Abstract
The binding of HMG 17 to stripped core mononucleosomes containing DNA from the avian beta-globin gene cluster was examined to determine whether binding in vitro in this developmentally-regulated gene domain was associated with transcriptional activity or DNaseI-sensitivity in intact nuclei. Mononucleosomes were prepared from primitive and definitive stage embryonic red blood cells of chick embryos, adult reticulocytes, adult reticulocytes in which embryonic rho-globin transcription was induced, and adult thymus cells. Preferential binding by HMG 17 to mononucleosomes containing the beta-globin gene cluster was confined to erythroid-derived mononucleosomes that contain the embryonic rho-globin gene, the adult beta-globin gene, and DNA sequences located between these two genes, but not to those that contain the embryonic epsilon-globin gene. Comparison of these results to the known patterns of transcription and DNaseI-sensitivity within the beta-globin gene cluster shows that HMG 17 binding, although tissue-specific, does not correlate directly with either DNaseI-sensitivity or active gene transcription, but is dependent on other factors present in core mononucleosomes from this active gene domain.
Full text
PDF


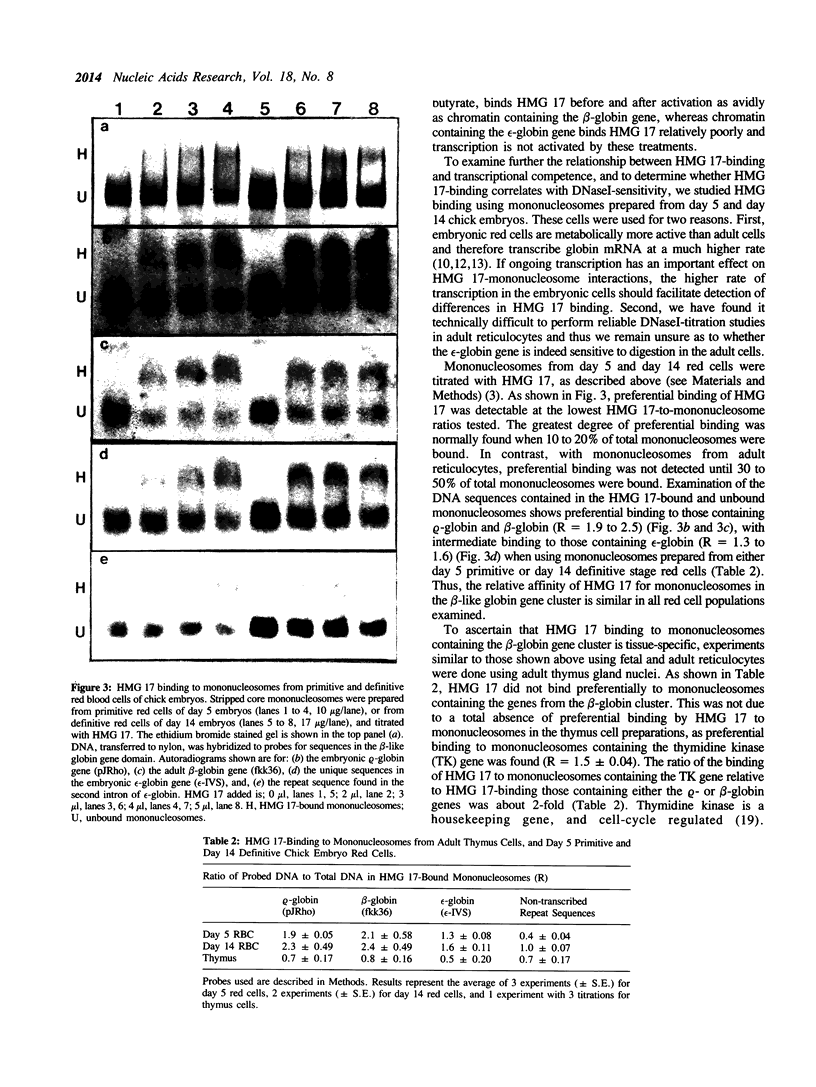


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright S. C., Wiseman J. M., Lange R. A., Garrard W. T. Subunit structures of different electrophoretic forms of nucleosomes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3673–3684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allis C. D., Richman R., Gorovsky M. A., Ziegler Y. S., Touchstone B., Bradley W. A., Cook R. G. hv1 is an evolutionarily conserved H2A variant that is preferentially associated with active genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1941–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Osheroff N., Fisher P. A. In situ localization of DNA topoisomerase II, a major polypeptide component of the Drosophila nuclear matrix fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4142–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhullar B. S., Candido E. P. An alternative procedure for the isolation of high mobility group proteins. Anal Biochem. 1981 Dec;118(2):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotherton T. W., Ginder G. D. Preferential in vitro binding of high mobility group proteins 14 and 17 to nucleosomes containing active and DNase I sensitive single-copy genes. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3447–3454. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns G. A., Ingram V. M. The erythroid cells and haemoglobins of the chick embryo. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Oct 25;266(877):225–305. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns L. J., Glauber J. G., Ginder G. D. Butyrate induces selective transcriptional activation of a hypomethylated embryonic globin gene in adult erythroid cells. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1536–1542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. Developmental regulation of beta-globin gene switching. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciejek E. M., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Actively transcribed genes are associated with the nuclear matrix. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):607–609. doi: 10.1038/306607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M., Sugarman B. J., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Chromosomal arrangement of the chicken beta-type globin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):669–677. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorbic T., Wittig B. Chromatin from transcribed genes contains HMG17 only downstream from the starting point of transcription. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2393–2399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorbic T., Wittig B. Isolation of oligonucleosomes from active chromatin using HMG17-specific monoclonal antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3363–3376. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einck L., Bustin M. Inhibition of transcription in somatic cells by microinjection of antibodies to chromosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6735–6739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einck L., Bustin M. The intracellular distribution and function of the high mobility group chromosomal proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Feb;156(2):295–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laroche T., Falquet J., Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure. Involvement of topoisomerase II. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):613–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit B., Panet A., Cedar H. Reconstitution of a deoxyribonuclease I-sensitive structure on active genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1787–1790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginder G. D., Whitters M. J., Pohlman J. K. Activation of a chicken embryonic globin gene in adult erythroid cells by 5-azacytidine and sodium butyrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3954–3958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Casimir C. Post-transcriptional regulation of the chicken thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1427–1446. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbes T. R., Thorne A. W., Crane-Robinson C. A direct link between core histone acetylation and transcriptionally active chromatin. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1395–1402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. Y., Barnard M. B., Xu M., Matsui S., Rose S. M., Garrard W. T. The active immunoglobulin kappa chain gene is packaged by non-ubiquitin-conjugated nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3738–3742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Sterner R., Allfrey V. G. Altered nucleosomes of active nucleolar chromatin contain accessible histone H3 in its hyperacetylated forms. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6943–6946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landes G. M., Villeponteau B., Pribyl T. M., Martinson H. G. Hemoglobin switching in chickens. Is the switch initiated post-transcriptionally? J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11008–11014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. Bidirectional control of the chicken beta- and epsilon-globin genes by a shared enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2548–2552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Lipsich L., Wigler M. Isolation of the chicken thymidine kinase gene by plasmid rescue. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):207–210. doi: 10.1038/285207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Chang D. Investigations of the possible functions for glycosylation in the high mobility group proteins. Evidence for a role in nuclear matrix association. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):679–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roninson I. B., Ingram V. M. Gene evolution in the chicken beta-globin cluster. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):515–521. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., LeVine H., 3rd, Bronson D., Cuatrecasas P. Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in neuronal nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9341–9344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandeen G., Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. The interaction of high mobility proteins HMG14 and 17 with nucleosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3757–3778. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A mammalian high mobility group protein recognizes any stretch of six A.T base pairs in duplex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Groudine M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D., Weintraub H. Hb switching in chickens. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):973–980. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow P. S., Varshavsky A. Affinity of HMG17 for a mononucleosome is not influenced by the presence of ubiquitin-H2A semihistone but strongly depends on DNA fragment size. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):387–401. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse Y. C., Javaherian K., Wang J. C. HMG17 protein facilitates the DNA catenation reaction catalyzed by DNA topoisomerases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 15;231(1):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S., Weintraub H. Isolation of a subclass of nuclear proteins responsible for conferring a DNase I-sensitive structure on globin chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):630–634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberry L. K., Morris S. M., Jr, Fisch J. E., Glynias M. J., Jenik R. A., Goodridge A. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA sequences for avian malic enzyme. Nutritional and hormonal regulation of malic enzyme mRNA levels in avian liver cells in vivo and in culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1337–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. Chromatin structure of the chicken beta-globin gene region. Sensitivity to DNase I, micrococcal nuclease, and DNase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7730–7736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]