Abstract
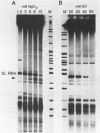
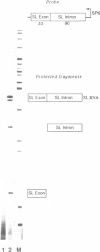
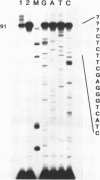
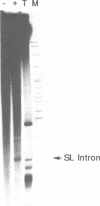
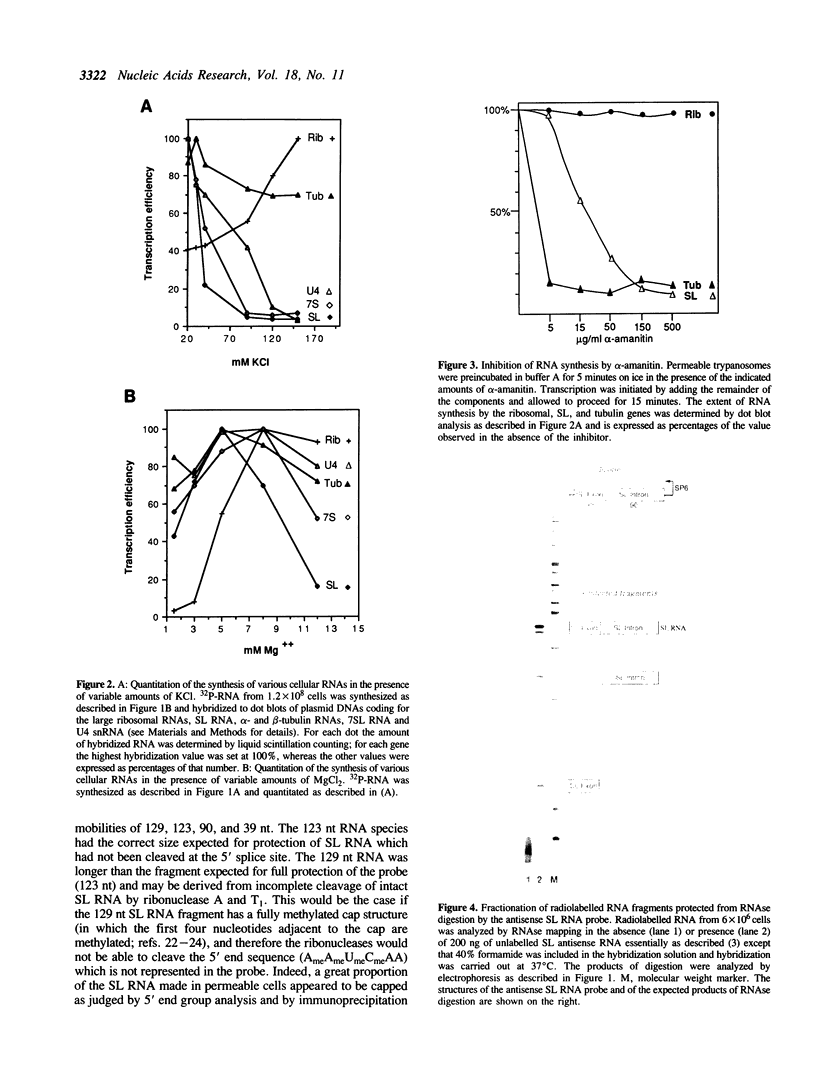
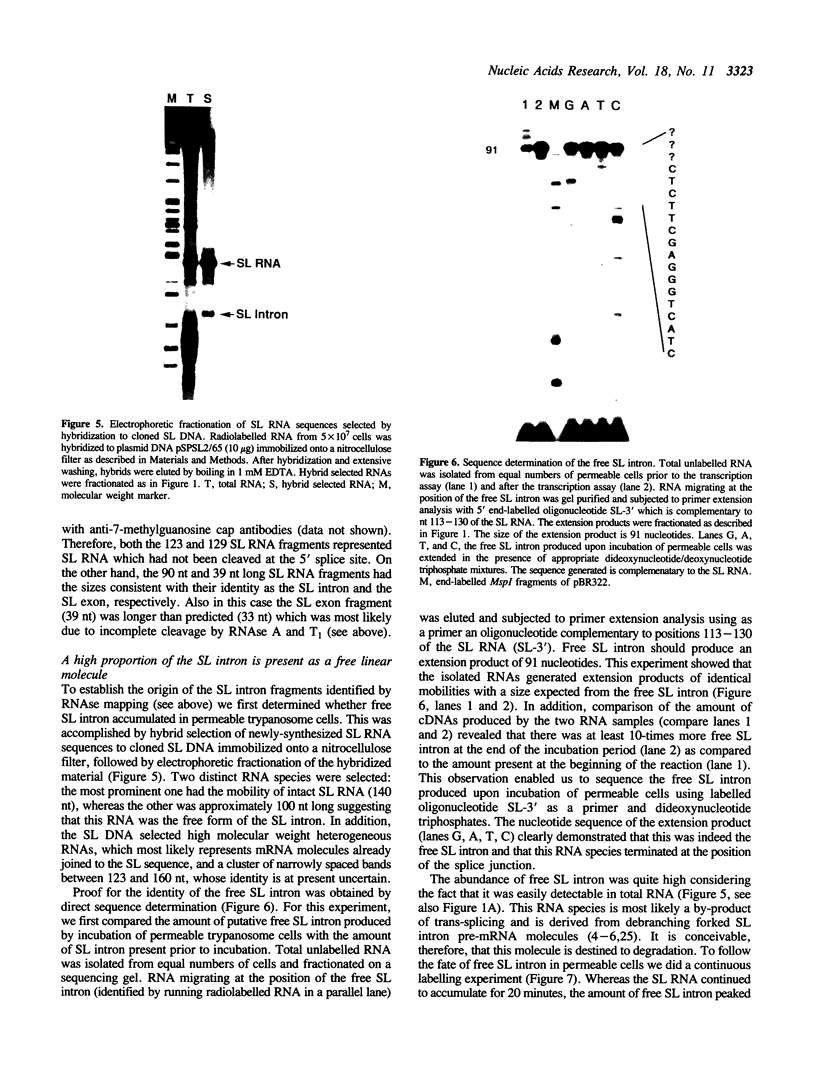
We have established conditions for Trypanosoma brucei permeable cells to study transcription and trans-splicing. We found that the concentration of monovalent and, to a lesser extent, divalent ions plays a critical role for the expression of a number of different genes. Most remarkably, the synthesis of the spliced leader (SL) RNA was optimal at 20 mM KCl, whereas higher potassium concentrations were inhibitory. In addition, MgCl2 concentrations above 3 mM led to the accumulation of a 3' end shortened SL RNA species, which has been previously reported not to participate in trans-splicing. Using conditions optimal for the synthesis of the SL RNA, we observed accurate trans-splicing of newly-synthesized alpha-tubulin RNA. Moreover, we detected the SL intron both joined to high molecular weight RNAs in the form of branched Y-structures and as a free linear molecule, which rapidly turned over. Furthermore, ionic concentrations that inhibit the synthesis of the SL RNA produced exclusively unspliced alpha-tubulin RNA, thus demonstrating that transcription and trans-splicing can be uncoupled.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben Amar M. F., Pays A., Tebabi P., Dero B., Seebeck T., Steinert M., Pays E. Structure and transcription of the actin gene of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2166–2176. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Osheim Y. N. Splice site selection, rate of splicing, and alternative splicing on nascent transcripts. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):754–765. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd J. C., Cross G. A. Transcripts coding for variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma brucei have a short, identical exon at their 5' end. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. A., Thornton D. A., Boothroyd J. C. Apparent discontinuous transcription of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface antigen genes. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):350–355. doi: 10.1038/311350a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Fiers W. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II in permeable, SV40-infected or noninfected, CVI cells; evidence for multiple promoters of SV40 late transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):215–236. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freistadt M. S., Cross G. A., Branch A. D., Robertson H. D. Direct analysis of the mini-exon donor RNA of Trypanosoma brucei: detection of a novel cap structure also present in messenger RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9861–9879. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. C., Swinkels B. W., Borst P. Post-transcriptional control of the differential expression of phosphoglycerate kinase genes in Trypanosoma brucei. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 20;201(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Keller W. Splicing of in vitro synthesized messenger RNA precursors in HeLa cell extracts. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden M., Blum B., DeLange T., Braun R., Seebeck T. Tubulin mRNAs of Trypanosoma brucei. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. J., Kooter J. M., Borst P. Inactivation of transcription by UV irradiation of T. brucei provides evidence for a multicistronic transcription unit including a VSG gene. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooter J. M., De Lange T., Borst P. Discontinuous synthesis of mRNA in trypanosomes. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2387–2392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02144.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Kooter J. M., Loosbroek N., Borst P. Mature mRNAs of Trypanosoma brucei possess a 5' cap acquired by discontinuous RNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4253–4266. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zomerdijk J. C., de Korte D., Borst P. In vivo labelling of intermediates in the discontinuous synthesis of mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1055–1062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., ten Asbroek A. L., Borst P. Controlled turnover and 3' trimming of the trans splicing precursor of Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10087–10103. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels F., Matthyssens G., Kronenberger P., Pays E., Dero B., Van Assel S., Darville M., Carvador A., Steinert M., Hamers R. Gene activation and re-expression of a Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1185–1192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhausen M., Nelson R. G., Sather S., Selkirk M., Agabian N. Identification of a small RNA containing the trypanosome spliced leader: a donor of shared 5' sequences of trypanosomatid mRNAs? Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90267-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., Castellot J. J., Jr, Pardee A. B. A permeable animal cell preparation for studying macromolecular synthesis. DNA synthesis and the role of deoxyribonucleotides in S phase initiation. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):1073–1080. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhich M. L., Boothroyd J. C. Polycistronic transcripts in trypanosomes and their accumulation during heat shock: evidence for a precursor role in mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3837–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Trypanosome mRNAs have unusual "cap 4" structures acquired by addition of a spliced leader. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8190–8194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph D., Huang J., Van der Ploeg L. H. Physical identification of branched intron side-products of splicing in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2539–2545. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. An RNA processing activity that debranches RNA lariats. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.2990042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather S., Agabian N. A 5' spliced leader is added in trans to both alpha- and beta-tubulin transcripts in Trypanosoma brucei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5695–5699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaeppi K., Deflorin J., Seebeck T. The major component of the paraflagellar rod of Trypanosoma brucei is a helical protein that is encoded by two identical, tandemly linked genes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1695–1709. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. E., Boothroyd J. C. Evidence for trans splicing in trypanosomes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90617-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. E., Boothroyd J. C. The cap of both miniexon-derived RNA and mRNA of trypanosomes is 7-methylguanosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):494–496. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. E., Boothroyd J. C. Trypanosome trans-splicing utilizes 2'-5' branches and a corresponding debranching activity. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1431–1437. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02960.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinkels B. W., Gibson W. C., Osinga K. A., Kramer R., Veeneman G. H., van Boom J. H., Borst P. Characterization of the gene for the microbody (glycosomal) triosephosphate isomerase of Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1291–1298. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi C., Ullu E. Polygene transcripts are precursors to calmodulin mRNAs in trypanosomes. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):455–463. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi C., Young A. S., Ruben L., Patton C. L., Richards F. F. Calmodulin genes in trypanosomes are tandemly repeated and produce multiple mRNAs with a common 5' leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Liu A. Y., Michels P. A., De Lange T., Borst P., Majumder H. K., Weber H., Veeneman G. H., Van Boom J. RNA splicing is required to make the messenger RNA for a variant surface antigen in trypanosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3591–3604. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]