heading was started April 19. Statistical analyses (t test) of differences in heading date were based on number of days between planting and heading for the different phenotypic groups. Mutant seeds are available from NordGen (Alnarp, Sweden; www.nordgen.org).
Cloning and DNA Sequence Analysis.
By using the A. thaliana ELF3 polypeptide (At2g25930) as query, partial barley Elf3 (HvElf3) DNA sequences were found in EST database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nucest), and a consensus sequence of 1,643 bp could be assembled (72% of the coding gene). The 1,643-bp HvElf3 DNA sequence was compared with randomly selected and sequenced BAC clones (http://webblast.ipk-gatersleben.de/barley/viroblast.php). HvElf3 is present on BAC clone HVVMRXALLhA0624F14 (34). A 5,075-bp MluI–MunI DNA region was selected for sequence analysis from genomic DNA of barley mutants. DNA isolation and sequencing was performed by LGC Genomics. GrainGenes (http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/GG2/ggdb.shtml) and HarvEST (http://harvest.ucr.edu/) were used for map viewing and sequence searching. The Rice Genome Annotation Project (http://rice.plantbiology.msu.edu/cgi-bin/gbrowse/rice/), Phytozome (http://www.phytozome.net/), and Gramene (http://www.gramene.org/) were used for plant comparative genomic analyses.
The barley Bonus Mat-a and the Kinai 5 (eam8.k) nucleotide sequences, as well as the draft assembly of BAC clone HVVMRXALLhA0624F14, have been deposited at the GenBank database under accession nos. JN180296, JN180297, and AC244853.1, respectively.
Genotyping of Mapping Population.
Barley leaves (10 cm) were sampled and dried for a minimum of 3 d in plastic bags containing 50 mL of silica gel (catalog no. 1327-36-2; Azelis). Genomic DNA was isolated from dried leaves by using the REDExtract-N-Amp Plant PCR Kit (Sigma). Dried leaf pieces of 0.5 cm were transferred to 96-well plates with well volumes of 200 μL. Then, 40 μL of extraction solution was added to the plant samples and incubated at 95 °C for 10 min, which was followed by addition of 40 μL of dilution solution and vortexing. PCR amplifications were performed according to the manufacturer's protocol by using REDExtract-N-Amp PCR ReadyMix, which contains JumpStart Taq antibody for specific hot-start amplification. Primers specific for the wild-type allele or the mutant eam8.k allele were used (Fig. S1B). Primers F1 (GTCTGATTGGATTGGAAAACCTAG) and R1 (TGGGAAATTTTGCAGTTGG) allowed specific amplification of the wild-type allele, because primers F1 and R1 are constructed in a region deleted in eam8.k. Primers F2 (ACAAGCTGCATGGCGATAC) and R2 (TTTCGGTCGATCCAGATG) exploited the inversion of eam8.k, which made them specific to the mutant allele. All PCRs were mixed in 96-well plates by a Freedom EVO 200 robot (Tecan Group). Gel electrophoresis was performed on precast agarose gels (2% E-Gel 96 with SYBR Safe; Invitrogen). Statistical analysis of the segregation in the mapping populations was performed with a Pearson's χ2 test.
Expression Analysis.
