Abstract
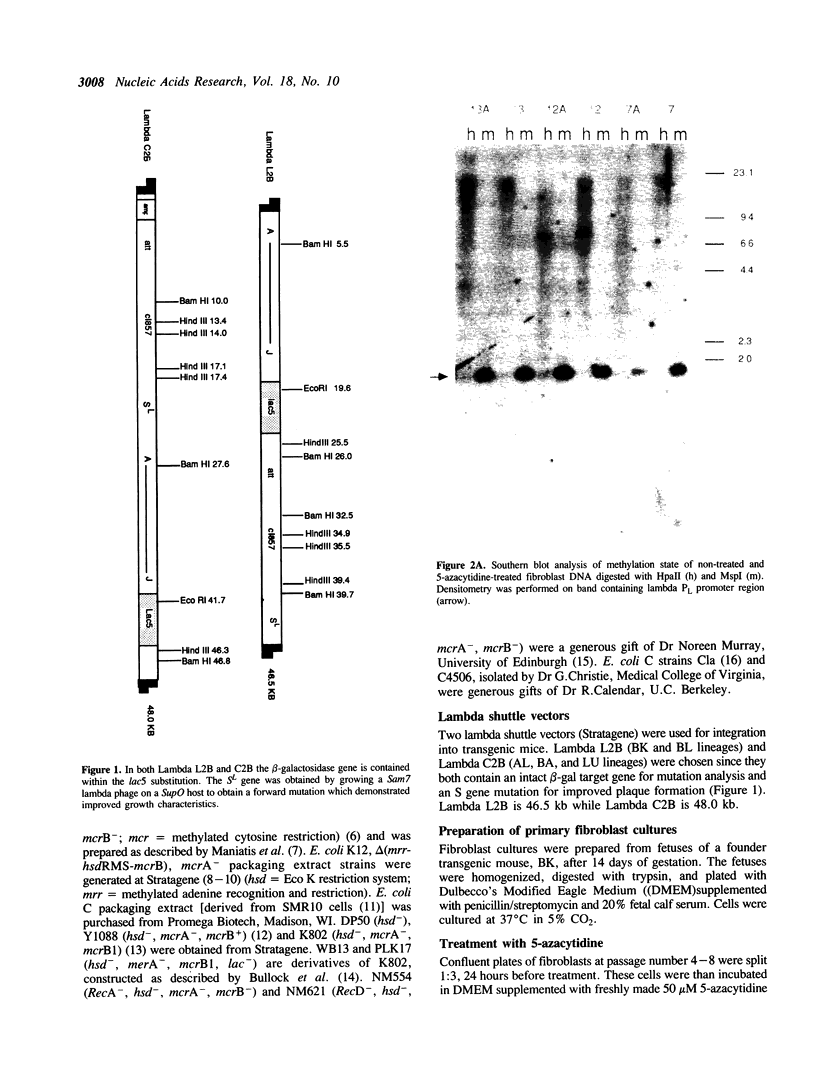
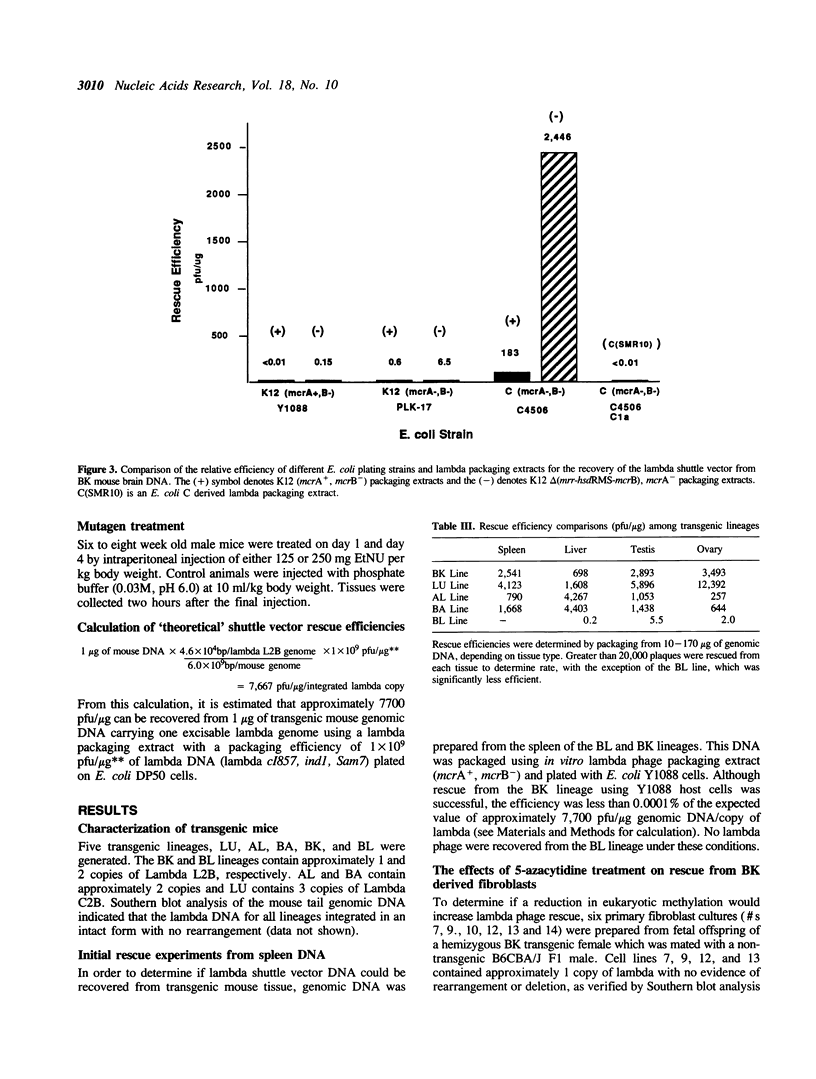
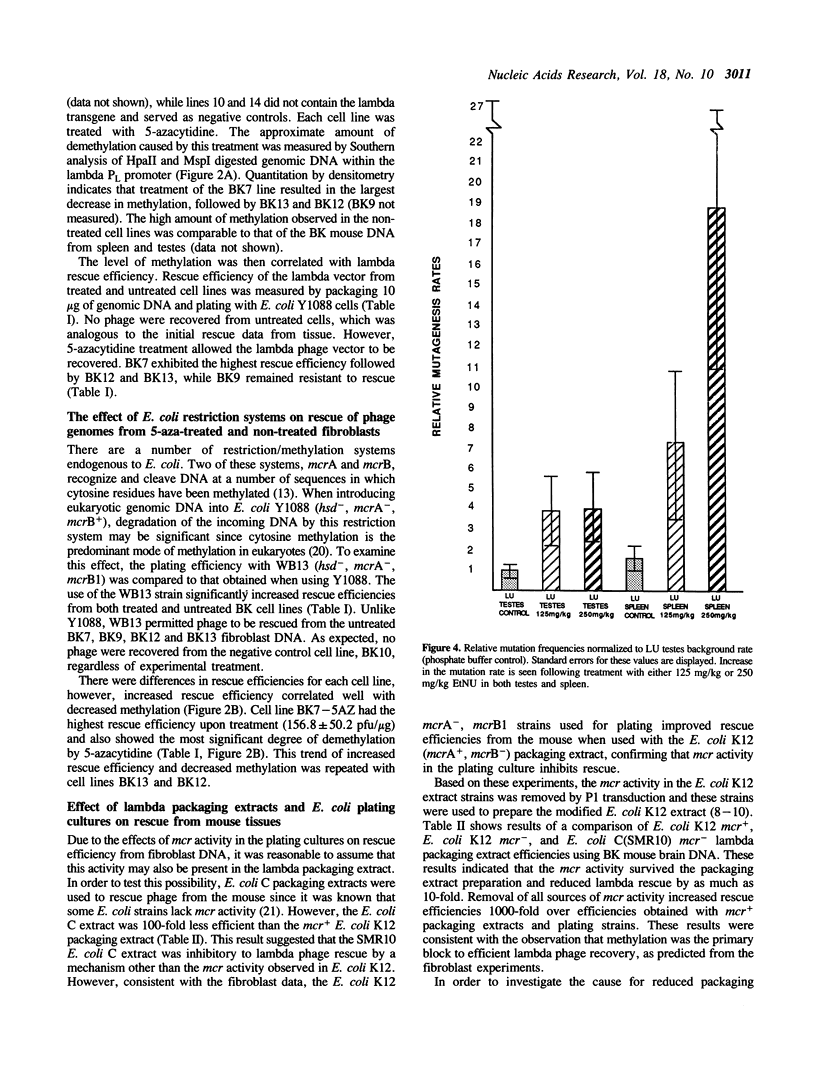
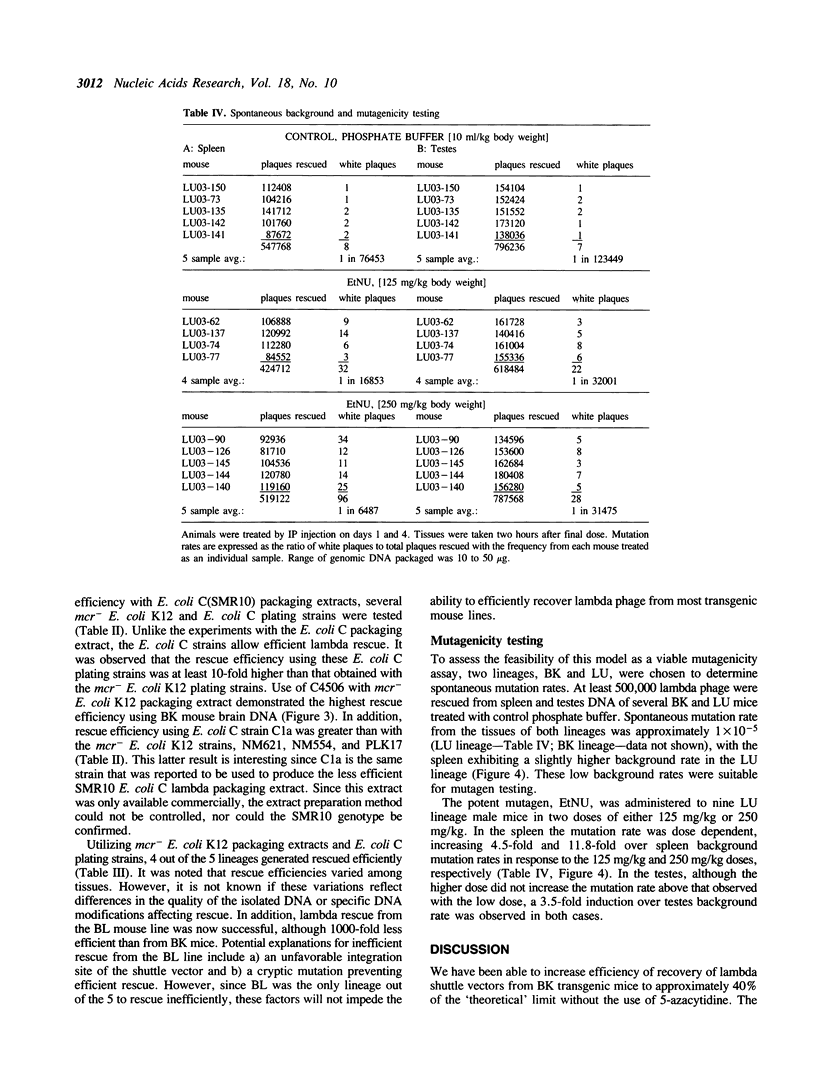
Transgenic mice suitable for the in vivo assay of suspected mutagens at the chromosome level have been constructed by stable integration of a lambda phage shuttle vector. The shuttle vector, which contains a beta-galactosidase (beta-gal) target gene, can be rescued from genomic DNA with in vitro packaging extracts. Mutations in the target gene are detected by a change in lambda phage plaque color on indicator agar plates. Initial rescue efficiencies of less than 1 plaque forming unit (pfu)/100 micrograms of genomic DNA were too low for mutation analysis. We determined the cause of the low rescue efficiencies by examining primary fibroblast cultures prepared from fetuses of lambda transgenic animals. The rescue efficiency of 5-azacytidine-treated cells increased 50-fold over non-treated controls indicating that methylation was inhibiting rescue. The inhibitory role of methylation was supported by the observation that mcr deficient E. coli plating strains and mcr deficient lambda packaging extracts further improved lambda rescue efficiency. Present rescue efficiencies of greater than 2000 pfu/copy/micrograms of genomic DNA represent a 100,000-fold improvement over initial rescue efficiencies, permitting quantitative mutational analysis. The background mutagenesis rate was estimated at 1 x 10(-5) in two