Abstract
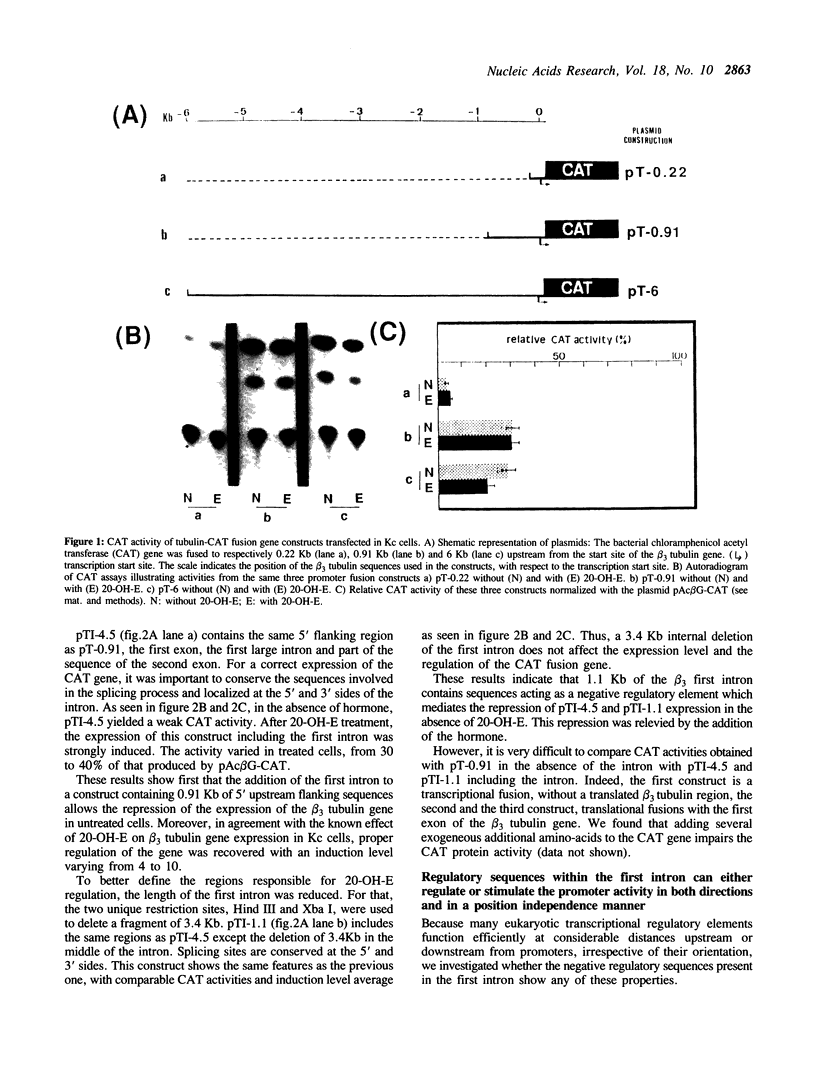
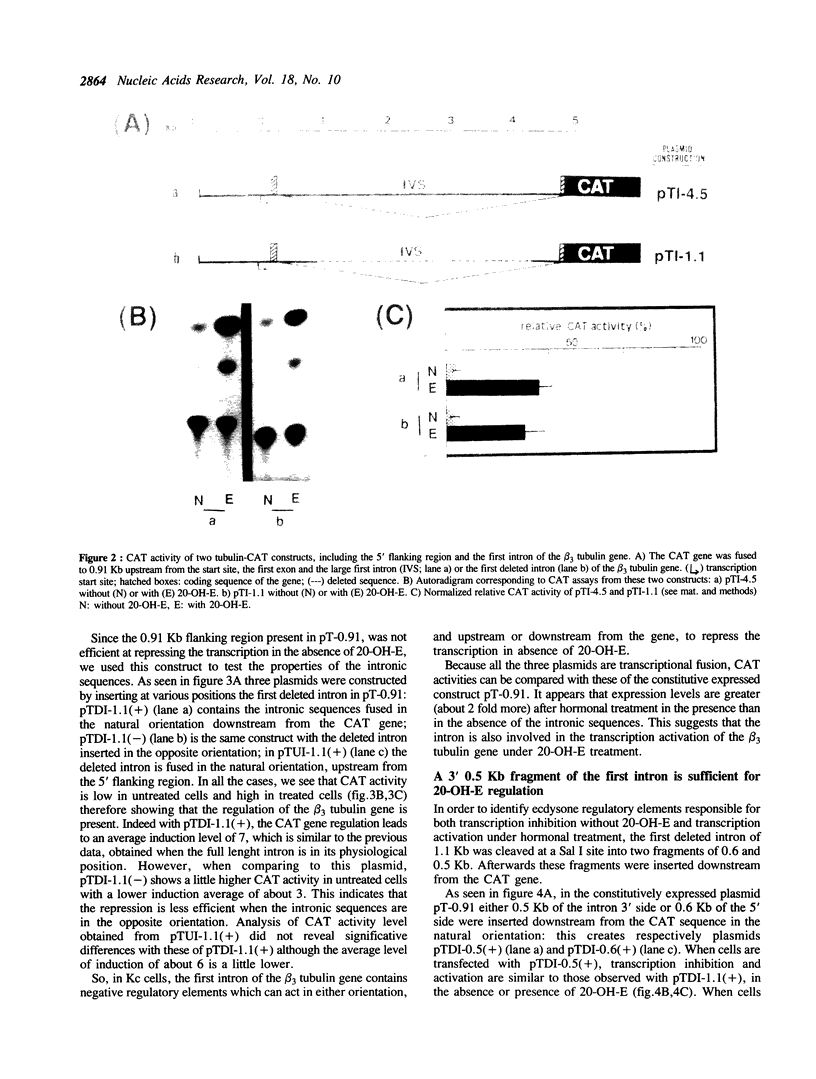
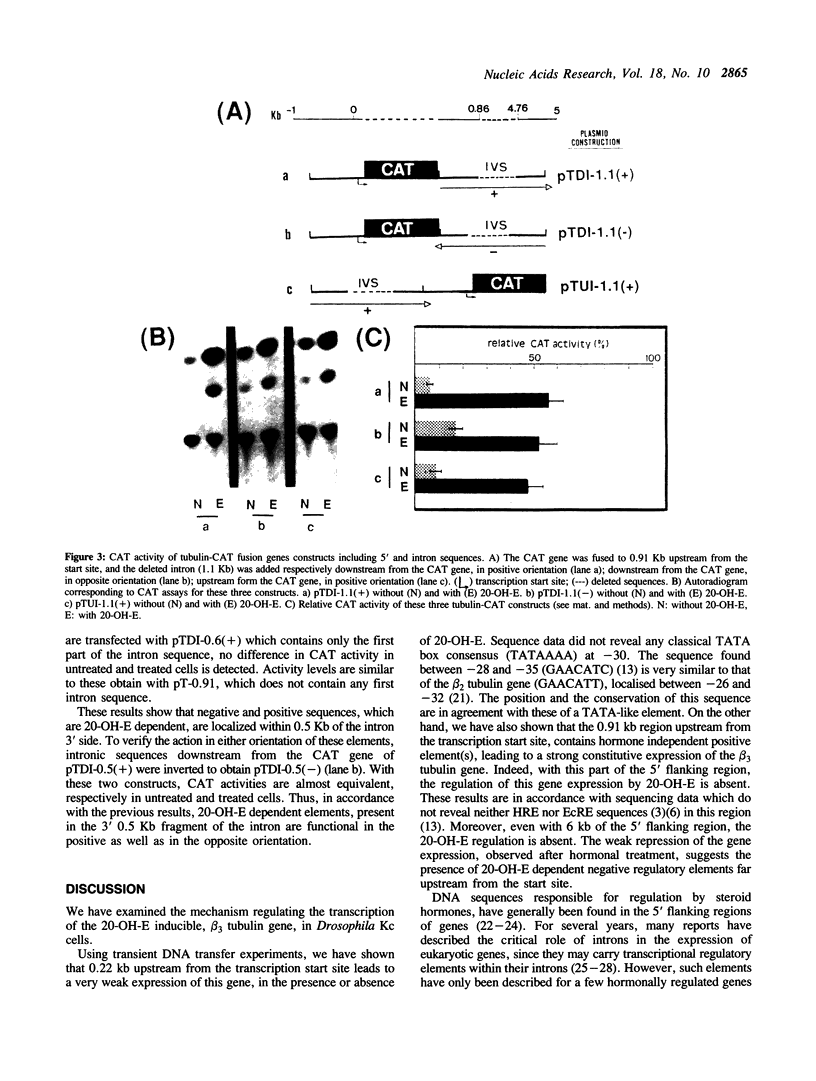
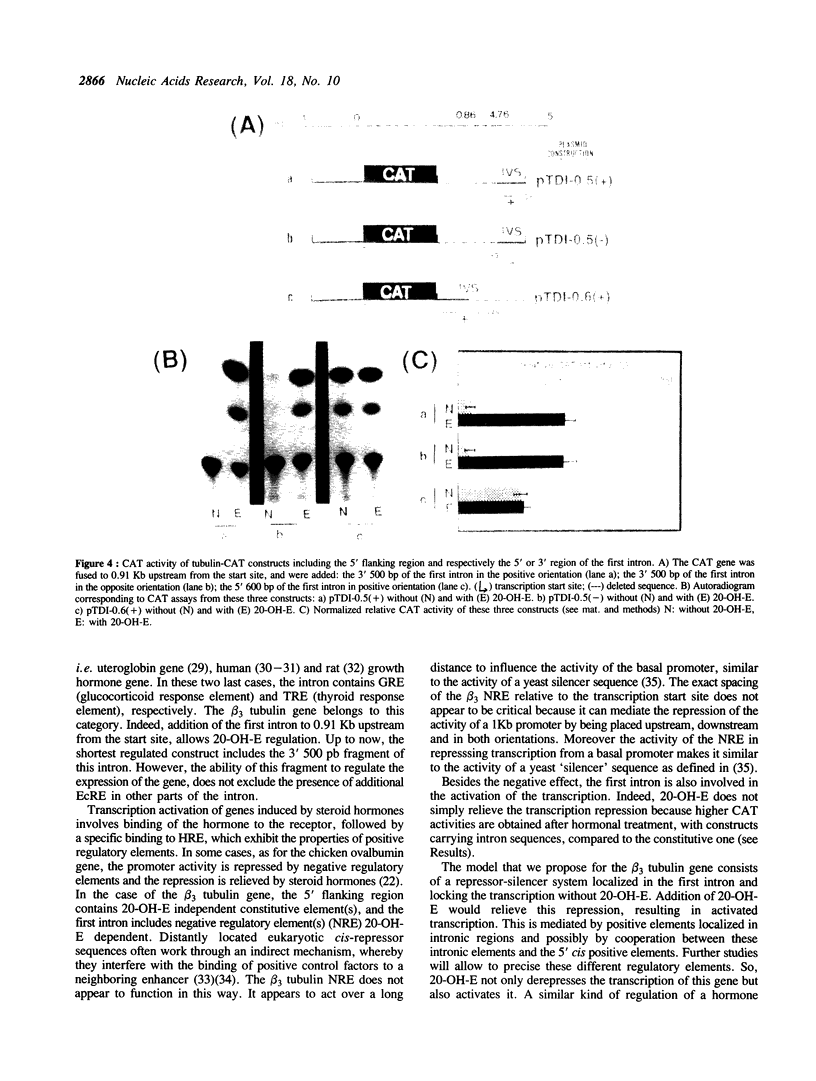
We have studied the transcriptional regulation of the beta 3 tubulin gene by the steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone (20-OH-E) in Drosophila Kc cells. A series of hybrid genes with varying tubulin gene lengths driving the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) gene were constructed. The promoter activity was assayed after transient expression in Kc cells, in the presence or absence of 20-OH-E. We find that 0.91Kb upstream from the transcription start site contain one or several hormone independent positive cis-acting elements, responsible for the constitutive expression of the beta 3 tubulin gene. In the large (4.5 Kb) first intron of this gene, we identified additional hormone dependent negative and positive regulatory elements, which can act in both directions and in a position-independence manner. Then, the negative intron element(s), which repress the transcription in the absence of 20-OH-E has characteristics of silencer.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailly A., Le Page C., Rauch M., Milgrom E. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the progesterone receptor to the uteroglobin gene: effects of hormone, antihormone and receptor phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3235–3241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. DNA binding specificity of steroid receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1065–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan S., Falkenburg D., Renkawitz-Pohl R. Characterization and developmental expression of beta tubulin genes in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2543–2548. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J., Liska D. J., Apone S., Devarayalu S. Interactions between the promoter and first intron are involved in transcriptional control of alpha 1(I) collagen gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4851–4857. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourouis M., Jarry B. Vectors containing a prokaryotic dihydrofolate reductase gene transform Drosophila cells to methotrexate-resistance. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1099–1104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courgeon A. M. Action of insect hormones at the cellular level. Morphological changes of a diploid cell line of Drosophila melanogaster, treated with ecdysone and several analogues in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Oct;74(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90384-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. Isolement, en cultures in vitro, de lignées cellulaires diploïdes de Drosophila melanogaster. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Mar 31;268(13):1771–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Scarpulla R. C. Both upstream and intron sequence elements are required for elevated expression of the rat somatic cytochrome c gene in COS-1 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):35–41. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasch A., Hinz U., Leiss D., Renkawitz-Pohl R. The expression of beta 1 and beta 3 tubulin genes of Drosophila melanogaster is spatially regulated during embryogenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):8–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00338387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasch A., Hinz U., Renkawitz-Pohl R. Intron and upstream sequences regulate expression of the Drosophila beta 3-tubulin gene in the visceral and somatic musculature, respectively. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3215–3218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaub M. P., Dierich A., Astinotti D., Touitou I., Chambon P. The chicken ovalbumin promoter is under negative control which is relieved by steroid hormones. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2313–2320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Corces V. G. Separate regulatory elements are responsible for the complex pattern of tissue-specific and developmental transcription of the yellow locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):996–1004. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graupner G., Wills K. N., Tzukerman M., Zhang X. K., Pfahl M. Dual regulatory role for thyroid-hormone receptors allows control of retinoic-acid receptor activity. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):653–656. doi: 10.1038/340653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler A. M., Maroy P. Ecdysteroid receptors in Drosophila melanogaster adult females. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 May;63(1-2):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. B., Galeazzi D. R., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Control of cytochrome P1-450 gene expression by dioxin. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1499–1502. doi: 10.1126/science.3856321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Sequence requirement for expression of the Drosophila melanogaster heat shock protein hsp22 gene during heat shock and normal development. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2011–2019. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiss D., Hinz U., Gasch A., Mertz R., Renkawitz-Pohl R. Beta 3 tubulin expression characterizes the differentiating mesodermal germ layer during Drosophila embryogenesis. Development. 1988 Dec;104(4):525–531. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. Cell-type specificity of regulatory elements identified by linker scanning mutagenesis in the promoter of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8451–8462. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Shermoen A. W., Heemskerk J., Beckendorf S. K. DNA sequence changes in an upstream DNase I-hypersensitive region are correlated with reduced gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1063–1067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestril R., Schiller P., Amin J., Klapper H., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Heat shock and ecdysterone activation of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp23 gene; a sequence element implied in developmental regulation. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1667–1673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels F., Gasch A., Kaltschmidt B., Renkawitz-Pohl R. A 14 bp promoter element directs the testis specificity of the Drosophila beta 2 tubulin gene. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1559–1565. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montpied P., Sobrier M. L., Chapel S., Couderc J. L., Dastugue B. 20-Hydroxyecdysone induces the expression of one beta-tubulin gene in Drosophila Kc cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 25;949(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. D., Marks A. R., Buckley D. I., Kapler G., Payvar F., Goodman H. M. The first intron of the human growth hormone gene contains a binding site for glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):699–702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natzle J. E., McCarthy B. J. Regulation of Drosophila alpha- and beta-tubulin genes during development. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Williams G. T. The intron requirement for immunoglobulin gene expression is dependent upon the promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6713–6724. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oro A. E., Hollenberg S. M., Evans R. M. Transcriptional inhibition by a glucocorticoid receptor-beta-galactosidase fusion protein. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1109–1114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. Activation of the Drosophila hsp27 promoter by heat shock and by ecdysone involves independent and remote regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1653–1658. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. An ecdysone response element in the Drosophila hsp27 promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3729–3734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippe R. A., Lorenzen S. I., Brenner D. A., Breindl M. Regulatory elements in the 5'-flanking region and the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the mouse alpha 1 type I collagen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2224–2227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage B. A., Tanis M. A., O'Connor J. D. Characterization of ecdysteroid receptors in cytosol and naive nuclear preparations of Drosophila Kc cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6373–6379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., de Magistris L., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. A major thyroid hormone response element in the third intron of the rat growth hormone gene. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):887–896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. P., Rabenau O., Karin M., Baxter J. D., Beato M. Glucocorticoid receptor binding and activation of a heterologous promoter by dexamethasone by the first intron of the human growth hormone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2984–2992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobrier M. L., Chapel S., Couderc J. L., Micard D., Lecher P., Somme-Martin G., Dastugue B. 20-OH-ecdysone regulates 60 C beta tubulin gene expression in Kc cells and during Drosophila development. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Sep;184(1):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobrier M. L., Couderc J. L., Chapel S., Dastugue B. Expression of a new beta tubulin subunit is induced by 20-hydroxyecdysone in Drosophila cultured cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90546-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