BW289 and Bowman plants were grown under a constant temperature regime of 20 ± 2 °C. Light was given between 7:00 AM and 7:00 PM at an intensity of 190 μmol⋅m−2⋅s−1. At the three-leaf stage, leaf material was harvested from five independent plants at the indicated time points. In the dark period, dim green light was used during the harvest procedure. Leaves for each time point were cut into 1-cm pieces and pooled. Portions of 100 mg were quick-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until further processing. Total RNA was isolated from pooled barley leaf material with the RNeasy Plant Mini Kit including the RNase-free DNase Set (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's recommendations. In addition, RNA was treated afterward with DNaseI (Fermentas) according to the manufacturer's instructions. RNA integrity was checked on a 2% (wt/vol) agarose gel containing guanidinium thiocyanate and ethidium bromide. The concentration and purity of the extracted RNA was additionally measured spectrophotometrically (Nanodrop 1000; Thermo Scientific). The absence of residual genomic DNA was assured by a standard PCR using AmpliTaq Gold DNA Polymerase (Ultra Pure; Applied Biosystems), gene-specific primers for HvElf3 (primer sequences as described below), and DNaseI-treated RNA as template. For real-time quantitative PCR, Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System was used in conjunction with SYBR Green RNA-to-CT 1-Step Kit (Applied Biosystems) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Cycling conditions were 30 min at 48 °C, 10 min at 95 °C, 50 cycles of 15 s at 95 °C, and 1 min at 60 °C. This process was followed by a melting-curve program (60–95 °C). Fluorescence data were acquired at the 60 °C step and during the melting-curve program. Three replicate reactions were performed for each RNA–primer combination in the same run. As reference gene, Gapdh was used with published primers (35). Forward and reverse primer sequences were 5′GTGAGGCTGGTGCTGATTACG and 5′TGGTGCAGCTAGCATTTGAGAC for HvGapdh, 5′TTGTTCTGCAGGCTGAGAAG and 5′CAAGCATCCCATCTGTAGCA for HvGigantea, and 5′CCTACCGACAACAAGCAGAA and 5′CATGAATTCCCCAGCTGTAG for HvElf3, respectively. The binding sites of the F-Elf3 and R-Elf3 primers are indicated in Fig. S1B. Primer concentrations for forward and reverse primers in the reactions were 200/200 nM for HvGapdh and HvGigantea and 200/450 nM for HvElf3. For transcript-level comparison, RNA material from the 16 and 04 o'clock Bowman samples was included as a standard in the quantitative PCR of BW289. Analysis of relative transcription levels of the respective sequences was performed by using 7500 Software V2.0.5 (Applied Biosystems, Life Technologies).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Carlsberg Foundation, the Nilsson-Ehle Foundation at the Royal Physiographic Society in Lund, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the European Commission under the Marie Curie Early-Stage Training Fellowship Program, European Research Area in Plant Genomics Project ERAPGFP/06.046A, and the Scottish Government Institute Research Program.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
*This Direct Submission article had a prearranged editor.
Data deposition: The sequences reported in this paper have been deposited in the GenBank database [accession nos. JN180296 (Bonus Mat-a), JN180297 (Kinai 5; eam8.k), and AC244853.1 (BAC clone HVVMRXALLhA0624F14)].
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1113009109/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Amasino R. Seasonal and developmental timing of flowering. Plant J. 2010;61:1001–1013. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kim WY, Hicks KA, Somers DE. Independent roles for EARLY FLOWERING 3 and ZEITLUPE in the control of circadian timing, hypocotyl length, and flowering time. Plant Physiol. 2005;139:1557–1569. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.067173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kozma-Bognár L, Káldi K. Synchronization of the fungal and the plant circadian clock by light. ChemBioChem. 2008;9:2565–2573. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Smith L. Cytology and genetics of barley. Bot Rev. 1951;17:1–355. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tester M, Langridge P. Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science. 2010;327:818–822. doi: 10.1126/science.1183700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stadler LJ. Mutations in barley induced by X-rays and radium. Science. 1928;68:186–187. doi: 10.1126/science.68.1756.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Muller HJ. Artificial transmutation of the gene. Science. 1927;66:84–87. doi: 10.1126/science.66.1699.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gustafsson Å. Mutation experiments in barley. Hereditas. 1941;27:225–242. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lundqvist U. 1992. Mutation research in barley. PhD thesis (Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Svalöv, Sweden) [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gustafsson Å. Mutations in agricultural plants. Hereditas. 1947;33:1–100. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Takahashi R, Yasuda S. Genetics of earliness and growth habit in barley. In: Nilan RA, editor. Second International Barley Genetic Symposium. Pullman, WA: Washington State University Press; 1969. pp. 388–408. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yasuda S. Linkage of the earliness gene eak and its pleiotropic effects under different growth conditions. Berichte des Ohara Institutes für landwirtschaftliche Biologie. Okayama Universität. 