separate lineages. Following treatment with the mutagen N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (EtNU), a dose dependent increase in the mutation rate was observed in DNA isolated from mouse spleen, with significant induction also observed in mouse testes DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper D. N. Eukaryotic DNA methylation. Hum Genet. 1983;64(4):315–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00292363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer P. M., Sarkar S. N., Summers W. C. Detection and analysis of UV-induced mutations in mammalian cell DNA using a lambda phage shuttle vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1041–1044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen J. A., Vijg J. E. coli C: a convenient host strain for rescue of highly methylated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9343–9343. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen J. A., de Leeuw W. J., Tan C. H., Zwarthoff E. C., Berends F., Lohman P. H., Knook D. L., Vijg J. Efficient rescue of integrated shuttle vectors from transgenic mice: a model for studying mutations in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7971–7975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretz P. L., Reid C. H., Greener A., Short J. M. Effect of lambda packaging extract mcr restriction activity on DNA cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5409–5409. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Kan Y. W. Versatile cosmid vectors for the isolation, expression, and rescue of gene sequences: studies with the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5225–5229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmaier W., Hauser H., de Wilke I. G., Schütz G. Gene shuttling: moving of cloned DNA into and out of eukaryotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1243–1256. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott J. E., Grant R. A., Ho Y. S., Platt T. Maximizing gene expression from plasmid vectors containing the lambda PL promoter: strategies for overproducing transcription termination factor rho. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):88–92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL W. L. X-ray-induced mutations in mice. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:327–336. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Murray N. E., Revel H., Blumenthal R. M., Westaway D., Reith A. D., Rigby P. W., Elhai J., Hanahan D. McrA and McrB restriction phenotypes of some E. coli strains and implications for gene cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1563–1575. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Wilson G. Escherichia coli K-12 restricts DNA containing 5-methylcytosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9070–9074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. M., Stahl M. M., Kobayashi I., Stahl F. W. Improved in vitro packaging of coliphage lambda DNA: a one-strain system free from endogenous phage. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki I., Bertani G. Growth abnormalities in Hfr derivatives of Escherichia coli strain C. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):365–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. L., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation, expression, and infectivity of retroviral genomes introduced into embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4098–4102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Glazer P. M., Malkevich D. Lambda phage shuttle vectors for analysis of mutations in mammalian cells in culture and in transgenic mice. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar-May;220(2-3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(89)90030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker P. A., Campbell A. J., Southern E. M., Murray N. E. Enhanced recovery and restriction mapping of DNA fragments cloned in a new lambda vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6725–6736. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock D. M., Crowther P. J., Doherty J., Jefferson S., DeCruz E., Noyer-Weidner M., Smith S. S., Michael M. Z., Graham M. W. Quantitative evaluation of Escherichia coli host strains for tolerance to cytosine methylation in plasmid and phage recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3469–3478. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




