Abstract
Nematodes are the only group of organisms in which both cis- and trans-splicing of nuclear mRNAs are known to occur. Most Caenorhabditis elegans introns are exceptionally short, often only 50 bases long. The consensus donor and acceptor splice site sequences found in other animals are used for both cis- and trans-splicing. In order to identify the machinery required for these splicing events, we have characterized the C. elegans snRNAs. They are similar in sequence and structure to those characterized in other organisms, and several sequence variations discovered in the nematode snRNAs provide support for previously proposed structure models. The C. elegans snRNAs are encoded by gene families. We report here the sequences of many of these genes. We find a highly conserved sequence, the proximal sequence element (PSE), about 65 bp upstream of all 21 snRNA genes thus far sequenced, including the SL RNA genes, which specify the snRNAs that provide the 5' exons in trans-splicing. The sequence of the C. elegans PSE is distinct from PSE's from other organisms.
Full text
PDF



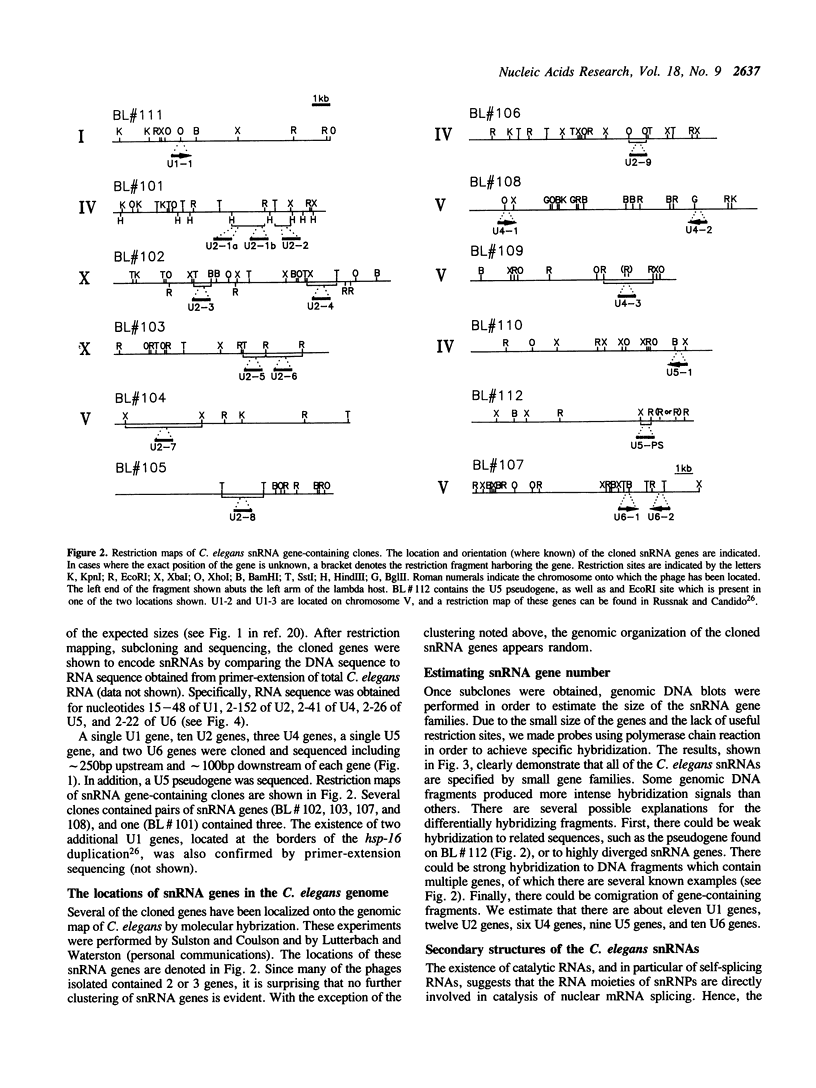
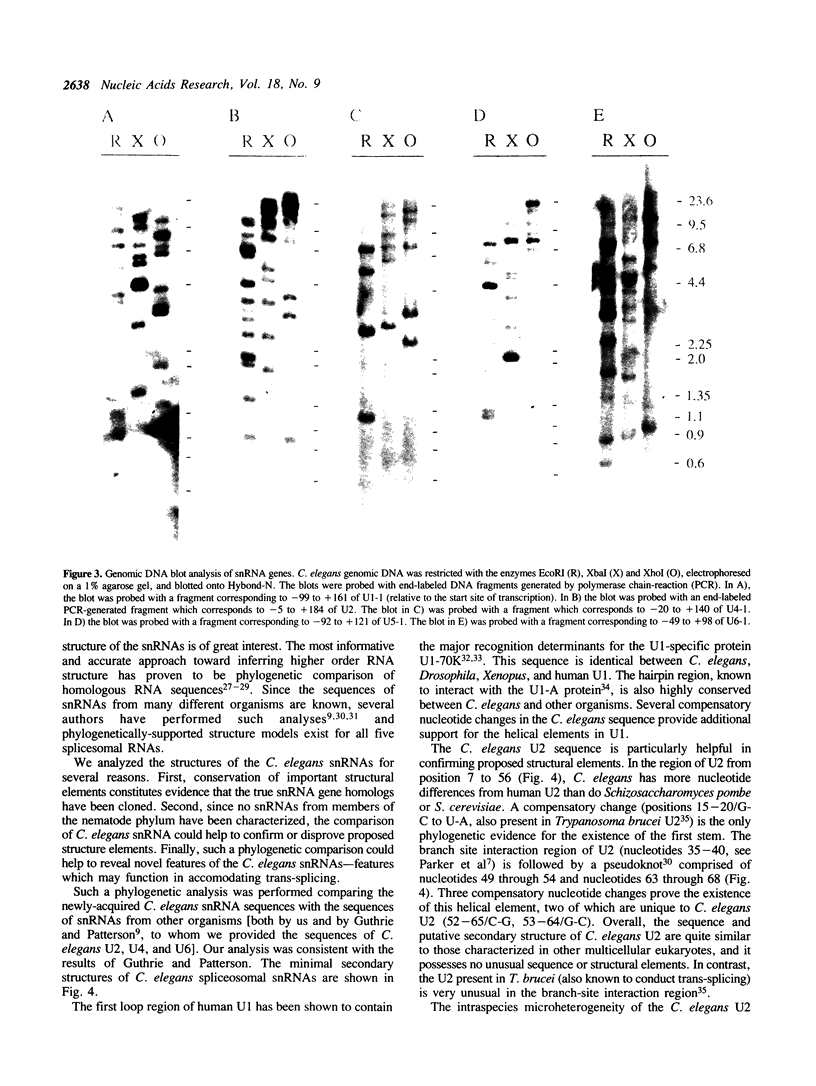
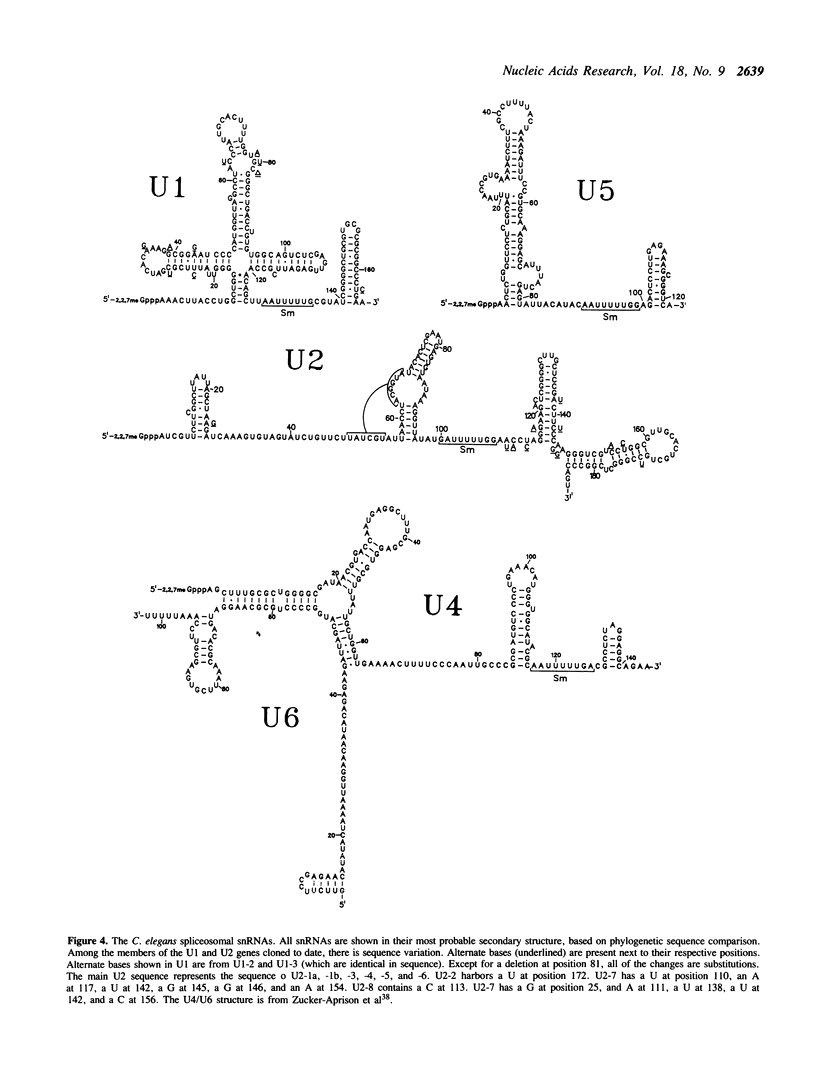



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso A., Jorcano J. L., Beck E., Hovemann B., Schmidt T. Drosophila melanogaster U1 snRNA genes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):825–836. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Saxe D., Marzluff W. F., Lobo S., Nesbitt M. N., Simon M. I. Mapping and gene order of U1 small nuclear RNA, endogenous viral env sequence, amylase, and alcohol dehydrogenase-3 on mouse chromosome 3. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Mar;14(2):133–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01534398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Thomas J. Cis and trans mRNA splicing in C. elegans. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Spliceosomal RNA U6 is remarkably conserved from yeast to mammals. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):213–218. doi: 10.1038/334213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Buckland R., Cortese R., Philipson L. Transcription signals in embryonic Xenopus laevis U1 RNA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1537–1543. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Klass M. R., Hirsh D. Analysis of the constancy of DNA sequences during development and evolution of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1333–1337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. 5S RNA secondary structure. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):505–507. doi: 10.1038/256505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Steitz J. A. A protein associated with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles recognizes the 3' splice site of premessenger RNA. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):973–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90812-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A. Affinity chromatography of splicing complexes: U2, U5, and U4 + U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in the spliceosome. