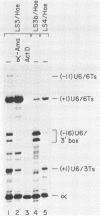
Abstract
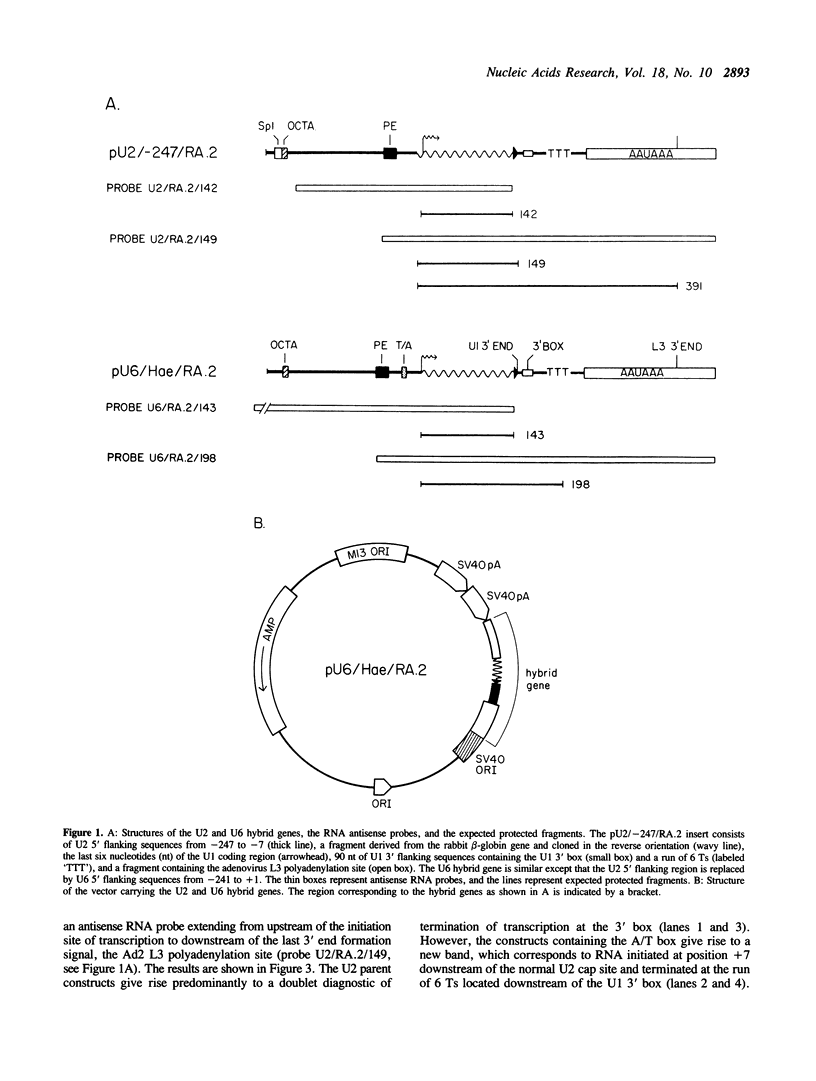
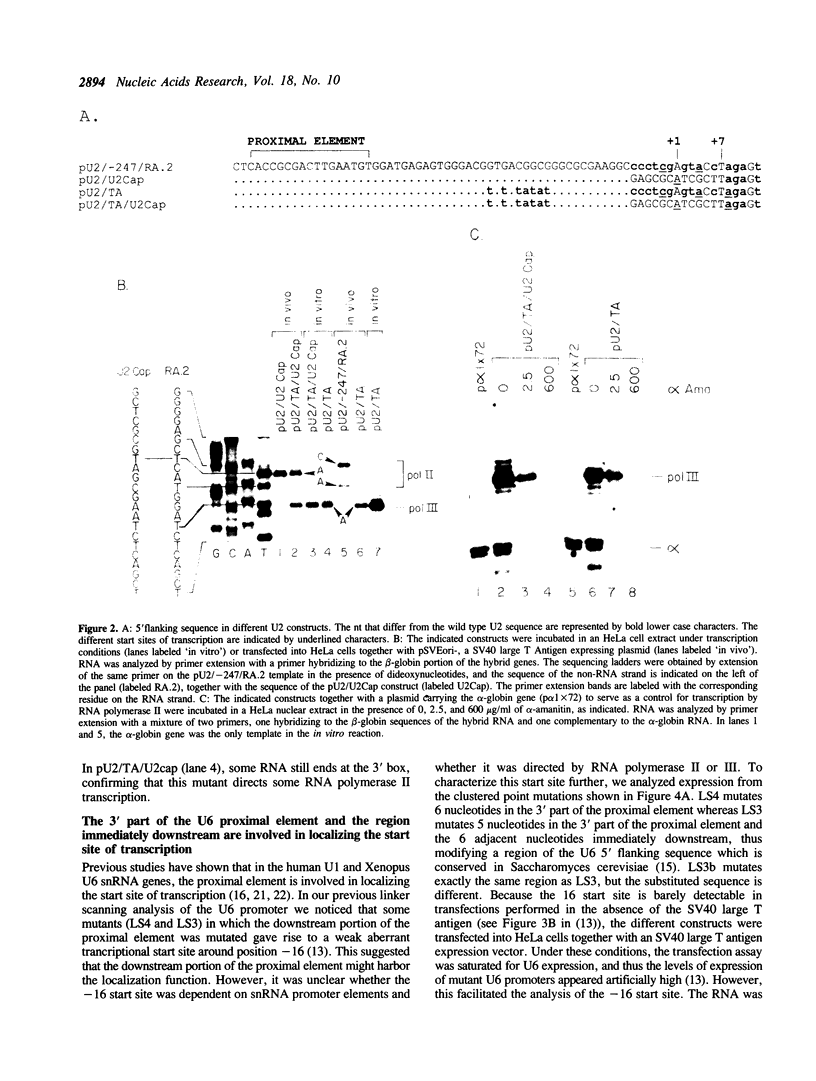
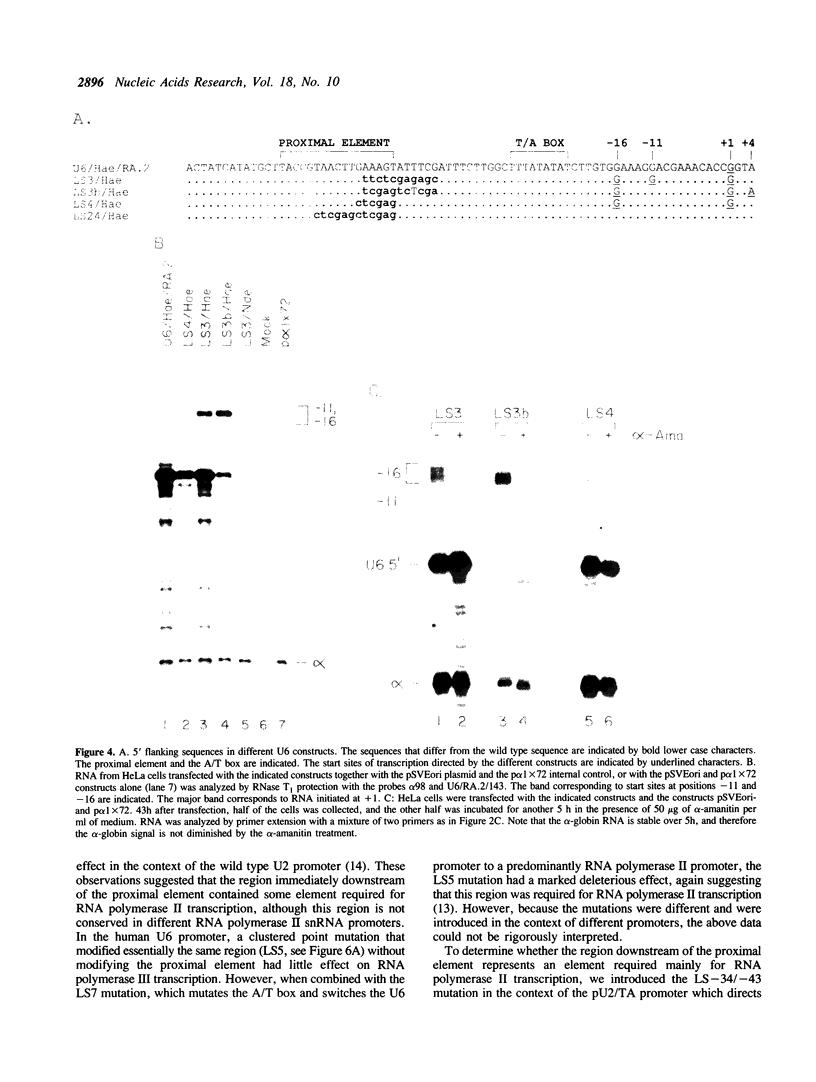
Although the human U2 and U6 snRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerases II and III respectively, their promoters are remarkably similar in structure. Both promoters contain a proximal element and an enhancer region with an octamer motif. The U6 promoter contains in addition an A/T rich region that defines it as an RNA polymerase III promoter. We have examined in further detail the contributions of sequences in the human U2 and U6 promoter regions to transcription by RNA polymerase II and III. We find that although the sequences surrounding the U2 cap site favor RNA polymerase II transcription, their presence cannot suppress a shift to RNA polymerase III specificity upon insertion of the U6 A/T box. In the U6 promoter, the 3' part of the proximal element homology is essential for efficient transcription and is also involved in localizing the start site of transcription. A region downstream of the proximal element homology is required for RNA polymerase II (but not for RNA polymerase III) transcription, both in the U2 promoter and in the U6 promoter. This element may be recognized by an RNA polymerase II transcription factor or by RNA polymerase II itself. The presence of this element in the U6 promoter raises the possibility that the human U6 gene is, under certain circumstances, transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ares M., Jr, Mangin M., Weiner A. M. Orientation-dependent transcriptional activator upstream of a human U2 snRNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1560–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark C., Weller P., Zabielski J., Janson L., Pettersson U. A distant enhancer element is required for polymerase III transcription of a U6 RNA gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):356–359. doi: 10.1038/328356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumruker T., Sturm R., Herr W. OBP100 binds remarkably degenerate octamer motifs through specific interactions with flanking sequences. