Abstract
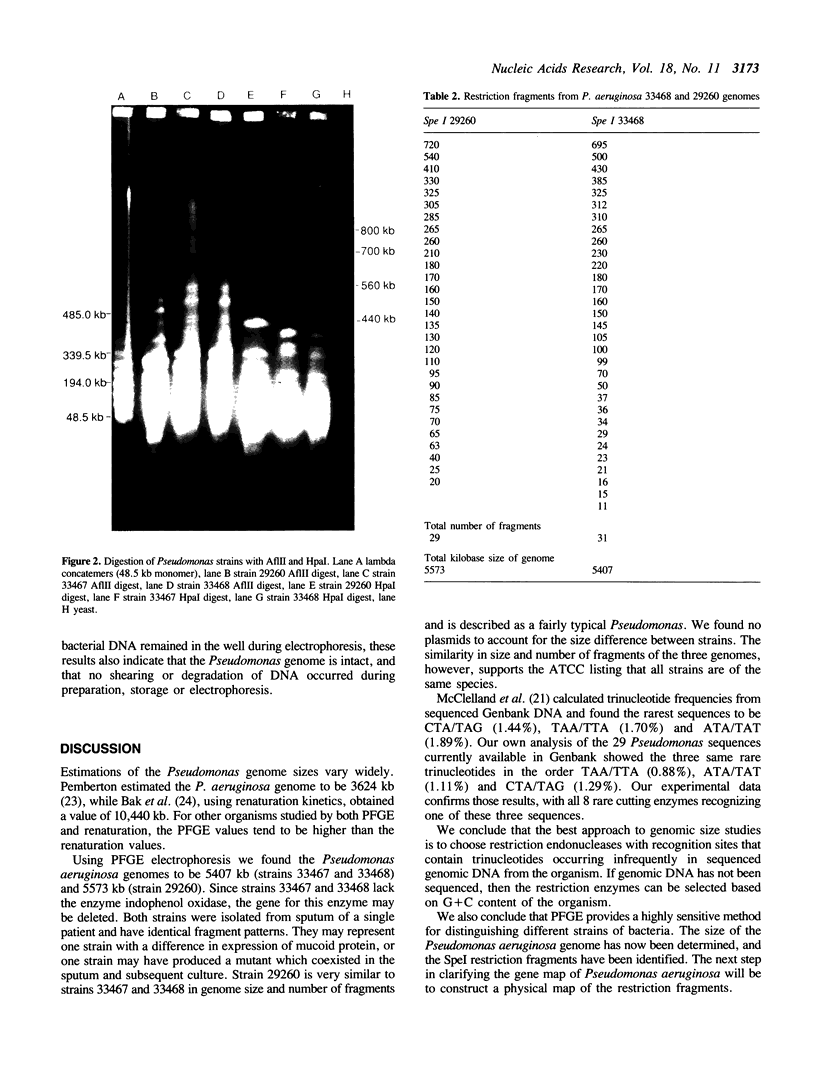
Genomic DNA size was measured in three strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, ATCC 29260 (exotoxin A), ATCC 33467 (type I smooth) and ATCC 33468 (type 2 mucoid) by transverse alternating field electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Because of the high (67%) G + C content of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, restriction enzymes that recognize sequences with at least 4 AT base pairs were expected to be rare cutters. Eight enzymes produced fragments greater than 200 kb in size: Dral (TTT/AAA), Asnl (ATT/AAT), Hpal (GTT/AAC), AfIII (C/TTAAG), Xbal (T/CTAGA), Spel (A/CTAGT), Sspl (AAT/ATT) and Ndel (CA/TATG). All eight enzymes recognized one of three rare tetranucleotide sequences, TTAA, CTAG or ATAT. Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 29260 has a genomic DNA size of 5573 kb. Strains 33467 and 33468 have identical restriction patterns and a possible deletion with a genomic size of 5407 kb.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bak A. L., Christiansen C., Stenderup A. Bacterial genome sizes determined by DNA renaturation studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):377–380. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft I., Wolk C. P. Pulsed homogeneous orthogonal field gel electrophoresis (PHOGE). Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7405–7418. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birren B. W., Lai E., Clark S. M., Hood L., Simon M. I. Optimized conditions for pulsed field gel electrophoretic separations of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7563–7582. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. M., Lai E., Birren B. W., Hood L. A novel instrument for separating large DNA molecules with pulsed homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1203–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.3045968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Laas W., Patterson D. Fractionation of large mammalian DNA restriction fragments using vertical pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):185–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01560665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton K. D., Wasilauskas B. L. Isolation of oxidase-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa from sputum culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):632–634. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.632-634.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauc L., Mitchell M., Goodgal S. H. Size and physical map of the chromosome of Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2474–2479. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2474-2479.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Smith H. O., Redfield R. J. Organization of the Haemophilus influenzae Rd genome. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3016–3024. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3016-3024.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. J., Smith H. O. Sizing of the Haemophilus influenzae Rd genome by pulsed-field agarose gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4402–4405. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4402-4405.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Zimm B. H. Separations of open-circular DNA using pulsed-field electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4054–4057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Factors that influence the production of exotoxin A. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):506–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Jones R., Patel Y., Nelson M. Restriction endonucleases for pulsed field mapping of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5985–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPeek F. D., Jr, Coyle-Morris J. F., Gemmill R. M. Separation of large DNA molecules by modified pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 1;156(2):274–285. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, edition 9. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):181–213. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.181-213.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M. Size of the chromosome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):748–752. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.748-752.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Corcoran L. N., Cocks B. G., Bergemann A. D., Whitley J. C., Finch L. R. Pulsed-field electrophoresis indicates larger-than-expected sizes for mycoplasma genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6015–6025. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Purification, specific fragmentation, and separation of large DNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:449–467. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Lawrance S. K., Gillespie G. A., Cantor C. R., Weissman S. M., Collins F. S. Strategies for mapping and cloning macroregions of mammalian genomes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:461–489. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Matsumoto T., Niwa O., Klco S., Fan J. B., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. An electrophoretic karyotype for Schizosaccharomyces pombe by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4481–4489. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., Wilkins R. J. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from C.albicans by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4401–4406. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F. A computer program allows the separation of a wide range of chromosome sizes by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):4853–4863. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]