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1294–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.3638792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C., Patterson B. Spliceosomal snRNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:387–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Kazmaier M., Mattaj I. W. In vitro assembly of U1 snRNPs. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3479–3485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02672.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. U4 and U6 RNAs coexist in a single small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3283–3293. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X. Y., Hirsh D. A second trans-spliced RNA leader sequence in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8640–8644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James B. D., Olsen G. J., Liu J. S., Pace N. R. The secondary structure of ribonuclease P RNA, the catalytic element of a ribonucleoprotein enzyme. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Association of U2, U4, U5, and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in a spliceosome-type complex in absence of precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5459–5462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings D. A., Mattaj I. W. Mutant U2 snRNAs of Xenopus which can form an altered higher order RNA structure are unable to enter the nucleus. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Oct;172(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Hirsh D. A trans-spliced leader sequence on actin mRNA in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90613-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. The two embryonic U1 RNA genes of Xenopus laevis have both common and gene-specific transcription signals. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1529–1535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren V., Ares M., Jr, Weiner A. M., Francke U. Human genes for U2 small nuclear RNA map to a major adenovirus 12 modification site on chromosome 17. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):115–116. doi: 10.1038/314115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren V., Bernstein L. B., Weiner A. M., Francke U. Human U1 small nuclear RNA pseudogenes do not map to the site of the U1 genes in 1p36 but are clustered in 1q12-q22. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2172–2180. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Zabel B. U., Manser T., Gesteland R., Sakaguchi A. Y. Localization of human U1 small nuclear RNA genes to band p36.3 of chromosome 1 by in situ hybridization. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 May;10(3):307–313. doi: 10.1007/BF01535252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Woese C. R. Secondary structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):403–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6163215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. R., Patterson R. J., Pederson T. Reconstitution of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4030–4037. