Abstract
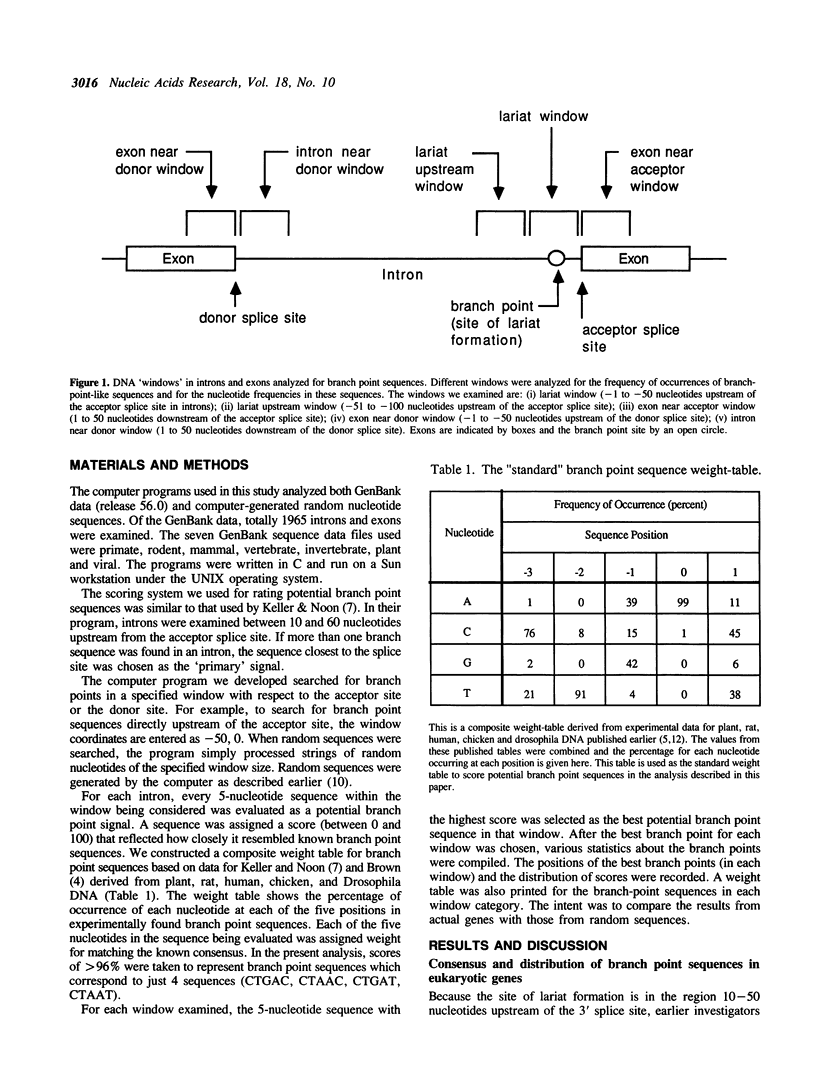
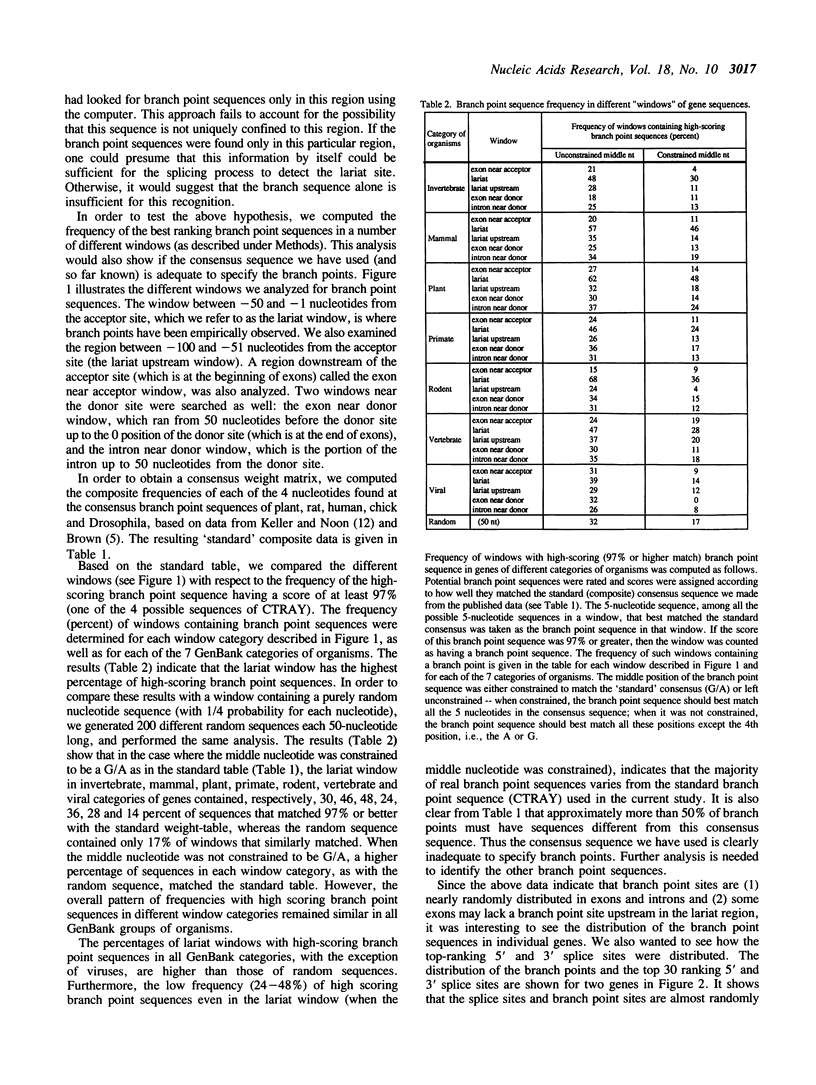
An intermediate stage in the process of eukaryotic RNA splicing is the formation of a lariat structure. It is anchored at an adenosine residue in intron between 10 and 50 nucleotides upstream of the 3' splice site. A short conserved sequence (the branch point sequence) functions as the recognition signal for the site of lariat formation. It has been generally assumed that the branch point is recognized mainly by the presence of its unique sequence where the lariat is formed. However, the known branch point consensus sequence is found to be distributed nearly randomly throughout the gene sequence with only a slightly higher frequency in the expected lariat region. Further, the known consensus sequence is found to be clearly inadequate to specify branch points. These observations have implications for understanding the mechanism of branch point recognition in the process of splicing, and the possible evolution of the branch point signal.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. W. A catalogue of splice junction and putative branch point sequences from plant introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9549–9559. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Feix G., Frendewey D. Accurate in vitro splicing of two pre-mRNA plant introns in a HeLa cell nuclear extract. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2749–2758. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmuth K., Barta A. Unusual branch point selection in processing of human growth hormone pre-mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2011–2020. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller E. B., Noon W. A. Intron splicing: a conserved internal signal in introns of animal pre-mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7417–7420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senapathy P. Origin of eukaryotic introns: a hypothesis, based on codon distribution statistics in genes, and its implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2133–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senapathy P. Possible evolution of splice-junction signals in eukaryotic genes from stop codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1129–1133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