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1400–1413. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Spliceosomal RNA U6 is remarkably conserved from yeast to mammals. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):213–218. doi: 10.1038/334213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Mouse RNAase MRP RNA is encoded by a nuclear gene and contains a decamer sequence complementary to a conserved region of mitochondrial RNA substrate. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90991-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Wright D., Reddy R. Upstream regulatory elements are necessary and sufficient for transcription of a U6 RNA gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):503–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K. Organization of sequences related to U6 RNA in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3379–3388. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA is directed by a conserved sequence located downstream of the coding region. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1827–1837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03857.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Lucito R. Elements required for transcription initiation of the human U2 snRNA gene coincide with elements required for snRNA 3' end formation. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3125–3134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Weiner A. M. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA requires compatible snRNA promoter elements. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Upstream elements required for efficient transcription of a human U6 RNA gene resemble those of U1 and U2 genes even though a different polymerase is used. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):196–204. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. A 7 bp mutation converts a human RNA polymerase II snRNA promoter into an RNA polymerase III promoter. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangin M., Ares M., Jr, Weiner A. M. Human U2 small nuclear RNA genes contain an upstream enhancer. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):987–995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04313.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Skuzeski J. T., Lund E., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Functional elements of the human U1 RNA promoter. Identification of five separate regions required for efficient transcription and template competition. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1795–1803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuzeski J. M., Lund E., Murphy J. T., Steinberg T. H., Burgess R. R., Dahlberg J. E. Synthesis of human U1 RNA. II. Identification of two regions of the promoter essential for transcription initiation at position +1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8345–8352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuo C. Y., Ares M., Jr, Weiner A. M. Sequences required for 3' end formation of human U2 small nuclear RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):193–202. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G., Benecke B. J., Penman S. Synthesis of two classes of small RNA species in vivo and in vitro. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4520–4525. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vegvar H. E., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. 3' end formation of U1 snRNA precursors is coupled to transcription from snRNA promoters. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]