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Wolin S., Guthrie C. A subset of yeast snRNA's contains functional binding sites for the highly conserved Sm antigen. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):328–331. doi: 10.1126/science.2948278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russnak R. H., Candido E. P. Locus encoding a family of small heat shock genes in Caenorhabditis elegans: two genes duplicated to form a 3.8-kilobase inverted repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1268–1278. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Dathan N. A., Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Identification of the RNA binding segment of human U1 A protein and definition of its binding site on U1 snRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4163–4170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuster E. O., Guthrie C. Two conserved domains of yeast U2 snRNA are separated by 945 nonessential nucleotides. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B. Surprises in polymerase III transcription. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):153–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90500-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Alibert C., Temsamani J., Reveillaud I., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. A protein that specifically recognizes the 3' splice site of mammalian pre-mRNA introns is associated with a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):755–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. D., Conrad R. C., Blumenthal T. The C. elegans trans-spliced leader RNA is bound to Sm and has a trimethylguanosine cap. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):533–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi C., Richards F. F., Ullu E. The U2 RNA analogue of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense: implications for a splicing mechanism in trypanosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8893–8903. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vankan P., Edoh D., Filipowicz W. Structure and expression of the U5 snRNA gene of Arabidopsis thaliana. Conserved upstream sequence elements in plant U-RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10425–10440. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vankan P., Filipowicz W. Structure of U2 snRNA genes of Arabidopsis thaliana and their expression in electroporated plant protoplasts. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):791–799. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuo C. Y., Ares M., Jr, Weiner A. M. Sequences required for 3' end formation of human U2 small nuclear RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):193–202. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Aprison E., Thomas J. D., Blumenthal T. C. elegans snRNAs: a model for U4/U6 base pairing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7188–7188. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]