1977;17:15–28. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Franckowiak J, Lundqvist U. Barley Genet Newsl. 2007;37:247–250. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dormling I, Gustafsson Å, Jung HR, von Wettstein D. Phytotron cultivation of Svalöf's Bonus barley and its mutant Svalöf's Mari. Hereditas. 1966;56:221–237. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yasuda S. Effects of the very early gene, eak, on yield and its components in barley. Barley Genet Newsl. 1978;8:125–127. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sigurbjörnsson B. Methods of mutation induction, including efficiency, and utilization of induced genetic variability. In: Gaul H, editor. Barley Genetics III. München: Verlag Karl Thiemig; 1975. pp. 84–95. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Valárik M, Linkiewicz AM, Dubcovsky J. A microcolinearity study at the earliness per se gene Eps-Am1 region reveals an ancient duplication that preceded the wheat-rice divergence. Theor Appl Genet. 2006;112:945–957. doi: 10.1007/s00122-005-0198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Paterson AH, et al. The Sorghum bicolor genome and the diversification of grasses. Nature. 2009;457:551–556. doi: 10.1038/nature07723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yu JW, et al. COP1 and ELF3 control circadian function and photoperiodic flowering by regulating GI stability. Mol Cell. 2008;32:617–630. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.09.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mayer KF, et al. Unlocking the barley genome by chromosomal and comparative genomics. Plant Cell. 2011;23:1249–1263. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.082537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Close TJ, et al. Development and implementation of high-throughput SNP genotyping in barley. BMC Genomics. 2009;10:582. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Druka A, et al. Genetic dissection of barley morphology and development. Plant Physiol. 2011;155:617–627. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.166249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rogozin IB, Pavlov YI. Theoretical analysis of mutation hotspots and their DNA sequence context specificity. Mutat Res. 2003;544:65–85. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5742(03)00032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhao J, Bacolla A, Wang G, Vasquez KM. Non-B DNA structure-induced genetic instability and evolution. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67:43–62. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0131-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dunford RP, Griffiths S, Christodoulou V, Laurie DA. Characterisation of a barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) homologue of the Arabidopsis flowering time regulator GIGANTEA. Theor Appl Genet. 2005;110:925–931. doi: 10.1007/s00122-004-1912-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hicks KA, Albertson TM, Wagner DR. EARLY FLOWERING3 encodes a novel protein that regulates circadian clock function and flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2001;13:1281–1292. doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.6.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kolmos E, et al. A reduced-function allele reveals that EARLY FLOWERING3 repressive action on the circadian clock is modulated by phytochrome signals in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2011;23:3230–3246. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.088195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and the United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization . OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2011-2020. Paris: OECD; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 29.United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization . How to Feed the World in 2050. Rome: United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fu C, et al. OsEF3, a homologous gene of Arabidopsis ELF3, has pleiotropic effects in rice. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 2009;11:751–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2008.00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Suárez-López P, et al. CONSTANS mediates between the circadian clock and the control of flowering in Arabidopsis. Nature. 2001;410:1116–1120. doi: 10.1038/35074138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jung JH, et al. The GIGANTEA-regulated microRNA172 mediates photoperiodic flowering independent of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2007;19:2736–2748. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.054528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yi C, Deng XW. COP1 - from plant photomorphogenesis to mammalian tumorigenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:618–625. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schulte D, et al. BAC library resources for map-based cloning and physical map construction in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) BMC Genomics. 2011;12:247. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Burton RA, Shirley NJ, King BJ, Harvey AJ, Fincher GB. The CesA gene family of barley. Quantitative analysis of transcripts reveals two groups of co-expressed genes. Plant Physiol. 2004;134:224–236. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.032904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.